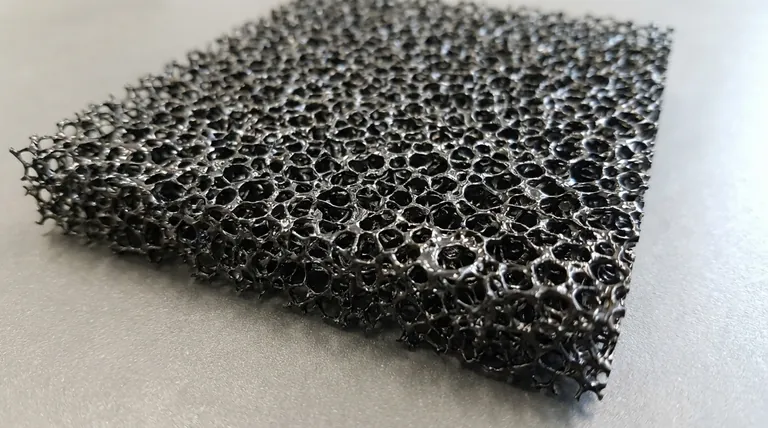
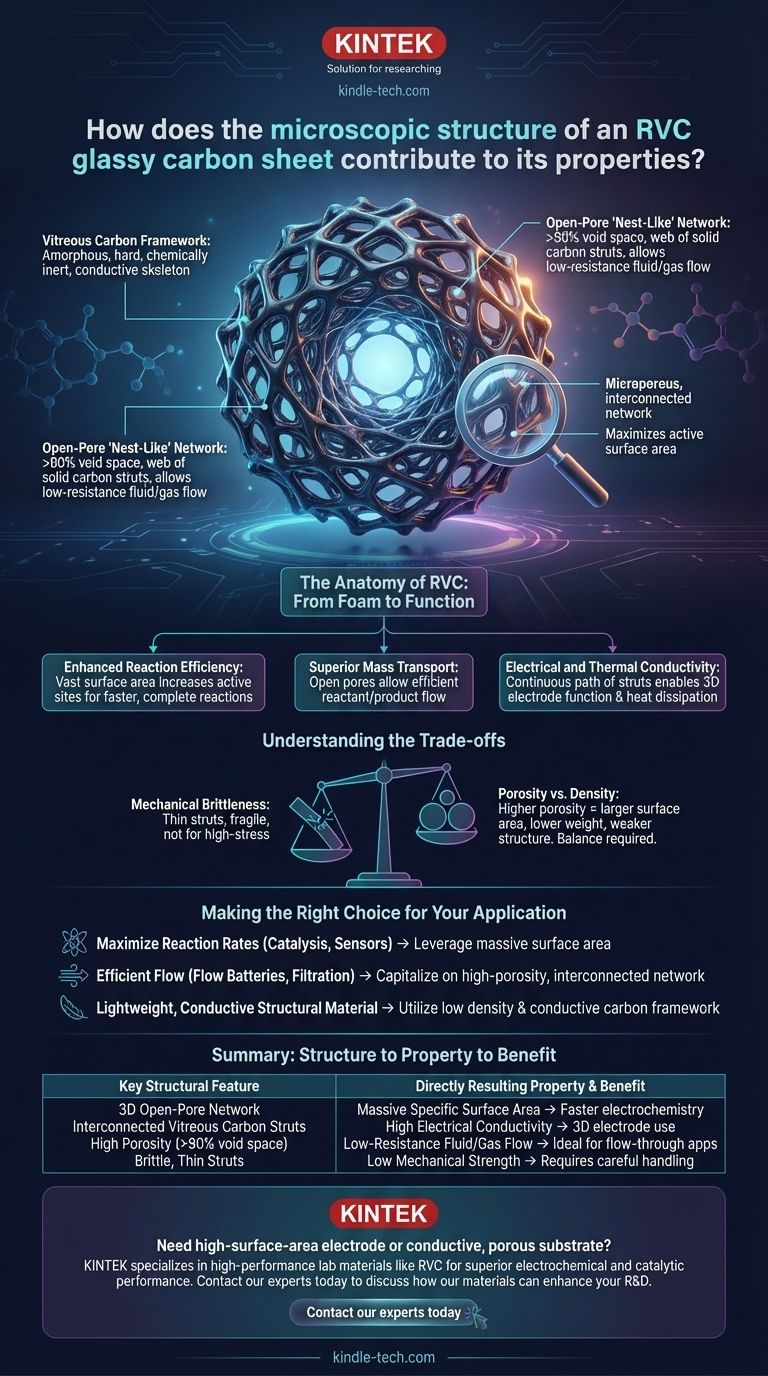
At its core, the microscopic structure of a Reticulated Vitreous Carbon (RVC) sheet is a three-dimensional, open-pore foam that resembles a bird's nest or a sponge. This unique architecture is directly responsible for its most valuable properties, creating an exceptionally large specific surface area. This maximizes the contact between the electrode material and the surrounding reactants, dramatically enhancing the rate and efficiency of chemical reactions.
The defining characteristic of RVC is not the carbon material itself, but its three-dimensional, porous architecture. This structure transforms a simple conductive material into a highly efficient platform for electrochemical reactions by maximizing active surface area and enabling fluid flow.

The Anatomy of RVC: From Foam to Function
To understand RVC's performance, we must first analyze its constituent parts and how they are arranged. Its properties emerge from the combination of the base material and its complex, interconnected geometry.
The Vitreous Carbon Framework
RVC is made from vitreous or "glassy" carbon, an amorphous (non-crystalline) form of carbon. Unlike graphite, its atoms are not arranged in neat layers. This results in a material that is hard, chemically inert, and electrically conductive, forming a stable skeleton for the foam structure.
The Open-Pore, 'Nest-Like' Network
The defining feature of RVC is its microporous, interconnected network. It is not a solid with holes drilled into it; rather, it is a web of solid carbon struts with a very high percentage of void space (often over 90%). This open structure allows fluids and gases to flow through the material with minimal resistance.
The Impact of Porosity on Surface Area
This high-porosity network creates an enormous specific surface area—the total exposed surface area per unit of mass or volume. A solid cube of carbon has only six faces for reactions to occur on. An RVC foam of the same external dimensions exposes the surface of every internal strut, multiplying the available reaction sites by orders of magnitude.
How Structure Translates to Performance
The physical architecture of RVC directly translates into tangible benefits for technical applications, primarily in electrochemistry and catalysis. The structure is engineered to solve key challenges in these fields.
Enhanced Reaction Efficiency
The vast surface area is the primary driver of RVC's value in electrocatalysis and electroanalysis. More surface area means more active sites where the electrode and reactants can meet. This directly increases the speed and completeness of electrochemical reactions, making processes more efficient and sensors more sensitive.
Superior Mass Transport
The open-pore structure is critical for maintaining high performance. It ensures efficient mass transport: reactants can easily flow into the foam to reach the internal active sites, and reaction products can easily flow out. This prevents bottlenecks that would otherwise slow down the reaction, a common limitation in flat electrode designs.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
While porous, the interconnected network of vitreous carbon struts provides a continuous path for electrons. This makes the entire foam structure electrically conductive, allowing it to function as a three-dimensional electrode. This same network is also effective at conducting and dissipating heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every use case. The unique structure of RVC introduces specific limitations that must be considered.
Mechanical Brittleness
While the vitreous carbon material itself is hard, the thin struts of the foam structure make it brittle and fragile. It cannot be used in applications requiring high mechanical strength, toughness, or resistance to physical abrasion.
Porosity vs. Density
There is an inherent trade-off between porosity and mechanical integrity. A higher porosity (more open space) yields a larger surface area and lower weight, but it also results in a weaker structure. The grade of RVC—often specified in pores per inch (PPI)—must be chosen to balance the need for surface area against the required physical robustness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice to use RVC should be driven by which of its structural properties best serves your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing reaction rates (e.g., in catalysis or sensors): Leverage RVC's massive specific surface area to increase the density of active sites.
- If your primary focus is efficient flow (e.g., in flow batteries or filtration): Capitalize on the high-porosity, interconnected network that enables low-resistance mass transport.
- If your primary focus is a lightweight, conductive structural material: Utilize the combination of low density and a continuous, electrically conductive carbon framework.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between RVC's architecture and its properties allows you to select and leverage this material with precision.
Summary Table:
| Key Structural Feature | Directly Resulting Property | Primary Application Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Open-Pore Network (Sponge-like) | Massive Specific Surface Area | Drastically increases reaction sites for faster, more efficient electrochemistry |
| Interconnected Vitreous Carbon Struts | High Electrical Conductivity | Enables use as a three-dimensional electrode |
| High Porosity (>90% void space) | Low-Resistance Fluid/Gas Flow | Ideal for flow-through applications like batteries and filtration |
| Brittle, Thin Struts | Low Mechanical Strength | Requires careful handling; not suitable for high-stress environments |
Need a high-surface-area electrode or a conductive, porous substrate for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including materials like RVC that are engineered for superior electrochemical and catalytic performance. Our expertise can help you select the right porous carbon solution to maximize reaction efficiency and mass transport in your specific application.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our materials can enhance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- What can carbon nanotubes be used for? Unlock Superior Performance in Batteries & Materials
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the material properties of carbon paper? Unlocking High Conductivity & Porosity for Your Lab



















