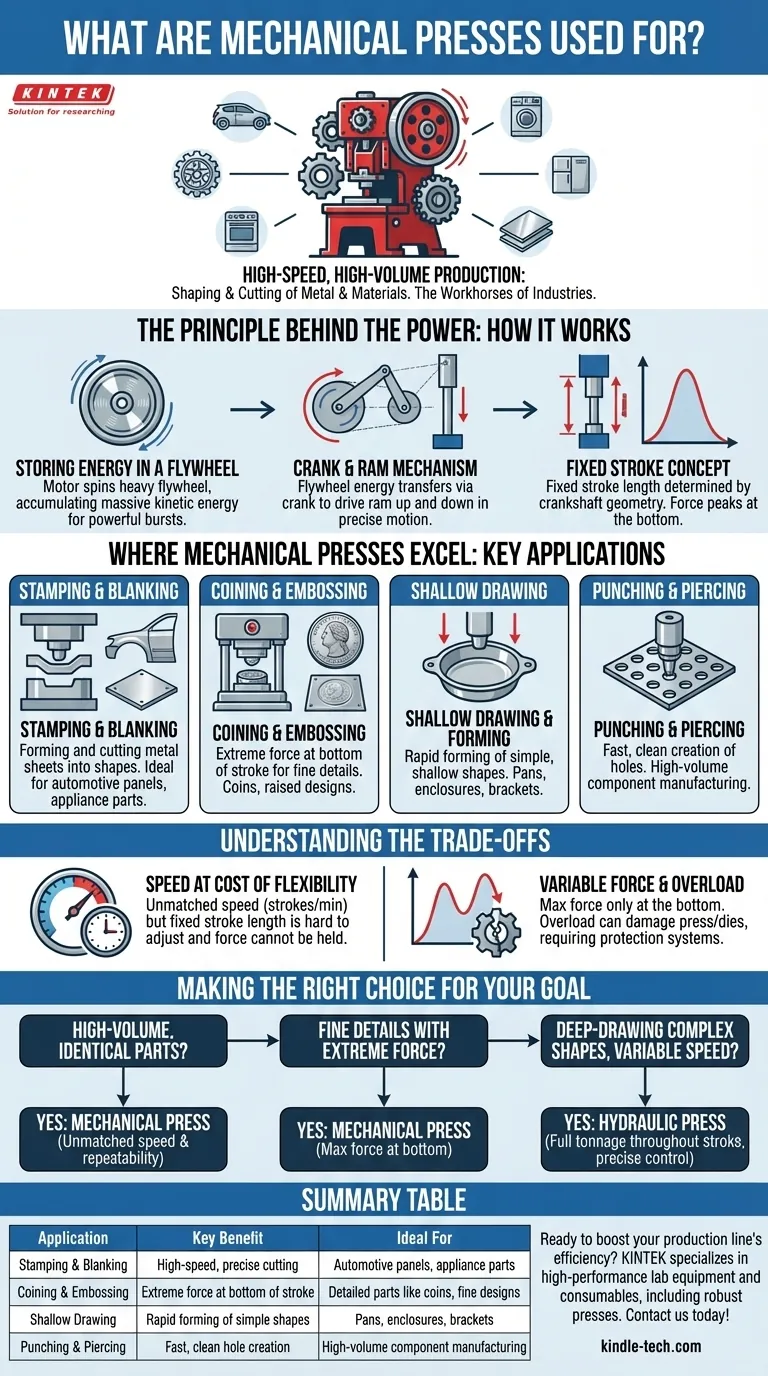
At their core, mechanical presses are used for high-speed, high-volume production tasks involving the shaping and cutting of metal and other materials. They are the workhorses of industries like automotive manufacturing and appliance production, valued for their exceptional speed, precision, and consistency in operations such as stamping, coining, and blanking.
The defining feature of a mechanical press is its use of a motor-driven flywheel to store energy, which is then transferred through a crank mechanism to deliver a rapid, powerful stroke. This design makes them ideal for repetitive, high-speed operations but less flexible than their hydraulic counterparts.

The Principle Behind the Power: How a Mechanical Press Works
A mechanical press operates on a principle of converting rotational motion into linear motion to apply force. This mechanism is key to understanding its best applications.
Storing Energy in a Flywheel
An electric motor spins a heavy flywheel, which accumulates a massive amount of kinetic energy. This continuous energy storage allows the press to deliver immense force in short bursts without needing an enormous motor.
The Crank and Ram Mechanism
The energy from the flywheel is transferred via a clutch and crank system, similar to the crankshaft in a car's engine. This mechanism drives a ram (or slide) up and down in a precise, repeatable motion.
The Concept of a Fixed Stroke
Unlike a hydraulic press where the stroke length and pressure can be varied, a mechanical press has a fixed stroke length determined by the geometry of its crankshaft. The force is also not constant, peaking near the bottom of the stroke.
Where Mechanical Presses Excel: Key Applications
The speed and precision of the fixed stroke make mechanical presses the superior choice for specific, high-volume manufacturing processes.
Stamping and Blanking
This is the most common application. Stamping uses a die to form a sheet of metal into a desired shape, like a car door panel. Blanking uses a die to punch out a piece of material from a larger sheet, often as the first step in a larger process.
Coining and Embossing
These processes require extremely high force applied at the very bottom of the stroke to create fine details. Coining forces metal to flow into the die's details (like making a coin), while embossing creates a raised or recessed design.
Shallow Drawing and Forming
Mechanical presses are excellent for forming sheet metal into relatively simple, shallow shapes. This includes creating pans, enclosures, and brackets where the material doesn't need to be stretched excessively.
Punching and Piercing
This involves creating holes in a workpiece. The high speed of a mechanical press allows for rapid, clean punching of single or multiple holes, making it ideal for mass production of components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a mechanical press involves clear trade-offs between speed and flexibility. Understanding these is critical for making an informed decision.
Speed Comes at the Cost of Flexibility
The primary advantage of a mechanical press is its cycle speed, often measured in strokes per minute. However, the fixed stroke length means it cannot be easily adjusted for jobs of different heights, and the force cannot be held for a set duration.
Variable Force Through the Stroke
A mechanical press only delivers its maximum rated tonnage at the very bottom of its stroke. The available force is much lower at the beginning and middle of the stroke, making it unsuitable for applications that require constant pressure throughout the forming process.
Overload Protection is Critical
Because the flywheel stores so much energy, accidentally applying too much force (e.g., due to incorrect die setup) can cause catastrophic damage to the press frame or dies. Modern presses have sophisticated overload protection systems to prevent this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of press is determined entirely by your production requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of identical parts: A mechanical press is almost always the correct choice due to its unmatched speed and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is creating fine details with extreme force: A mechanical press is ideal for coining and embossing, where maximum force is needed at the bottom of the stroke.
- If your primary focus is deep-drawing complex shapes or tasks requiring variable speed and pressure: A hydraulic press is a better alternative, offering full tonnage throughout the stroke and precise control over ram movement.
By aligning the unique characteristics of the mechanical press with your manufacturing goals, you ensure efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness in your operation.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Stamping & Blanking | High-speed, precise cutting | Automotive panels, appliance parts |
| Coining & Embossing | Extreme force at bottom of stroke | Detailed parts like coins, fine designs |
| Shallow Drawing | Rapid forming of simple shapes | Pans, enclosures, brackets |
| Punching & Piercing | Fast, clean hole creation | High-volume component manufacturing |
Ready to boost your production line's efficiency? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including robust mechanical presses tailored for laboratory and industrial needs. Our solutions ensure precision, speed, and reliability for your metal forming tasks. Contact us today to find the perfect press for your high-volume manufacturing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How do you prepare samples for IR spectroscopy as KBr disks? Master the Technique for Clear, Accurate Spectra
- What is the content of filter press solids? A Direct Reflection of Your Input Slurry
- What creates heat in a hydraulic system? Understanding Energy Loss and Pressure Drop
- Is a hydraulic press a hydraulic system? A Complete Guide to Its Core Principles
- How do you prepare KBr pellets for FTIR analysis? Master the Technique for High-Quality IR Spectra
- What is the minimum sample required for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Material Analysis
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press ensure the performance of solid electrolyte layers in sodium batteries?
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press facilitate LAGP-PEO composite membrane formation? Achieve 76μm Precision



















