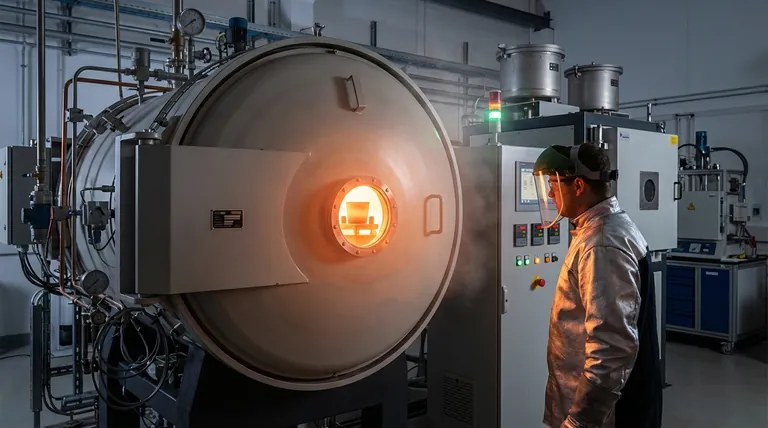
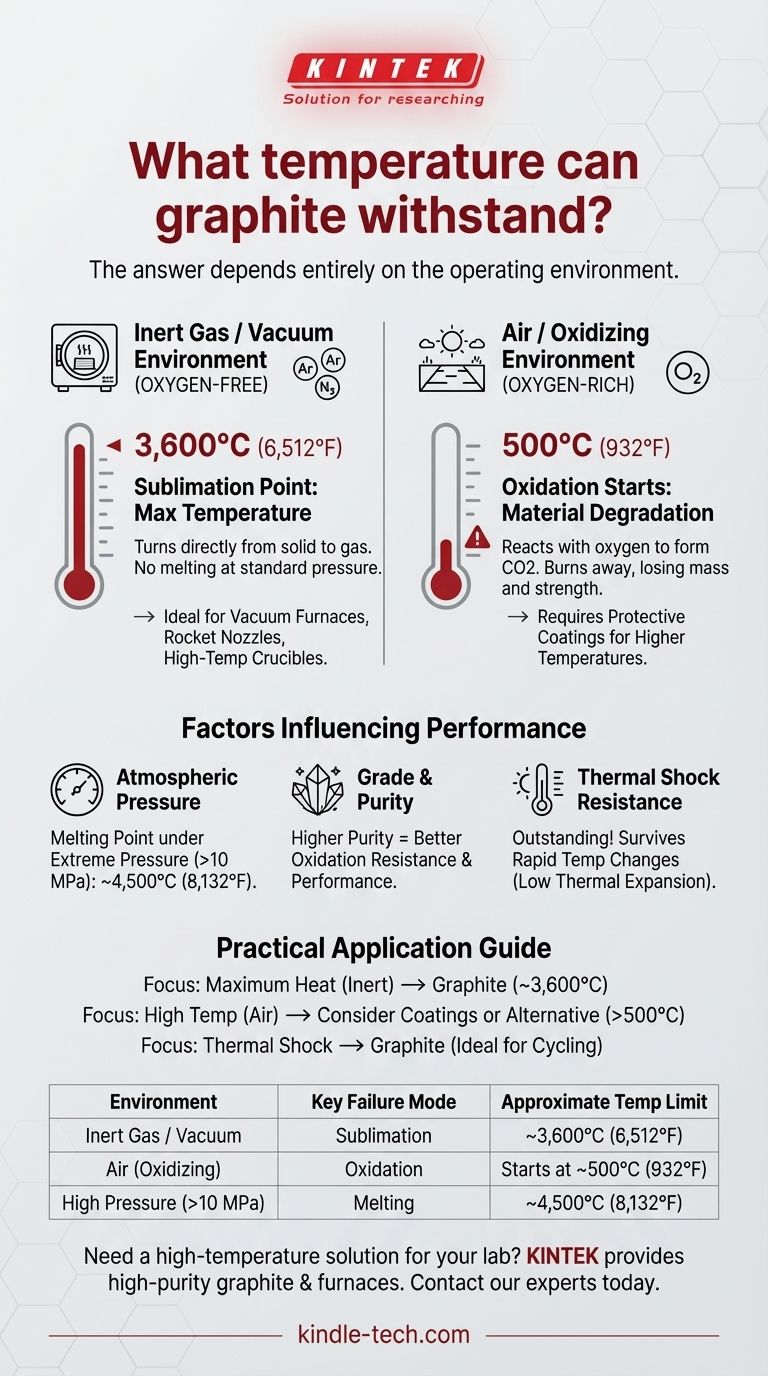
The maximum temperature graphite can withstand is fundamentally determined by its environment. Under inert conditions, pure graphite can handle temperatures up to its sublimation point of approximately 3,600°C (6,512°F). However, in the presence of oxygen, its performance changes dramatically, as it will begin to oxidize and degrade at temperatures as low as 500°C (932°F).
The true thermal limit of graphite is not a single number. Its exceptional high-temperature stability can only be realized in a vacuum or an inert atmosphere, while its practical limit in air is dictated by a much lower oxidation temperature.

The Two Failure Modes of Graphite at High Temperature
To understand graphite's limits, you must distinguish between its behavior in an oxygen-free environment versus an oxygen-rich one. These two scenarios present entirely different thermal ceilings.
Sublimation in an Inert Environment
In a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen), graphite does not melt at standard pressures. Instead, it sublimates, turning directly from a solid into a gas.
This process begins around 3,600°C (6,512°F). This represents the absolute maximum temperature the material can endure before its atomic bonds break down. This property makes it invaluable for applications like vacuum furnace components, rocket nozzles, and high-temperature crucibles.
Oxidation in the Presence of Oxygen
When exposed to air or any other oxidizing environment, graphite's failure mode is no longer sublimation but oxidation. It is, after all, a form of carbon.
This chemical reaction can begin at temperatures as low as 500°C (932°F), where the carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. The material essentially burns away, losing mass and structural integrity long before it reaches its sublimation point.
Factors That Influence Graphite's Performance
The specific temperature limit is not just about atmosphere; it also depends on pressure and the material's specific properties.
Atmospheric Pressure
While graphite sublimates at standard pressure, it can be forced to melt into liquid carbon under extreme conditions.
This requires immense pressure, typically over 100 times standard atmospheric pressure (10 MPa). Under these conditions, the melting point of graphite is approximately 4,500°C (8,132°F). This is relevant only in highly specialized scientific or industrial processes.
Grade and Purity
Commercial graphite comes in many grades. The presence of impurities or binders can lower the temperature at which oxidation begins.
Higher-purity, high-density grades of graphite generally offer better performance and a slightly higher resistance to oxidation compared to lower-purity variants.
Thermal Shock Resistance
One of graphite's most significant advantages is its remarkably low coefficient of thermal expansion.
This means it expands and contracts very little when heated or cooled. This property gives it outstanding thermal shock resistance, allowing it to survive rapid temperature changes that would fracture most ceramics.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
Choosing graphite requires a clear-eyed view of its trade-offs. Misunderstanding its primary weakness is the most common source of failure in engineering applications.
The Oxidation Problem is the Primary Hurdle
For any application intended to operate in air, oxidation is the real-world ceiling. Unless you are designing for a vacuum or inert gas environment, the 3,600°C sublimation point is an irrelevant figure. The practical limit is around 500°C.
Protective Coatings Are a Workaround
To use graphite in oxidizing environments above 500°C, special protective coatings (like silicon carbide) can be applied. These coatings act as an oxygen barrier, allowing the graphite to be used at much higher temperatures, but they add complexity and cost.
Mechanical Strength Varies with Temperature
Uniquely, graphite's mechanical strength increases with temperature, peaking at around 2,500°C, where it can be twice as strong as it is at room temperature. Above this point, its strength begins to decline as it approaches the sublimation temperature.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice must be guided by a clear assessment of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat resistance in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite is one of the best materials available, remaining stable up to its sublimation point of ~3,600°C.
- If your primary focus is use in an open-air, high-temperature environment: Standard graphite is unsuitable above 500°C; you must consider either a different material or graphite with a protective anti-oxidation coating.
- If your primary focus is surviving rapid temperature cycling: Graphite's excellent thermal shock resistance makes it an ideal choice for components like crucibles, molds, or furnace linings.
Understanding the critical role of the operating environment is the key to successfully harnessing graphite's exceptional thermal properties.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Key Failure Mode | Approximate Temperature Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas / Vacuum | Sublimation | ~3,600°C (6,512°F) |
| Air (Oxidizing) | Oxidation | Starts at ~500°C (932°F) |
| High Pressure (>10 MPa) | Melting | ~4,500°C (8,132°F) |
Need a high-temperature solution for your lab?
Graphite's performance is entirely dependent on its operating environment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables—including high-purity graphite components and furnaces with controlled atmospheres—to ensure your materials perform reliably under extreme conditions.
Whether you require crucibles, furnace elements, or custom components that leverage graphite's exceptional thermal stability and shock resistance, our experts can help you select the perfect grade and configuration for your specific application.
Let's discuss your high-temperature challenges. Contact our team today to find a solution that maximizes performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of graphite? Unlock Superior Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? For Extreme Heat, Purity, and Efficiency
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials
- What is the temperature range of a graphite furnace? Unlock up to 3000°C for advanced materials processing.
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity



















