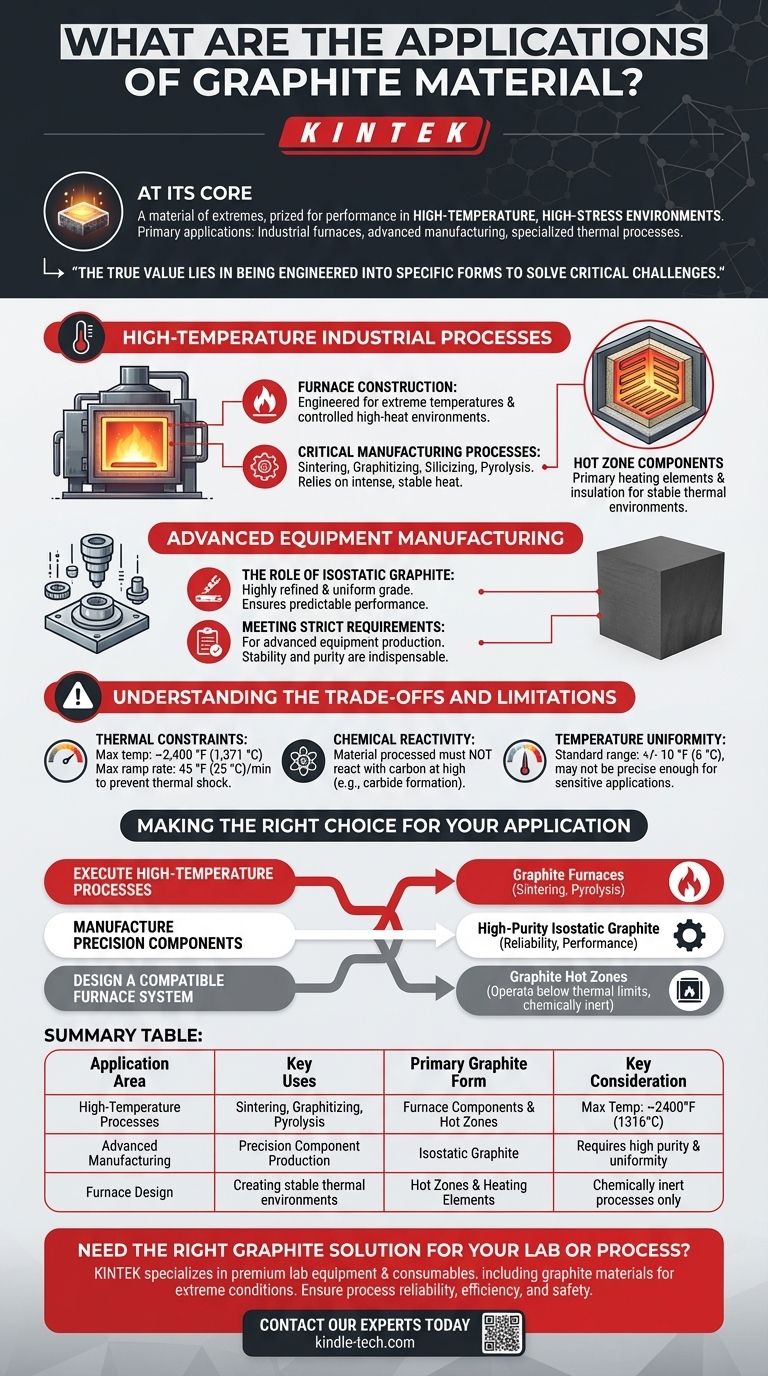
At its core, graphite is a material of extremes, prized for its performance in high-temperature, high-stress environments where conventional materials would fail. Its primary applications are found in industrial furnaces, advanced manufacturing, and specialized thermal processes due to its exceptional thermal stability and chemical inertness.
The true value of graphite lies not in a single application, but in its ability to be engineered into specific forms—like isostatic graphite or furnace components—that solve critical challenges in extreme industrial and technological processes.

High-Temperature Industrial Processes
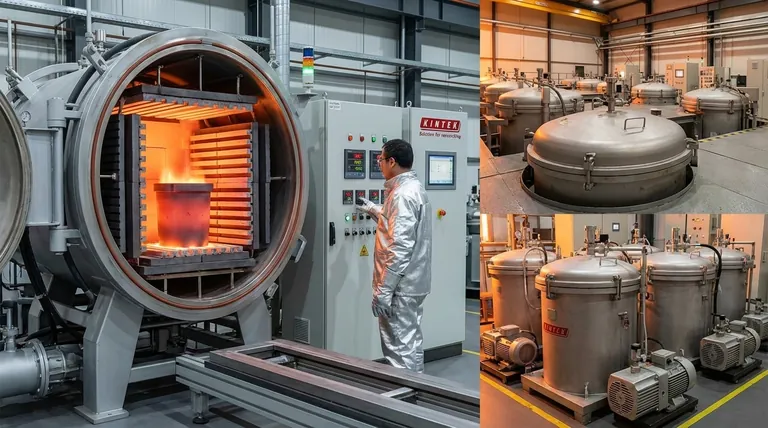
Graphite's ability to withstand and conduct extreme heat makes it a cornerstone material for many industrial heating applications. It forms the very heart of furnaces designed for specialized manufacturing.
Furnace Construction
Graphite furnaces are specifically engineered to generate the extremely high temperatures required for demanding industrial processes. They provide the controlled, high-heat environment necessary to transform materials at a molecular level.
Critical Manufacturing Processes
These furnaces are essential for processes like sintering, graphitizing, silicizing, and pyrolysis. Each of these methods relies on the intense, stable heat that graphite components can uniquely provide and endure.
Hot Zone Components
Within these furnaces, graphite hot zones are used as the primary heating elements and insulation. They are a reliable choice for creating a stable thermal environment for the material being processed.
Advanced Equipment Manufacturing
Beyond raw heat, certain forms of graphite offer the precision and reliability required for producing high-technology components.
The Role of Isostatic Graphite
Isostatic graphite is a highly refined and uniform grade of the material. Its consistent structure ensures predictable performance under demanding conditions, free from the impurities or inconsistencies that could cause failure.
Meeting Strict Requirements
This specialized graphite is designed to meet the strict requirements for materials used in advanced equipment production. Its stability and purity make it indispensable for manufacturing components where precision and reliability are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, graphite is not a universal solution. Its application is governed by specific operational constraints that must be respected for successful and safe implementation.
Thermal Constraints
Graphite furnace components often have defined limits. For instance, a typical hot zone may have a maximum operating temperature of 2,400 °F (1,371 °C) and a maximum temperature ramp rate of 45 °F (25 °C) per minute to prevent thermal shock and damage.
Chemical Reactivity
Graphite is fundamentally carbon. Therefore, it can only be used when the material being processed does not react with carbon at high temperatures. Any potential for chemical interaction, such as carbide formation, must be carefully evaluated.
Temperature Uniformity
The thermal control offered by graphite components has practical limits. A standard graphite hot zone might only guarantee a temperature uniformity range of +/- 10 °F (6 °C), which may not be precise enough for the most sensitive applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right graphite material is about matching its specific properties to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is executing high-temperature processes: Graphite furnaces are the industry standard for jobs like sintering or pyrolysis that demand extreme, stable heat.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing precision components: High-purity grades like isostatic graphite are necessary to meet the strict reliability and performance standards of advanced equipment.
- If your primary focus is designing a compatible furnace system: Graphite hot zones are an excellent choice, provided your process operates below the material's thermal limits and is chemically inert to carbon.
Ultimately, understanding graphite's properties and limitations empowers you to leverage its remarkable capabilities in the world's most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Primary Graphite Form | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Processes | Sintering, Graphitizing, Pyrolysis | Furnace Components & Hot Zones | Max Temp: ~2400°F (1316°C) |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Precision Component Production | Isostatic Graphite | Requires high purity & uniformity |
| Furnace Design | Creating stable thermal environments | Hot Zones & Heating Elements | Chemically inert processes only |
Need the Right Graphite Solution for Your Lab or Process?
Graphite's performance is critical for success in high-temperature applications like sintering and advanced manufacturing. Selecting the correct grade and form—from durable furnace components to high-purity isostatic graphite—is essential for achieving your results.
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including graphite materials designed for extreme conditions. We help laboratories and manufacturers like yours select the ideal graphite products to ensure process reliability, efficiency, and safety.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's graphite solutions can enhance your application's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a graphite furnace? Unlock up to 3000°C for advanced materials processing.
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- Can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking its extreme 3,600°C potential in inert environments
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity



















