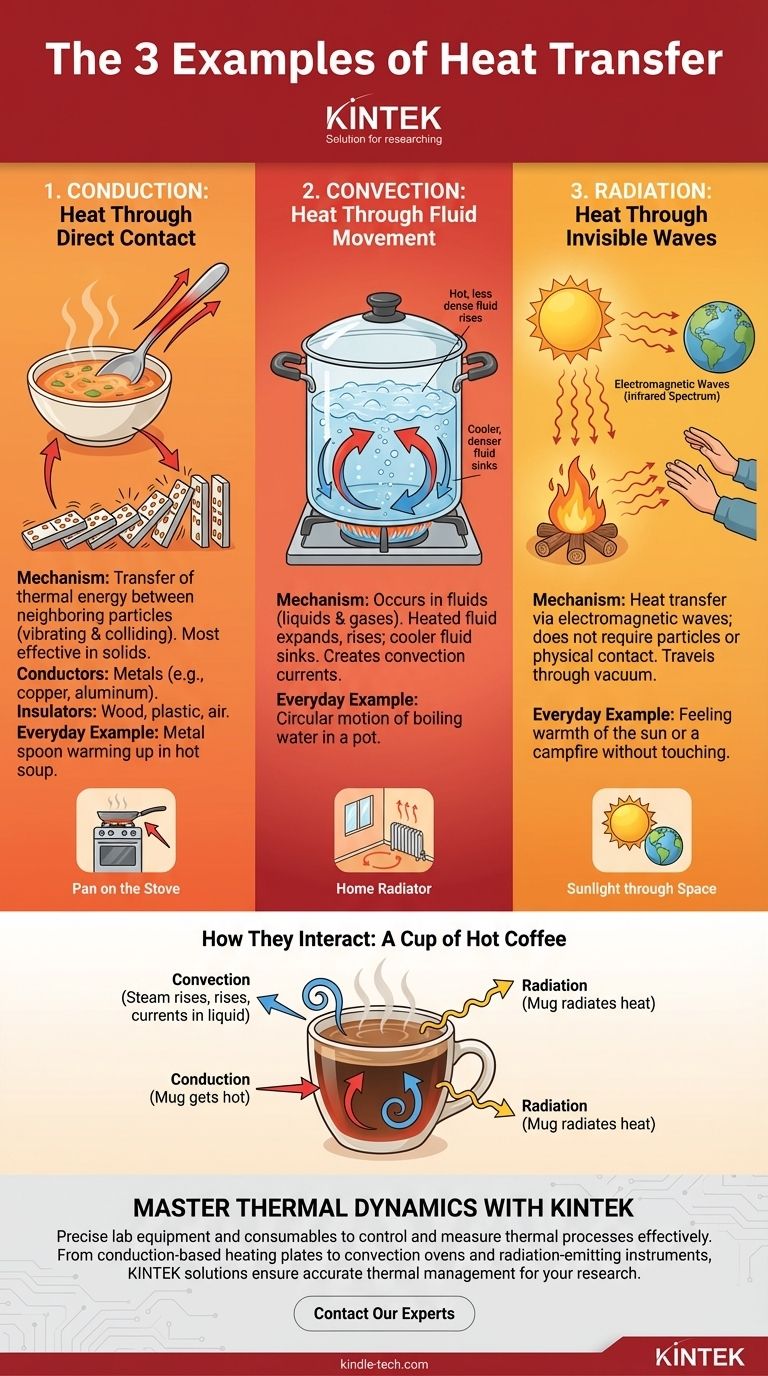
The three fundamental examples of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is heat moving through a solid object, like a metal spoon warming up in hot soup. Convection is heat transferred by the movement of fluids, such as the circular motion of boiling water in a pot. Radiation is heat moving through electromagnetic waves, which is how you feel the warmth of the sun or a campfire without touching it.
Heat is simply energy in transit, and it always moves from a warmer object to a cooler one. Understanding the three distinct ways it travels—through direct contact (conduction), fluid flow (convection), and invisible waves (radiation)—is the key to grasping thermal dynamics in everything from engineering to everyday life.

Conduction: Heat Through Direct Contact
The Mechanism
Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy between neighboring particles in a substance. The particles themselves do not move from place to place, but they vibrate and collide, passing energy from one to the next like a series of falling dominoes.
This process is most effective in solids, where particles are tightly packed.
The Role of Materials
Materials that transfer heat easily, like copper and aluminum, are called conductors. This is why pots and pans are made of metal.
Materials that transfer heat poorly, such as wood, plastic, and air, are called insulators. This is why pan handles are often made of plastic or wood to protect your hand.
Everyday Example: A Pan on the Stove
When you place a metal pan on an electric stove, the burner's heat energizes the particles at the bottom of the pan. These particles vibrate rapidly, colliding with their neighbors and transferring that energy progressively up and through the entire pan.
Convection: Heat Through Fluid Movement
The Mechanism
Convection only occurs in fluids—liquids and gases—where particles are free to move. When a fluid is heated from below, it expands, becomes less dense, and rises.
Cooler, denser fluid from above then sinks to take its place, gets heated, and rises in turn. This continuous circulation is called a convection current.
Where It Occurs
You can see convection in action when boiling water or when watching smoke rise from a chimney. It is also the primary mechanism that drives wind and ocean currents on a global scale.
Everyday Example: A Home Radiator
A radiator or space heater warms the air directly next to it. This hot air rises toward the ceiling, pushing the cooler air at the top of the room down toward the floor. The cool air is then drawn toward the heater, creating a circular flow that gradually warms the entire room.
Radiation: Heat Through Invisible Waves
The Mechanism
Radiation is unique because it does not require any particles or physical contact to transfer heat. It travels as electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared spectrum.
This energy can travel through the vacuum of space, which is why we feel the heat of the sun despite it being 93 million miles away.
Key Difference from Other Modes
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The hotter the object, the more radiation it emits. Unlike conduction or convection, you can feel this heat instantly from a distance.
Everyday Example: A Campfire
When you stand near a campfire, you feel its warmth on your face and hands. This heat is not primarily from hot air (convection) reaching you, but from the infrared radiation traveling in straight lines from the fire to you.
How These Modes Interact in the Real World
In most situations, all three modes of heat transfer are happening simultaneously, though one may be dominant. Recognizing their interplay is key to a complete understanding.
A Cup of Hot Coffee
Consider a simple mug of coffee.
- Conduction: Heat transfers from the hot coffee directly to the ceramic mug, making the mug hot to the touch. If you put a metal spoon in it, the spoon's handle will get warm via conduction.
- Convection: Steam rises from the surface, carrying heat away into the air. Within the coffee itself, subtle convection currents circulate as the liquid at the top cools and sinks.
- Radiation: The warm outer surface of the mug radiates heat outwards. You can feel this by holding your hand near the mug without touching it.
Identifying Heat Transfer in Your Environment
By understanding these principles, you can better analyze and control the flow of heat for specific goals.
- If your primary focus is insulation: You must block all three modes. A thermos uses a vacuum to stop conduction and convection, and a reflective silver lining to stop radiation.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating (like cooking): You rely on conduction from the pan, convection from hot air in an oven or boiling water, and radiation from a broiler.
- If your primary focus is understanding climate: You see the sun heating the Earth via radiation, the ground heating the air above it via conduction, and that warm air rising to create wind via convection.
Once you recognize these three processes, you begin to see the invisible flow of energy that shapes the world around you.
Summary Table:
| Mode of Heat Transfer | How It Works | Key Characteristic | Everyday Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Direct particle-to-particle contact | Requires a solid medium | Metal spoon heating in hot soup |
| Convection | Movement of fluids (liquids/gases) | Creates circular currents | Boiling water in a pot |
| Radiation | Electromagnetic waves (infrared) | Travels through a vacuum | Feeling warmth from the sun |
Master Thermal Dynamics with KINTEK
Understanding heat transfer is fundamental to laboratory work, whether you're designing experiments, operating equipment, or analyzing results. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need to control and measure thermal processes effectively.
From conduction-based heating plates to convection ovens and radiation-emitting instruments, our products ensure accurate and reliable thermal management for your research and testing needs. Let us help you optimize your lab's thermal processes for better outcomes.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What products are manufactured with titanium? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Materials
- How does a high-speed homogenizer prepare m-BN and PNF dispersions? Achieve Uniform Molecular-Level Integration
- How does sintering work ceramics? Unlock the Process for Dense, High-Strength Materials
- What varieties of high-temperature furnaces are available? Find the Perfect Lab Furnace for Your Thermal Research
- What are CBD distillates? Discover the Key Differences Between Full, Broad & Isolate
- What is the difference between DC sputtering and DC magnetron sputtering? Unlock Higher Deposition Rates
- What are the structures of molds? Discover the Microscopic Filaments That Build a Colony
- How does a pyrolysis plant work? Transform Waste into Fuel and Chemicals











