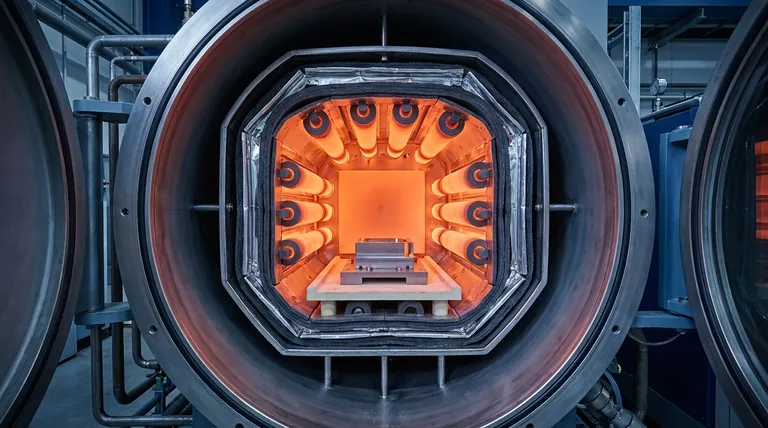
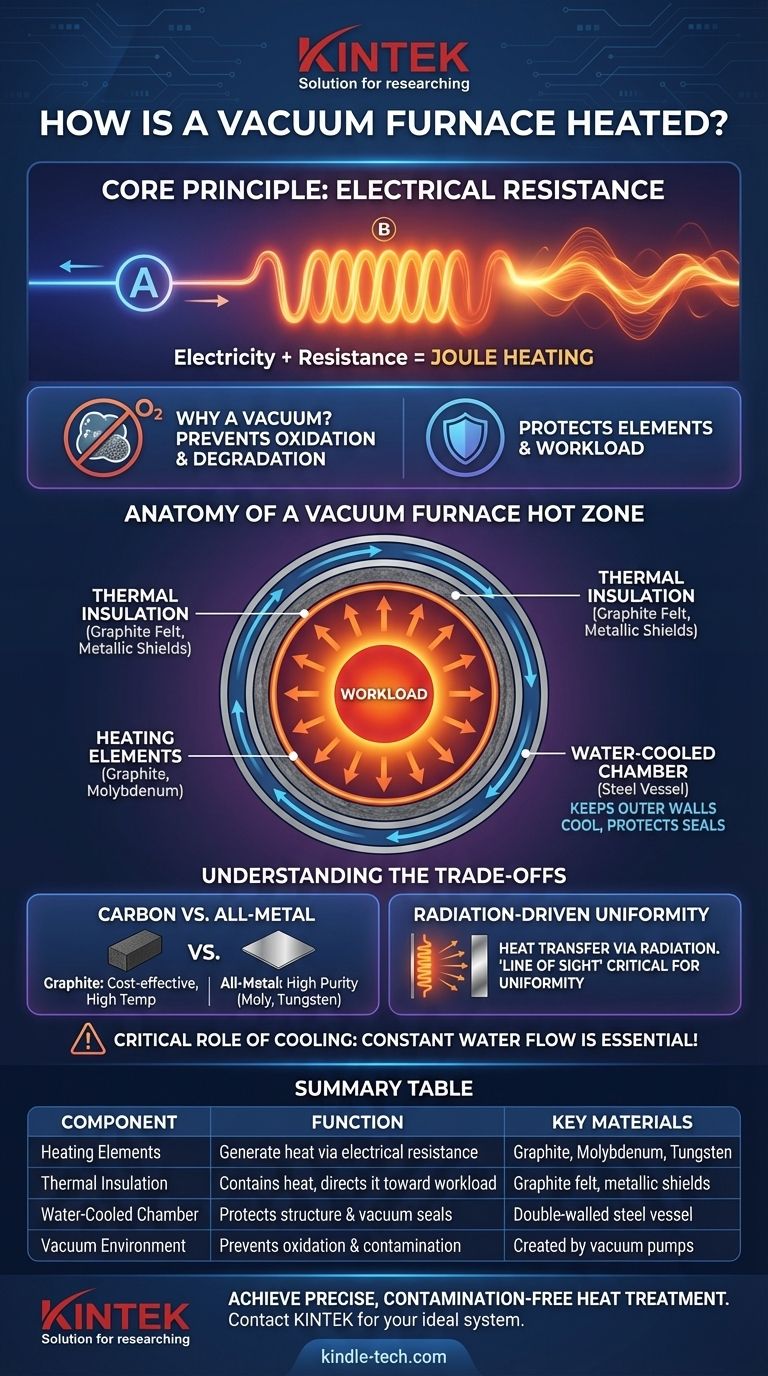
At its core, a vacuum furnace generates heat through electrical resistance. This process involves passing a high electrical current through specialized components called heating elements. These elements, designed to withstand extreme temperatures, glow hot and radiate thermal energy to the workload inside the furnace chamber, all while operating within a vacuum environment.
A vacuum furnace doesn't burn fuel; it uses electricity to heat elements inside a highly insulated "hot zone." This entire assembly is contained within a water-cooled steel vessel, which keeps the outer walls cool and maintains the integrity of the vacuum.

The Principle: Controlled Resistance Heating
The heating system of a vacuum furnace is fundamentally a powerful, precision-controlled electric heater. The underlying principle is simple and effective.
How Resistance Generates Heat
When electricity flows through a material, it encounters resistance. This opposition to the electrical current generates heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating or resistance heating.
Vacuum furnace designers harness this principle by selecting materials with specific resistive properties that can operate reliably at very high temperatures.
Why a Vacuum is Necessary
Heating materials to high temperatures in the presence of air would cause rapid oxidation and degradation. By removing the air to create a vacuum, the furnace provides an inert atmosphere that protects both the heating elements and the parts being processed from unwanted chemical reactions.
Anatomy of a Vacuum Furnace Hot Zone
The "hot zone" is the heart of the furnace, containing the heating system and the workload. It is engineered to generate, contain, and uniformly distribute heat.
The Heating Elements
These are the components that actually produce the heat. They are typically made from materials with extremely high melting points and stability in a vacuum.
Common materials include:
- Graphite: A cost-effective and highly versatile choice for temperatures up to and beyond 2200°C (4000°F).
- Molybdenum (Moly): An all-metal option used for high-purity applications where carbon contamination from graphite is a concern. Often used in sheet or rod form.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂): Ceramic-based elements that can be used in some vacuum applications, but are more common in furnaces that also operate with air.
The arrangement of these elements around the workload is critical for ensuring temperature uniformity, as heat transfer in a vacuum occurs primarily through radiation, not convection.
Thermal Insulation
The intense heat generated by the elements must be directed inward toward the workload. This is the job of the insulation package.
Insulation typically consists of multiple layers of graphite felt, ceramic fiberboard, or reflective metallic shields (like molybdenum or stainless steel). This package minimizes heat loss to the outer chamber, improving energy efficiency and process control.
The Water-Cooled Chamber
The entire hot zone assembly is housed within a double-walled steel vessel. Water is constantly circulated between these walls.
This water-cooling system is not an optional feature; it is critical for furnace operation. It keeps the outer chamber, seals, and power connections at a safe temperature, preventing the furnace from destroying itself and ensuring the vacuum seals remain intact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of heating element and hot zone design involves critical trade-offs that impact furnace capability, cost, and application.
Carbon vs. All-Metal Hot Zones
A graphite-based hot zone is the industry standard for most heat-treating and brazing applications due to its cost and high-temperature performance.
However, at very high temperatures, graphite can sublimate, potentially introducing carbon into the process. For applications demanding extreme purity, such as medical implants or aerospace electronics, a more expensive all-metal hot zone using molybdenum or tungsten elements and shields is required.
Radiation-Driven Uniformity
In a vacuum, there is no air to circulate and distribute heat via convection. Heat transfer is dominated by thermal radiation.
This means "line of sight" from the heating element to the part is crucial. The strategic placement of elements on all sides of the workload is the primary method for achieving the temperature uniformity mentioned in furnace specifications.
The Critical Role of Cooling
The constant need for water flow is an absolute operational requirement. A loss of cooling water while the elements are hot can lead to a catastrophic failure, damaging the chamber and compromising vacuum integrity. This is why industrial furnaces are equipped with backup water systems and numerous safety interlocks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding the heating system allows you to match the furnace technology to your specific material processing goal.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating or brazing: A furnace with a robust graphite hot zone offers the best combination of performance and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or avoiding carbon contamination: An all-metal hot zone with molybdenum or tungsten elements is the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is processing large, complex shapes uniformly: Pay close attention to the furnace's element design, which should provide 360-degree heating coverage.
By understanding these core principles, you can better select and operate a vacuum furnace as a precise instrument for advanced material engineering.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Generate heat via electrical resistance | Graphite, Molybdenum, Tungsten |
| Thermal Insulation | Contains heat, directs it toward workload | Graphite felt, metallic shields |
| Water-Cooled Chamber | Protects furnace structure and vacuum seals | Double-walled steel vessel |
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation and contamination | Created by vacuum pumps |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free heat treatment?
The right vacuum furnace is critical for your success in applications like aerospace component brazing, medical implant annealing, or advanced materials research. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision-engineered vacuum furnace solutions.
Our experts will help you select the ideal system—whether you need a cost-effective graphite hot zone or a high-purity all-metal system—to ensure superior temperature uniformity and process control for your specific materials.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your thermal processing requirements and discover the perfect vacuum furnace for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















