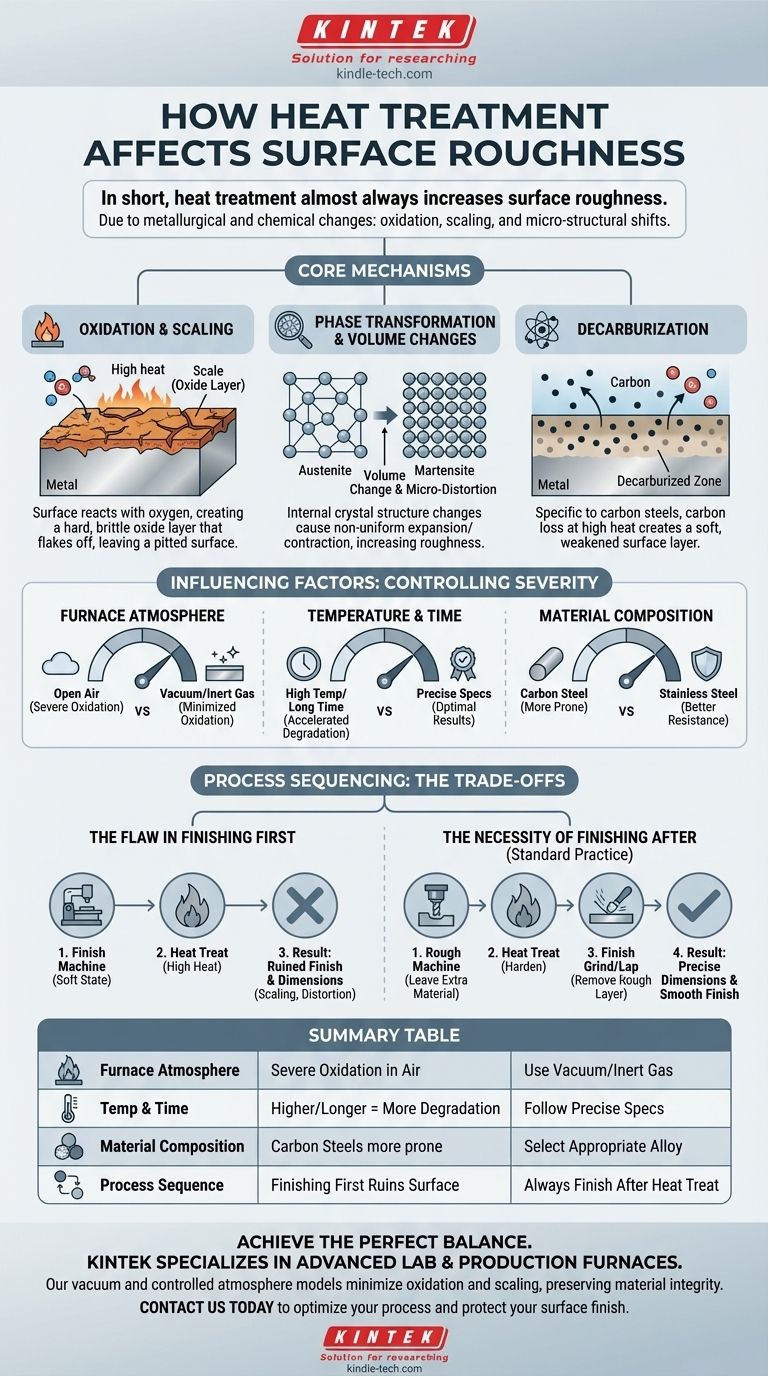
In short, heat treatment almost always increases surface roughness. This degradation occurs because high temperatures induce metallurgical and chemical changes on the material's surface, primarily through oxidation, scaling, and microscopic shifts in the material's structure. As a result, a part that was smooth before heat treatment will be noticeably rougher afterward.
The central challenge in manufacturing is that the processes required to achieve desired bulk properties (like hardness through heat treatment) are often detrimental to surface properties (like finish and dimensional accuracy). Therefore, precision finishing operations must be planned to occur after heat treatment, not before.

The Core Mechanisms: Why Heat Treatment Increases Roughness
To control the final outcome of a part, it's essential to understand the specific phenomena that degrade the surface during heat treatment. These are not flaws in the process but inherent physical and chemical consequences of heating metals to high temperatures.
Oxidation and Scaling
The most significant factor, especially in steels, is the formation of a surface oxide layer, commonly known as scale.
At elevated temperatures, the metal's surface reacts with oxygen present in the furnace atmosphere. This creates a hard, brittle layer of metallic oxide that is rough and uneven. As the part cools, this scale often flakes off, leaving behind a pitted and irregular surface that is far rougher than the original.
Phase Transformation and Volume Changes
Heat treatment is designed to change the metal's internal crystal structure, or phase. For example, in steel, heating transforms the structure to austenite, and rapid cooling (quenching) transforms it to hard martensite.
These phase transformations are accompanied by slight changes in volume. This expansion and contraction do not happen perfectly uniformly across the surface, leading to microscopic distortions that increase roughness.
Decarburization
Specific to carbon steels, decarburization is the loss of carbon atoms from the surface layer. The high heat allows carbon to diffuse to the surface and react with the furnace atmosphere.
This creates a soft, weakened surface layer with different properties than the core material. This phenomenon contributes to surface imperfections and can negatively impact wear resistance and fatigue life.
Factors That Influence the Severity of Change
You can manage the degree of surface degradation by controlling several key variables in the heat treatment process.
Furnace Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace is the most critical control factor.
A furnace open to ambient air will cause the most severe oxidation and scaling. In contrast, using a vacuum furnace or a controlled atmosphere filled with inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) dramatically reduces oxidation, preserving the surface finish much more effectively.
Temperature and Time
The principles of chemical reactions apply here: higher temperatures and longer durations at those temperatures will accelerate both oxidation and decarburization.
Following precise specifications for time and temperature for a given alloy is crucial to minimizing unwanted surface effects while still achieving the desired core properties.
Material Composition
Different metals and alloys react differently to heat. Stainless steels, for example, contain chromium, which forms a passive, protective oxide layer that resists further scaling much better than plain carbon steel.
Understanding your material's specific properties is key to predicting how its surface will respond.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Machining Before vs. After
The impact of heat treatment on surface finish creates a fundamental sequencing problem in manufacturing: you cannot achieve both final hardness and final finish in the same step.
The Flaw in Finishing First
It is much easier and faster to machine a metal in its softer, annealed state. However, if you machine a part to its final precise dimensions and smooth finish before heat treating it, the process will ruin your work.
The scaling, distortion, and volume changes from heat treatment will destroy both the dimensional accuracy and the surface finish.
The Necessity of Finishing After
The universally accepted practice for precision components is to finish them after heat treatment.
This involves leaving extra material on the part before heat treating, a step known as rough machining. After the part is hardened, a secondary finishing process, such as grinding, lapping, or hard turning, is used to remove the rough surface layer and bring the part to its final, precise dimensions. While machining hardened materials is slower and requires more robust tooling, it is the only way to meet tight tolerances.
How to Sequence Your Process
Your manufacturing plan must account for the effects of heat treatment from the very beginning. The correct sequence depends entirely on the component's final requirements.
- If your primary focus is high precision and a fine surface finish: Your process must be: rough machine, heat treat, and then finish grind or lap. This is the standard for bearings, gears, and molds.
- If your primary focus is strength with non-critical surface finish: You may be able to use the part in its as-heat-treated condition. This is common for structural components where surface roughness is not a functional concern.
- If your goal is to minimize finish degradation during heat treatment: Specify the use of a vacuum or controlled atmosphere furnace. This adds cost but can significantly reduce the amount of material that needs to be removed in post-treatment finishing operations.
Ultimately, successful manufacturing requires planning your entire process chain with the understanding that heat treatment is a transformative step for both the core and the surface of your material.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Surface Roughness | How to Control |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Atmosphere | Ambient air causes severe oxidation/scaling. | Use vacuum or inert gas atmospheres. |
| Temperature & Time | Higher temps and longer times accelerate degradation. | Follow precise material specifications. |
| Material Composition | Stainless steels resist scaling better than carbon steels. | Select appropriate alloy for the application. |
| Process Sequence | Finishing before heat treatment ruins the surface. | Always perform precision finishing operations after heat treatment. |
Achieve the perfect balance of core hardness and surface finish for your precision components.
The right equipment is critical for controlling heat treatment outcomes. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab and production furnaces, including vacuum and controlled atmosphere models, designed to minimize surface oxidation and scaling. This preserves your material's integrity and reduces costly post-treatment finishing.
Our experts understand the challenges of sequencing rough machining, heat treatment, and final finishing. We provide the reliable equipment and consumables your laboratory needs to ensure repeatable, high-quality results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your heat treatment process and protect your surface finish.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the future of synthetic diamonds? Reshaping the Market with Lab-Grown Technology
- Why is magnetron sputtering used? For High-Quality, High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is the primary function of a vacuum drying oven in Pyr-IHF synthesis? Ensure High-Purity Cathode Material Quality
- What are the functions of laboratory shakers and centrifuges in phosphorus extraction? Optimize Sample Purification
- What is plasma melting? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Processing for High-Performance Alloys
- Is biomass cheaper than other energy sources? Unpacking the True Cost of Biomass Energy
- What products are surface hardening? A Guide to Processes, Agents, and Applications



















