In most practical applications, a properly executed aluminum brazed joint is often stronger and more reliable than a welded one. While a perfect weld bead can theoretically match the strength of the base metal, the intense, localized heat of welding often weakens the surrounding aluminum, creating a failure point. Brazing uses lower, more evenly distributed heat, preserving the integrity of the base metal and creating a joint that can be stronger than the aluminum itself.
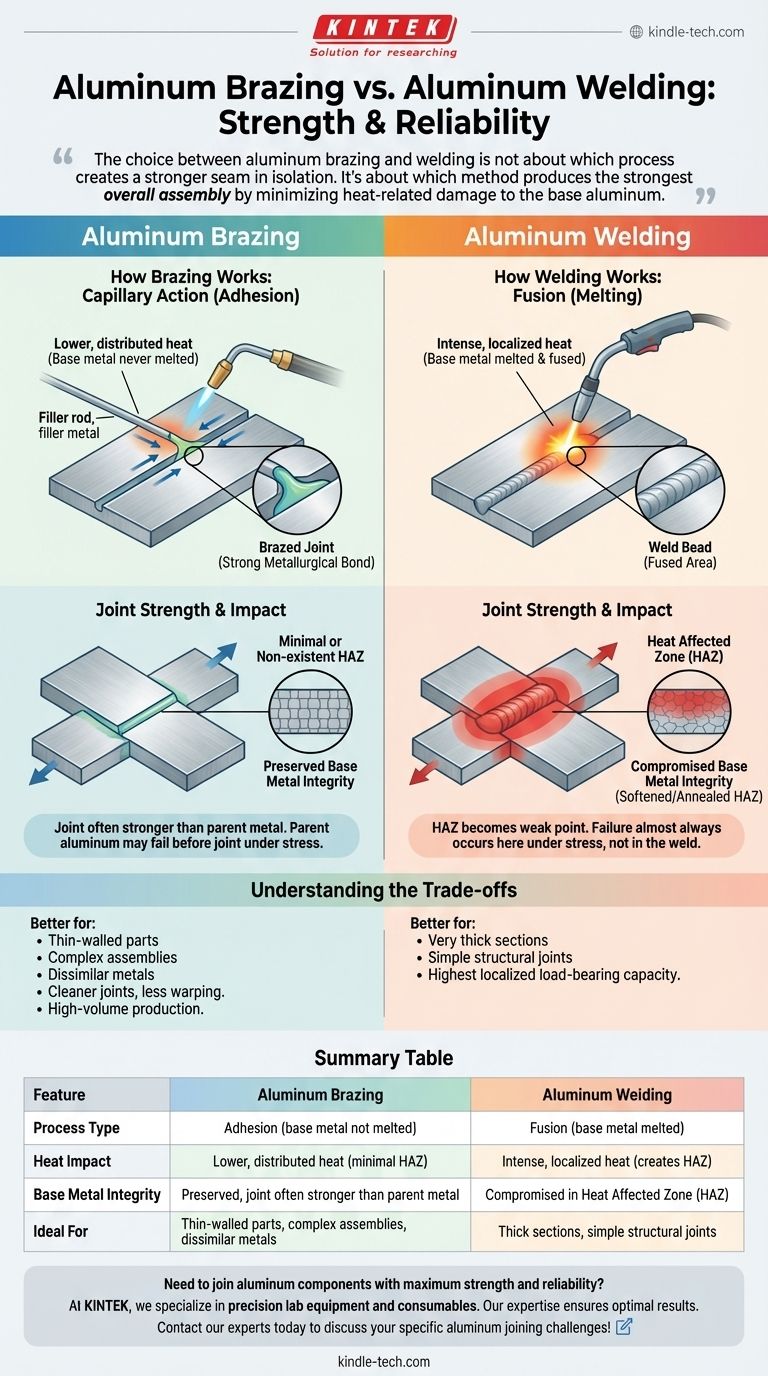
The choice between aluminum brazing and welding is not about which process creates a stronger seam in isolation. It's about which method produces the strongest overall assembly by minimizing heat-related damage to the base aluminum.

The Fundamental Difference: Fusion vs. Adhesion
To understand the strength comparison, you must first understand how each process works. The core difference lies in their interaction with the base metal.
How Welding Works: Fusion
Welding joins metals by melting and fusing them together, often with a compatible filler material.
This creates a single, continuous piece of metal. The goal is to achieve a metallurgical bond where the weld becomes an integral part of the parent material.
How Brazing Works: Capillary Action
Brazing joins metals using a filler material that has a lower melting point than the base metal.
The base aluminum parts are heated, but never melted. The filler metal melts, is drawn into the tight-fitting joint via capillary action, and forms an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond as it cools.
A Direct Comparison of Joint Strength
The debate over strength isn't about the joint itself, but about how the process affects the material around it. This is especially critical with heat-treated aluminum alloys.
The Strength of a Welded Joint
A textbook TIG or MIG weld on aluminum can be very strong. The fused area can match the tensile strength of the parent metal.
The problem, however, is not the weld bead itself.
The Impact of the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
The intense, concentrated heat of welding creates a Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) in the area immediately surrounding the weld.
In this zone, the aluminum's temper is compromised—it is effectively annealed and softened. This HAZ becomes the weak point of the assembly, and it is almost always where a failure will occur under stress, not in the weld itself.
The Strength of a Brazed Joint
Brazing uses significantly lower temperatures that are distributed more evenly across the joint.
This process has a much less severe impact on the aluminum's base temper, resulting in a minimal or non-existent HAZ. A well-designed brazed joint is so strong that under destructive testing, the parent aluminum next to the joint will often fail before the brazed seam does.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither process is universally "better." The optimal choice is dictated by the specific requirements of the application.
When Welding Is the Better Choice
Welding is often preferred for very thick sections or simple structural joints where the HAZ can be managed through design or post-weld heat treatment. It excels in applications demanding the highest possible load-bearing capacity in a localized seam.
When Brazing Is the Better Choice
Brazing is superior for thin-walled parts where welding would cause burn-through or warping. It is also ideal for complex assemblies and provides cleaner, more uniform joints with less post-finishing required. Its ability to join dissimilar metals is another significant advantage.
Skill and Preparation Requirements
Both processes demand extremely high levels of cleanliness. However, welding aluminum is notoriously difficult and requires a high degree of operator skill to manage the heat and prevent defects. Brazing can be a more repeatable and controllable process, making it better suited for high-volume production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct method, shift your focus from "which is stronger" to "which better serves my project's goal."
- If your primary focus is raw strength on thick, simple parts: A high-quality weld may be suitable, but you must design around the weakened Heat Affected Zone.
- If your primary focus is preserving base metal integrity and minimizing distortion: Brazing is the superior choice, resulting in a more reliable overall assembly.
- If you are working with thin materials or complex geometries: Brazing offers far greater control and dramatically reduces the risk of warping and damage.
Ultimately, the best joining method is the one that maintains the strength and integrity of the entire finished part.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Aluminum Brazing | Aluminum Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Adhesion (base metal not melted) | Fusion (base metal melted) |
| Heat Impact | Lower, distributed heat (minimal HAZ) | Intense, localized heat (creates HAZ) |
| Base Metal Integrity | Preserved, joint often stronger than parent metal | Compromised in Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) |
| Ideal For | Thin-walled parts, complex assemblies, dissimilar metals | Thick sections, simple structural joints |
Need to join aluminum components with maximum strength and reliability?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables for material joining applications. Our expertise ensures you achieve optimal results whether you're brazing or welding. Let us help you select the right tools and materials for superior joint integrity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific aluminum joining challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints



















