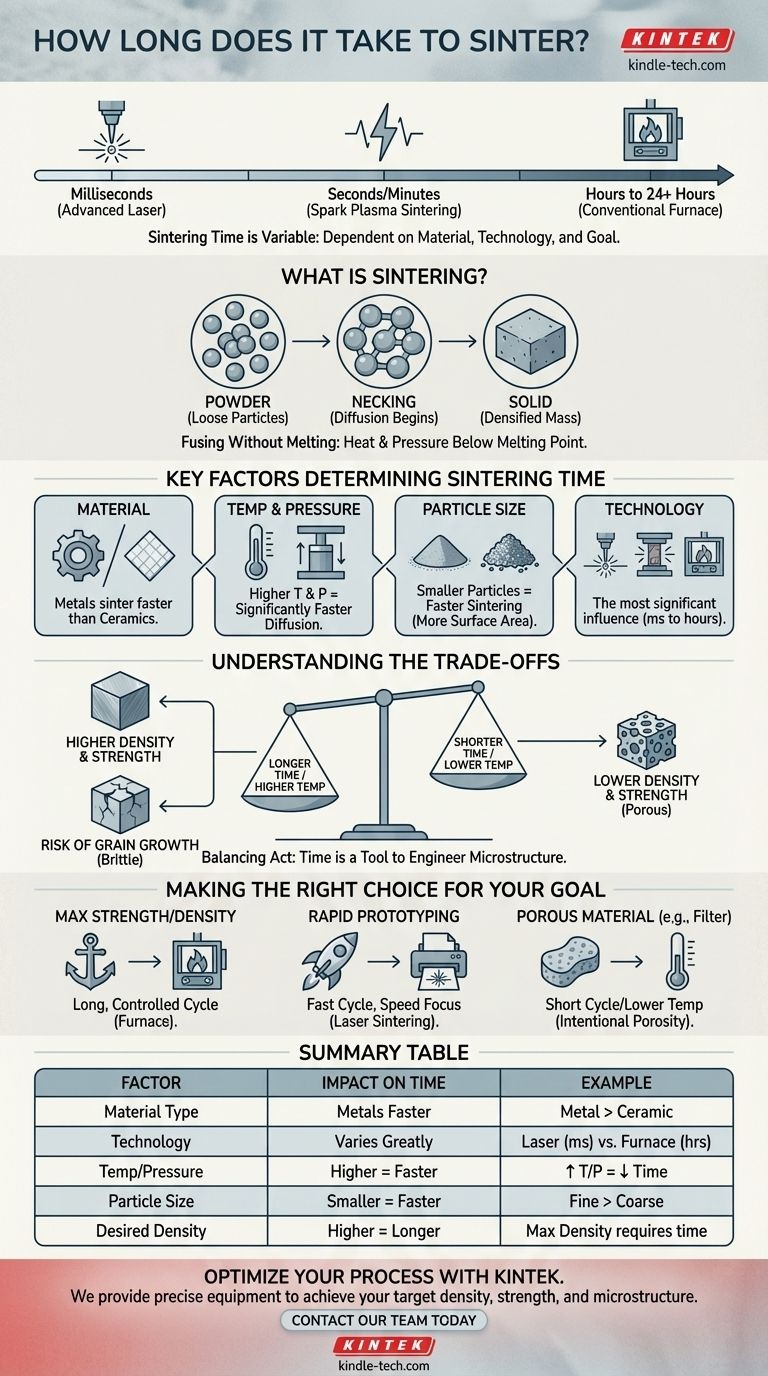
Sintering time is not a single number; it can range from a few milliseconds for advanced laser techniques to over 24 hours for large ceramic components in a conventional furnace. The duration is entirely dependent on the material being used, the specific technology applied, and the desired final properties of the part.
The question isn't just "how long does it take," but rather, "what combination of time, temperature, and pressure will achieve the desired density and strength for a specific material?" Sintering is a controlled process where time is a variable used to engineer a final outcome.

What Exactly is Sintering?
The Core Principle: Fusing Without Melting
Sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms a powder into a solid, dense object using heat and pressure. Crucially, the temperature is kept below the material's melting point.
Instead of liquefying, the atoms at the contact points of the powder particles become agitated by the heat. They begin to diffuse across the particle boundaries, effectively building "necks" that fuse the individual particles together into a single, solid mass.
Why Not Just Melt It?
This process is essential for materials with exceptionally high melting points, like tungsten or certain ceramics, where melting is impractical or prohibitively expensive.
It also allows for the creation of unique material properties. For example, by controlling the process, you can create parts that are intentionally porous, which is impossible to achieve by simply casting from a molten state.
Key Factors That Determine Sintering Time
The vast range in sintering duration comes down to a few key variables. Understanding these factors is essential to controlling the final product.
The Material Being Processed
Different materials have vastly different atomic diffusion rates. Metals generally sinter faster than ceramics, which often require higher temperatures and much longer hold times to allow for the slower diffusion process to complete.
Temperature and Pressure
There is a direct relationship between temperature, pressure, and time. Increasing the temperature or applying external pressure accelerates atomic diffusion, significantly reducing the required sintering time. Advanced techniques like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) leverage this principle.
Particle Size and Shape
The initial state of the powder is critical. Smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, which provides more contact points and energy to drive the diffusion process, leading to faster sintering.
The Sintering Technology
This is the most significant factor influencing the time.
- Conventional Furnace Sintering: This is a batch process that can take many hours, often exceeding 24 hours for large or complex ceramic parts.
- Laser Sintering (SLS/DMLS): A high-power laser sinters powder layer by layer, with each layer taking only seconds or milliseconds to fuse. This is common in 3D printing.
- Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): This advanced method passes a pulsed electrical current through the powder, generating intense localized heat at particle contact points. It can fully densify some materials in minutes instead of hours.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering process is a balancing act. Faster is not always better, and every choice has consequences for the final part.
Time vs. Density and Strength
Generally, a longer sintering cycle (or one at a higher temperature) results in a more complete fusion of particles. This leads to a denser, stronger final part with fewer internal voids. Rushing the process can leave you with a weaker, more porous component.
The Risk of Grain Growth
A major pitfall of sintering for too long or at too high a temperature is grain growth. The internal crystalline structures (grains) within the material can begin to enlarge, which can paradoxically make the final part more brittle and prone to fracture.
Cost vs. Speed
Conventional furnaces represent a lower capital investment but have high energy costs and long cycle times. Advanced, rapid techniques like SPS or laser sintering require extremely expensive equipment but offer unparalleled speed and control, making them suitable for high-value applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your optimal sintering time depends entirely on what you are trying to achieve with the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: You will likely use a longer, carefully controlled cycle in a conventional or vacuum furnace to ensure full densification without excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or high-volume production: Advanced methods like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) are the clear choice, where speed is the dominant factor.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous material (e.g., a filter): You will use a shorter cycle or lower temperature to intentionally halt the process before the part becomes fully dense.
Ultimately, time is just one tool you have to manipulate a material's microstructure and achieve the precise performance characteristics you need.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Sintering Time |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Metals sinter faster than ceramics. |
| Technology Used | Laser (ms) vs. Conventional Furnace (24+ hrs). |
| Temperature/Pressure | Higher levels significantly reduce time. |
| Particle Size | Smaller particles sinter much faster. |
| Desired Density | Maximum strength requires longer cycles. |
Struggling to determine the optimal sintering cycle for your materials? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve your target density, strength, and microstructure. Let us help you optimize your process for superior results. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics



















