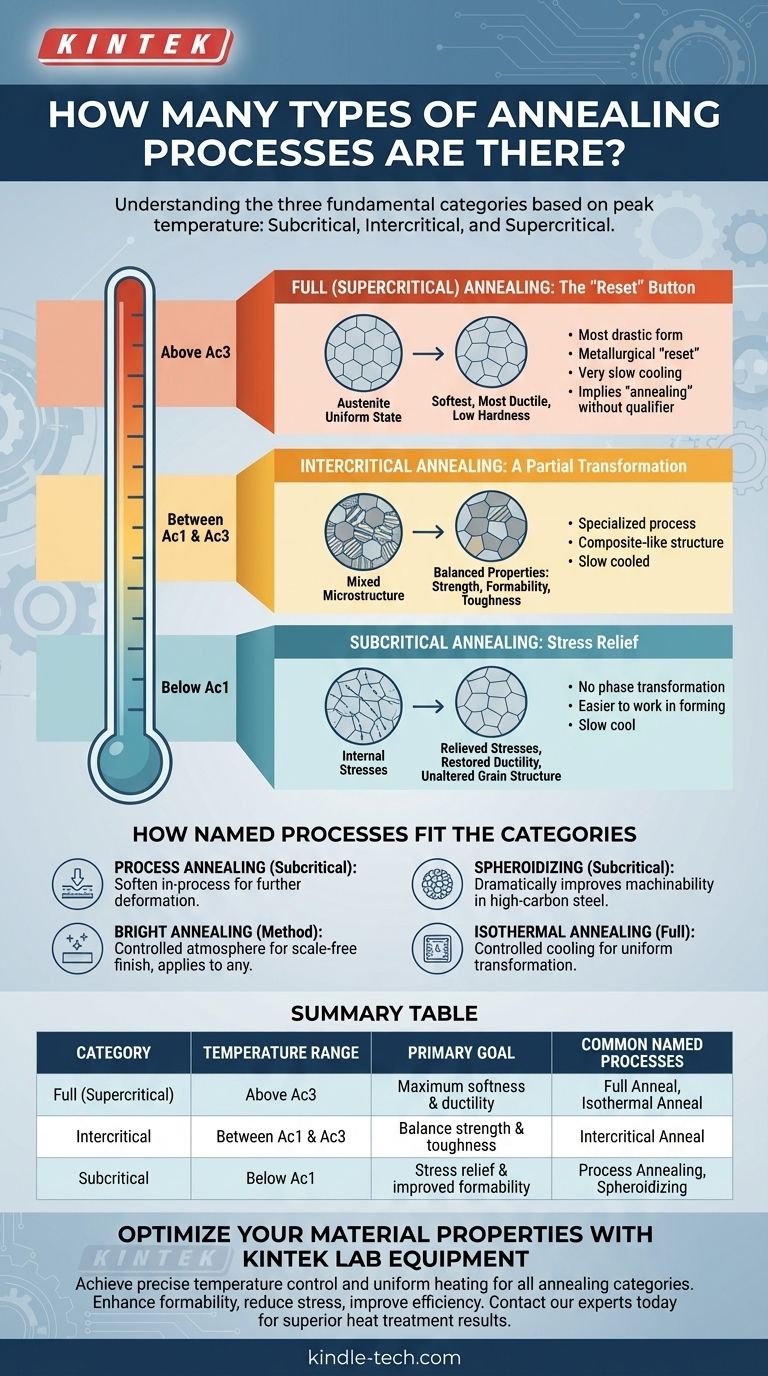
While there are over a dozen specifically named annealing processes, they are best understood not as a long list, but as variations within three fundamental categories. These categories are defined by the peak temperature the metal is heated to relative to its critical transformation points. The choice of process is dictated entirely by the desired final properties of the material.
The key is to stop trying to memorize the dozen-plus named processes. Instead, focus on the three core temperature ranges—subcritical, intercritical, and supercritical—as this is what truly determines whether you are simply relieving stress, creating a hybrid structure, or performing a full "reset" on the material's properties.
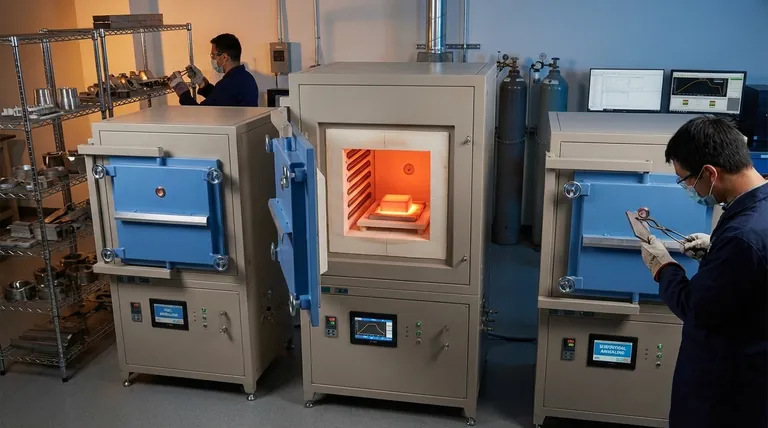

The Three Fundamental Categories of Annealing
Nearly every named annealing process falls into one of three groups based on temperature. Understanding these categories is the foundation for selecting the correct heat treatment.
Full (Supercritical) Annealing: The 'Reset' Button
This process involves heating the steel above its upper critical temperature (Ac3), where its entire grain structure transforms into a uniform state called austenite. It is then cooled very slowly.
This is the most drastic form of annealing, effectively acting as a metallurgical "reset." It produces the softest, most ductile state with the lowest hardness and highest internal uniformity. When a specification simply calls for "annealing" without a qualifier, it typically implies a full anneal.
Intercritical Annealing: A Partial Transformation
As the name suggests, this involves heating the material to a temperature between its lower (Ac1) and upper (Ac3) critical points. It is then slow-cooled.
Because it doesn't reach the temperature for full transformation, the result is a mixed microstructure. This is a specialized process used to create a composite-like structure within the steel, balancing properties like strength, formability, and toughness in ways that a full anneal cannot.
Subcritical Annealing: Stress Relief without Structural Change
This process involves heating the material to a temperature just below the lower critical point (Ac1) and then cooling it slowly.
Since the temperature never reaches the point of phase transformation, the fundamental grain structure is not altered. The primary purpose is to relieve internal stresses built up during cold working (like drawing, stamping, or bending) and to restore some ductility. This makes the material easier to work with in subsequent forming operations.
How Named Processes Fit the Categories
The long list of specific annealing names can be confusing. Most of these are simply industry terms for processes that fall into the three main categories, often named for their specific purpose or method.
Process Annealing
This is a form of subcritical annealing. Its name comes from its purpose: to soften a material in-process, between different cold working steps, to make further deformation possible without fracture.
Spheroidizing
This is another specialized subcritical annealing process. It involves a long hold time just below the Ac1 temperature to force iron carbides in the steel's microstructure to form small, round spheres. This structure dramatically improves the machinability of high-carbon steels.
Bright Annealing
This term does not refer to a temperature range but to the method. Any of the three core processes can be performed as a "bright anneal" by heating and cooling the material in a controlled atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent surface oxidation, resulting in a clean, scale-free finish.
Isothermal Annealing
This is a more controlled variation of full annealing. After heating above Ac3, the part is cooled rapidly to a specific temperature below Ac1 and held there for a set time to achieve a highly uniform transformation. It offers more precise results than a simple slow cool but is more complex and costly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an annealing process is a matter of balancing competing material properties, costs, and production time.
Softness vs. Strength
This is the central trade-off. A full anneal achieves maximum softness and ductility, which comes at the cost of minimum hardness and tensile strength. Subcritical annealing, by contrast, retains much of the strength gained from cold working while only providing stress relief.
Time vs. Cost
The slower the cooling rate and the longer the hold times, the softer the final product generally is. However, furnace time is expensive. Processes like spheroidizing or long-cycle full anneals can take many hours, significantly increasing energy consumption and production costs.
Grain Size Control
During any anneal that involves recrystallization (full or intercritical), holding the material at temperature for too long can cause the newly formed grains to grow too large. While this further increases softness, excessively large grains can drastically reduce a material's toughness and lead to a poor surface finish after forming, a condition known as "orange peel."
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your annealing process based on the functional requirements of the finished part.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness and ductility for severe forming: Choose a full (supercritical) annealing process to completely recrystallize the microstructure.
- If your primary focus is relieving stress from cold working: Use a subcritical process like process annealing to restore formability without significantly altering strength.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability in high-carbon steel: Spheroidizing is the specific subcritical process designed for this exact purpose.
- If your primary focus is a precise balance of strength and toughness: An intercritical or specialized cycle like isothermal annealing offers more control over the final microstructure.
Ultimately, selecting the right annealing process begins with a clear definition of your material's required end-state.
Summary Table:
| Category | Temperature Range | Primary Goal | Common Named Processes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full (Supercritical) Annealing | Above upper critical (Ac3) | Maximum softness and ductility | Full Anneal, Isothermal Anneal |
| Intercritical Annealing | Between lower (Ac1) and upper (Ac3) critical points | Balance strength and toughness | Intercritical Anneal |
| Subcritical Annealing | Below lower critical (Ac1) | Stress relief and improved formability | Process Annealing, Spheroidizing |
Optimize Your Material Properties with KINTEK Lab Equipment
Selecting the right annealing process is critical for achieving your desired material outcomes—whether it's maximum softness, stress relief, or improved machinability. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab furnaces and consumables that deliver precise temperature control and uniform heating for all three annealing categories.
Our equipment ensures reliable results for processes like full annealing, spheroidizing, and bright annealing, helping you enhance material formability, reduce internal stresses, and improve production efficiency.
Ready to achieve superior heat treatment results? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific annealing needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification



















