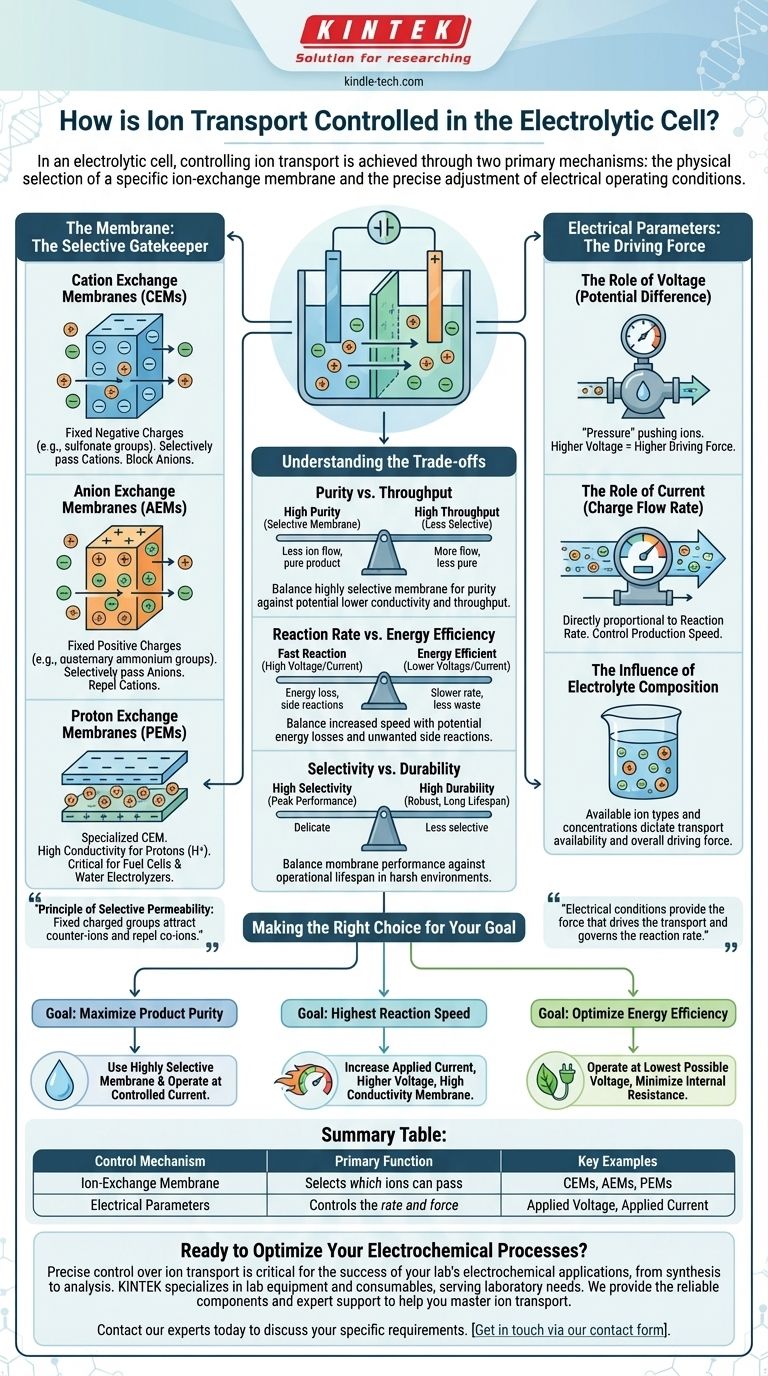
In an electrolytic cell, controlling ion transport is achieved through two primary mechanisms: the physical selection of a specific ion-exchange membrane and the precise adjustment of electrical operating conditions. The membrane acts as a selective gatekeeper, determining which ions can cross, while parameters like voltage and current dictate the rate and force of that movement.
The core principle is to create a highly selective environment. The membrane separates the cell and allows only desired ions to pass, while electrical parameters provide the driving force to control the speed and efficiency of the electrochemical reaction.

The Membrane: The Selective Gatekeeper
The ion-exchange membrane is a physical barrier that separates the anode and cathode compartments. Its primary function is to prevent the mixing of products and reactants while allowing specific ions to pass through, completing the electrical circuit.
The Principle of Selective Permeability
These membranes are not simple filters. They are engineered polymers with fixed charged groups embedded within their structure. These fixed charges attract ions of the opposite charge (counter-ions) and repel ions of the same charge (co-ions), enabling selective transport.
Cation Exchange Membranes (CEMs)
CEMs contain fixed negative charges (e.g., sulfonate groups). This negatively charged matrix allows positively charged ions (cations) to pass through while blocking negatively charged ions (anions).
Anion Exchange Membranes (AEMs)
Conversely, AEMs contain fixed positive charges (e.g., quaternary ammonium groups). This structure permits the passage of negatively charged ions (anions) while repelling cations.
Proton Exchange Membranes (PEMs)
A PEM is a specialized type of cation exchange membrane. It is specifically designed to have exceptionally high conductivity for protons (H+ ions), making it a critical component in applications like hydrogen fuel cells and water electrolyzers.
Electrical Parameters: The Driving Force
While the membrane sets the rules for which ions can pass, the electrical conditions provide the force that drives the transport and governs the reaction rate.
The Role of Voltage
Voltage (or potential difference) is the "pressure" that pushes the ions across the membrane and drives the electrochemical reaction. A higher voltage increases the driving force on the ions.
The Role of Current
Current is the measure of the rate of charge flow. In an electrolytic cell, the applied current is directly proportional to the rate at which the electrochemical reaction occurs. Controlling the current gives you direct control over the production speed.
The Influence of Electrolyte Composition
The types and concentrations of ions present in the electrolyte are fundamental. The system can only transport ions that are available, and the concentration gradient between the compartments also contributes to the overall driving force for ion migration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precise control of ion transport involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to designing an effective and efficient process.
Purity vs. Throughput
A highly selective membrane will yield a very pure product by preventing unwanted ions from crossing. However, this high selectivity can sometimes result in lower ionic conductivity, slowing down the overall rate of transport and reducing throughput.
Reaction Rate vs. Energy Efficiency
Increasing the voltage and current will speed up the reaction rate. However, pushing the system too hard increases energy losses due to electrical resistance (ohmic losses) and can initiate unwanted side reactions, lowering the overall energy efficiency.
Selectivity vs. Durability
The chemical environment and operating temperature of the cell can degrade the membrane over time. The most selective membranes may not be the most robust, requiring a choice between peak performance and operational lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective determines how you should balance these control mechanisms.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product purity: Prioritize a highly selective ion-exchange membrane specific to your target ion and operate at a controlled current to minimize side reactions.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest reaction speed: You will need to increase the applied current, which may require a higher voltage and a membrane with high ionic conductivity, potentially at the cost of energy efficiency.
- If your primary focus is optimizing energy efficiency: Operate at the lowest possible voltage that still achieves the desired reaction rate, and ensure the electrolyte composition and membrane are chosen to minimize internal resistance.
Mastering ion transport is a strategic balance between the physical selectivity of the membrane and the electrical force you apply to the system.
Summary Table:
| Control Mechanism | Primary Function | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Ion-Exchange Membrane | Selects which ions can pass | Cation Exchange Membranes (CEMs), Anion Exchange Membranes (AEMs), Proton Exchange Membranes (PEMs) |
| Electrical Parameters | Controls the rate and force of ion movement | Applied Voltage (driving force), Applied Current (reaction rate) |
Ready to Optimize Your Electrochemical Processes?
Precise control over ion transport is critical for the success of your lab's electrochemical applications, from synthesis to analysis. The right equipment is fundamental to achieving high purity, throughput, and energy efficiency.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the reliable components and expert support to help you master ion transport in your electrolytic cells. Our range includes high-quality ion-exchange membranes and compatible lab equipment designed for consistent performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how we can help you achieve superior control and results in your lab. Get in touch via our contact form to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
People Also Ask
- What is the volume range of the coating evaluation electrolytic cell? A Guide to Choosing the Right Size
- What is the operating principle of a flat plate corrosion electrolytic cell? A Guide to Controlled Materials Testing
- How does a three-electrode electrolytic cell function? Precision Testing for 8620 Steel in Corrosive Environments
- What role does a water-jacketed electrolytic cell play in variable-temperature electrochemical corrosion measurements?
- How is a high-precision electrolytic cell used to evaluate metal corrosion resistance? Validate DCT Results Accurately



















