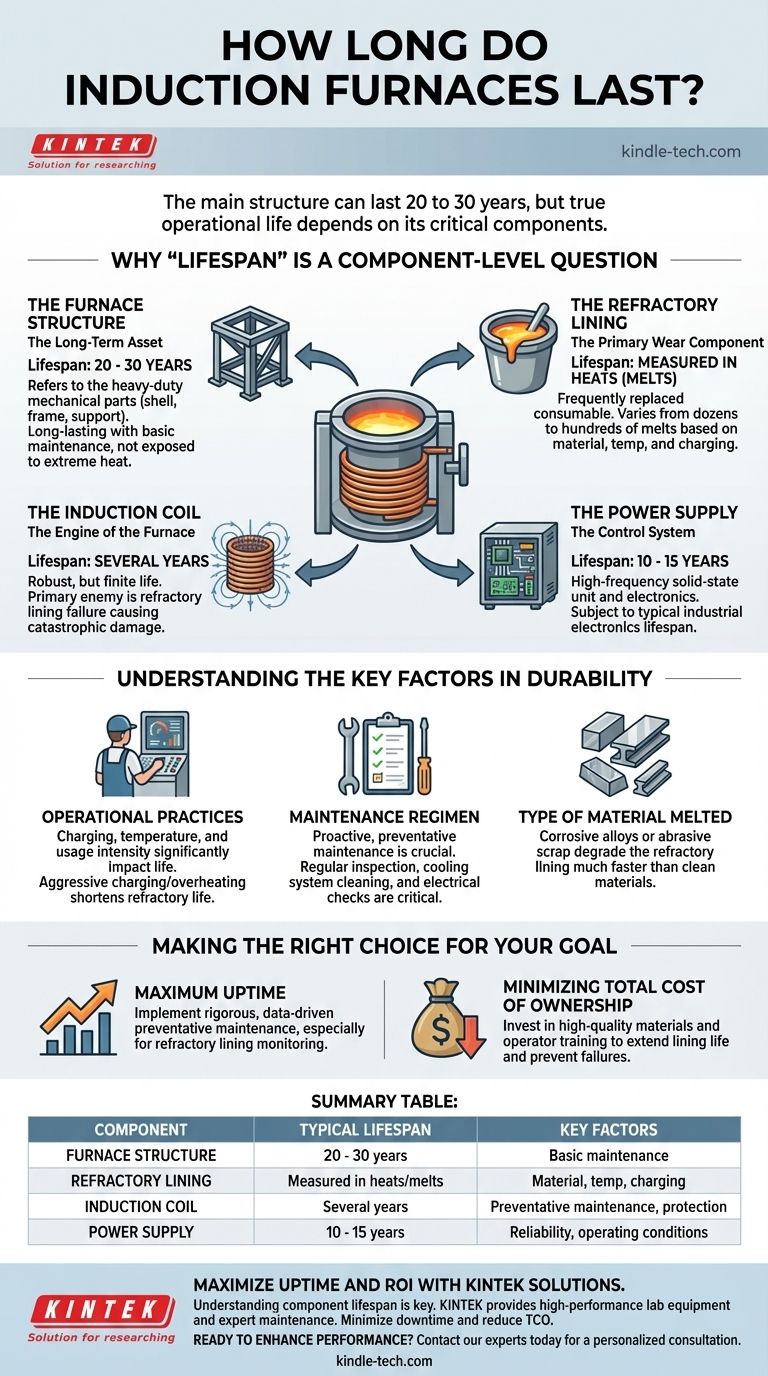
In simple terms, the main structure of an induction furnace can be expected to last 20 to 30 years. However, this figure only represents the durable frame and support systems. The true operational life of the furnace is dictated by its core components, which have much shorter and more variable replacement cycles.
Understanding the lifespan of an induction furnace requires a two-part perspective. While the steel frame is a long-term asset, the furnace's day-to-day reliability and performance depend entirely on the lifecycle of its critical, and much shorter-lived, wear components.
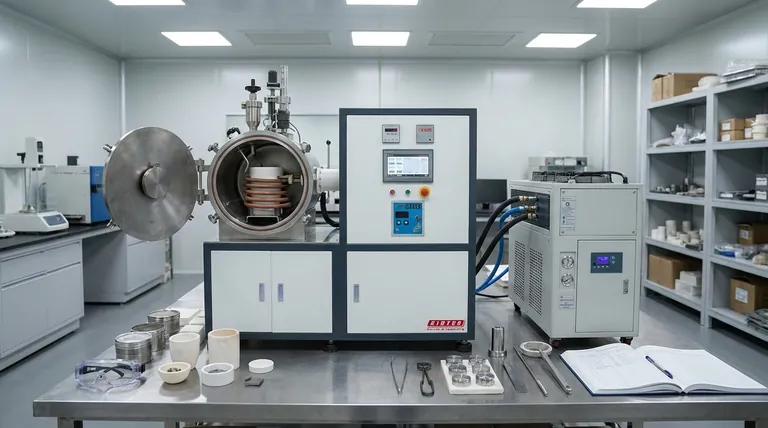

Why "Lifespan" is a Component-Level Question
Thinking of an induction furnace as a single entity with one lifespan is a common oversimplification. A better approach is to view it as a system of parts, each with its own expected service life determined by its function and intensity of use.
The Furnace Structure: The Long-Term Asset
The 20 to 30-year lifespan typically refers to the heavy-duty mechanical components. This includes the steel shell, tilting frame, and support structure.
These parts are not subject to the extreme heat and electrical forces inside the furnace and, with basic maintenance, provide a very long and predictable service life.
The Refractory Lining: The Primary Wear Component
The refractory lining is the crucible that holds the molten metal. It is designed to be a consumable item and is the most frequently replaced part of the furnace.
Its lifespan isn't measured in years, but rather in the number of heats (melts), hours, or days of operation. This can range from a few dozen melts to several hundred, depending heavily on the metal being melted, operating temperatures, and charging practices.
The Induction Coil: The Engine of the Furnace
The induction coil is the critical component that generates the magnetic field to heat and melt the metal. It is a robust part, but its life is finite and highly dependent on operating conditions.
A well-maintained coil can last for several years. However, its primary enemy is a refractory lining failure, where molten metal can break through and cause catastrophic, immediate damage to the coil.
The Power Supply: The Control System
The power supply (often a high-frequency solid-state unit) and its associated electronics manage the entire melting process.
These systems are highly reliable but are subject to the typical lifespan of industrial electronics. You can generally expect 10 to 15 years of service before major component refurbishment or replacement becomes a consideration.
Understanding the Key Factors in Durability
The actual lifespan you experience from each component is not fixed. It is directly influenced by how the equipment is used and maintained.
Operational Practices
How the furnace is charged with material, the temperature it's run at, and whether it operates continuously or intermittently all have a significant impact. Aggressive charging or overheating can drastically shorten the life of the refractory lining.
Maintenance Regimen
A proactive, preventative maintenance schedule is the single most important factor in maximizing lifespan. Regular inspection of the lining for wear, ensuring the cooling system for the coil is clean and effective, and checking electrical connections are all critical tasks.
Type of Material Melted
The properties of the charge material play a direct role. Highly corrosive alloys or charges with sharp, abrasive scrap will degrade the refractory lining much faster than clean, smooth materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To move from a general lifespan estimate to a practical operational strategy, you must align your maintenance and operational procedures with your primary business objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum uptime and production: Implement a rigorous, data-driven preventative maintenance schedule, especially for monitoring and replacing the refractory lining before it can fail.
- If your primary focus is minimizing the total cost of ownership: Invest in high-quality refractory materials and comprehensive operator training to extend the life of each lining and prevent catastrophic failures that can damage the much more expensive induction coil.
Ultimately, a well-maintained induction furnace is a multi-decade asset whose true value is realized by managing the lifecycle of its most critical working parts.
Summary Table:
| Component | Typical Lifespan | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Structure | 20 - 30 years | Basic maintenance; not subject to extreme heat. |
| Refractory Lining | Measured in heats/melts | Material melted, temperature, charging practices. |
| Induction Coil | Several years | Preventative maintenance; protection from lining failure. |
| Power Supply | 10 - 15 years | Reliability of industrial electronics; operating conditions. |
Maximize your induction furnace's uptime and ROI with KINTEK solutions.
Understanding the lifespan of your critical components is the first step to optimizing your melting operations. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable furnace components and expert maintenance support. We help laboratories like yours minimize downtime and reduce the total cost of ownership.
Ready to enhance your furnace's performance and longevity? Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM



















