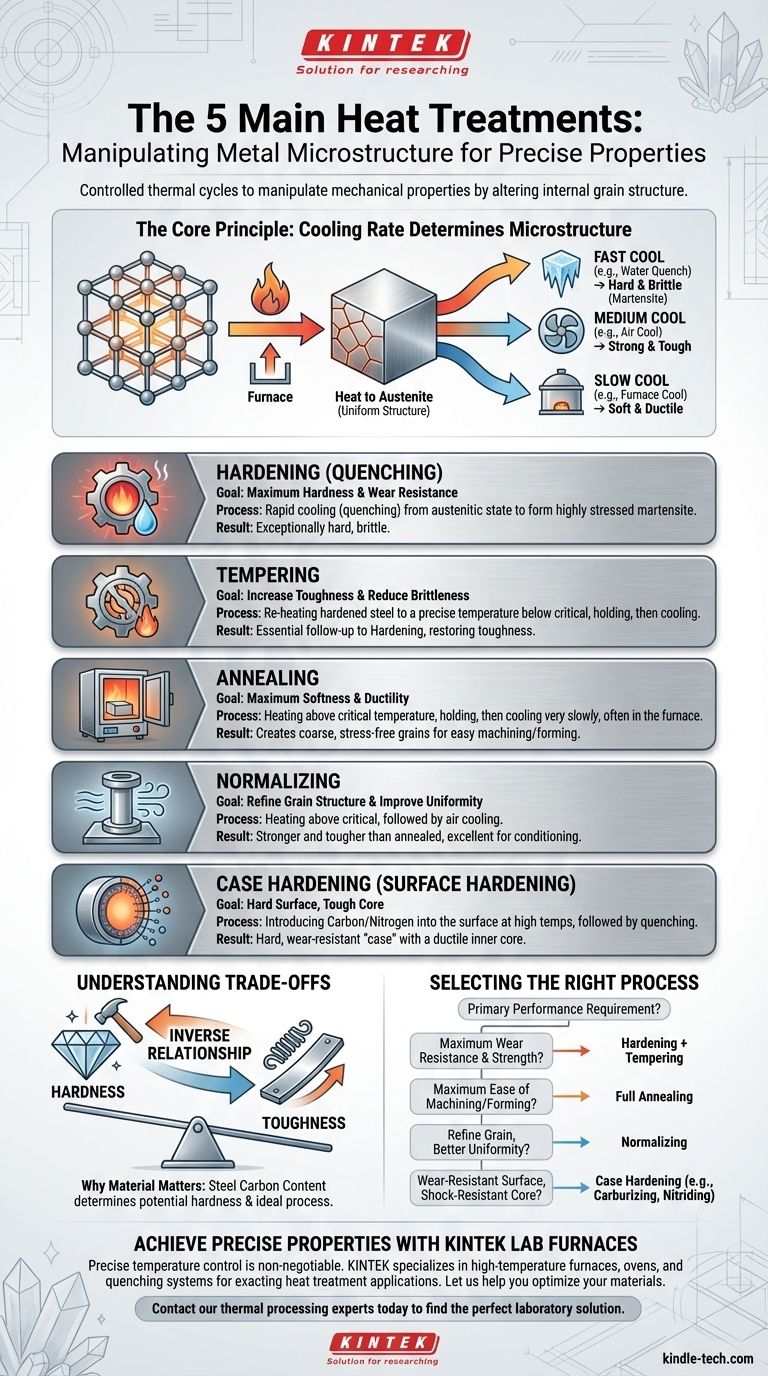
The five primary heat treatment processes for metals are hardening, tempering, annealing, normalizing, and case hardening. Each is a highly controlled cycle of heating and cooling designed to deliberately alter a metal's internal structure. The goal is to manipulate its mechanical properties—like hardness, toughness, and ductility—to match the precise demands of a specific application.
Heat treatment is not about making a metal generically "stronger." It is about precisely adjusting the trade-off between hardness and toughness by controlling the metal's crystalline microstructure to achieve a predictable engineering outcome.
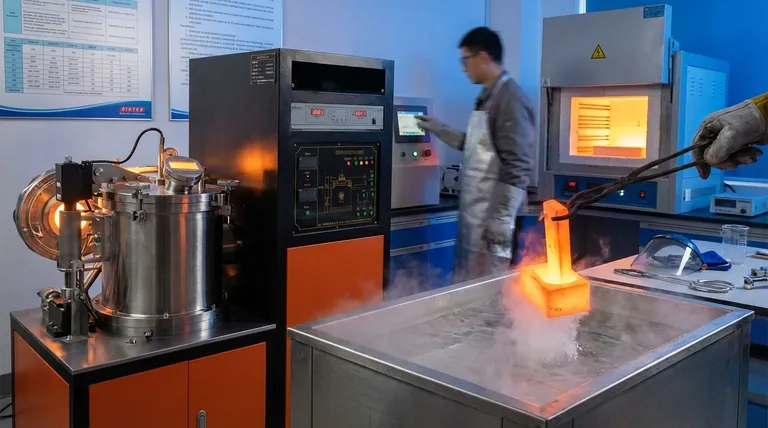

The Core Principle: Manipulating Microstructure
To understand heat treatment, you must first understand that solid metals have an internal crystal structure, often called "grain structure." The size, shape, and composition of these grains dictate the metal's mechanical properties.
The Role of Temperature and Time
Heating a steel part above a critical temperature (the "austenitizing" temperature) causes its crystal structure to transform into a uniform, solid solution called austenite. What happens next is determined entirely by the rate of cooling.
The Critical Impact of Cooling Rate
The speed at which the metal is cooled from its austenitic state locks in a specific final microstructure. A very fast cool creates a hard structure, while a very slow cool creates a soft one. Each of the primary processes is simply a defined method for controlling this cooling rate.
A Breakdown of the Five Primary Processes
Each process targets a distinct outcome by following a specific heating and cooling profile. While they are often discussed separately, processes like hardening and tempering are almost always used together.
1. Hardening (Quenching)
Hardening is a process designed to achieve maximum hardness and wear resistance in a steel component.
The part is heated above its critical temperature to form austenite, then cooled with extreme rapidity by plunging it into a quenching medium like water, oil, or brine. This "freezes" the carbon atoms in a highly stressed, needle-like crystal structure called martensite, which is exceptionally hard and brittle.
2. Tempering
A part that has only been hardened is too brittle for almost any practical use. Tempering is the essential follow-up process that restores toughness.
The hardened part is re-heated to a precise temperature below its critical point and held for a specific time. This process relieves the internal stresses within the martensitic structure, slightly reducing hardness but dramatically increasing toughness and ductility.
3. Annealing
Annealing is a process used to make a metal as soft and ductile as possible.
The metal is heated above its critical temperature, held to ensure a uniform temperature, and then cooled very slowly, typically by leaving it to cool inside the furnace. This slow cooling allows the grains to reform into a coarse, stress-free structure that is easy to machine, form, or stamp.
4. Normalizing
Normalizing is a process used to refine the grain structure, creating a more uniform and desirable combination of hardness and strength than in the as-rolled or annealed state.
The part is heated above its critical temperature and then allowed to cool in still air. This cooling rate is faster than furnace cooling (annealing) but much slower than quenching (hardening). The result is a fine-grained microstructure that is stronger and tougher than an annealed part, making it an excellent conditioning treatment before a final hardening process.
5. Case Hardening (Surface Hardening)
Case hardening creates a component with two distinct sets of properties: a very hard, wear-resistant outer surface (the "case") and a softer, tougher inner core.
This is typically done on low-carbon steels, which cannot be hardened by simple quenching. The process involves introducing elements like carbon (carburizing) or nitrogen (nitriding) into the surface of the steel at high temperatures. After this chemical change, the part is quenched, hardening only the high-carbon surface layer while leaving the low-carbon core tough and ductile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment is always an exercise in managing compromises. The most fundamental trade-off is between hardness and toughness.
The Inverse Relationship
Hardness is the ability of a material to resist abrasion and indentation. Toughness is the ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. For most steels, these two properties are inversely related.
As you increase hardness through a process like quenching, the material's toughness decreases, making it more brittle. As you increase toughness through a process like tempering or annealing, its hardness decreases.
Why Material Selection Matters
The effectiveness of these processes is entirely dependent on the material's chemistry. The most crucial factor for steel is its carbon content.
A high-carbon steel can become extremely hard through quenching, while a low-carbon steel will not harden significantly without a process like case hardening. The specific alloy composition determines the ideal temperatures, soak times, and cooling rates required.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Application
Your choice of heat treatment should be driven directly by the primary performance requirement of the finished component.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and strength: Your path is hardening (quenching) immediately followed by tempering to restore necessary toughness.
- If your primary focus is maximum ease of machining or cold forming: Choose full annealing to put the material in its softest possible state.
- If your primary focus is refining the grain structure of a raw component for better uniformity and machinability: Normalizing is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is a wear-resistant surface with a shock-resistant core: You need a case hardening process like carburizing or nitriding.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about understanding how to use controlled thermal cycles to produce the precise microstructure for the job at hand.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening | Maximum Hardness & Wear Resistance | Rapid cooling (quenching) to form martensite |
| Tempering | Increase Toughness & Reduce Brittleness | Heats hardened steel to a specific temperature below critical point |
| Annealing | Maximum Softness & Ductility | Very slow cooling (often in the furnace) |
| Normalizing | Refine Grain Structure & Improve Uniformity | Air cooling for a stronger, tougher result than annealing |
| Case Hardening | Hard Surface, Tough Core | Adds carbon/nitrogen to the surface before quenching |
Achieve Precise Material Properties with KINTEK Lab Furnaces
Selecting and executing the correct heat treatment is critical for your component's performance. Whether your application requires the extreme hardness from hardening, the machinability from annealing, or the wear-resistant surface of case hardening, precise temperature control is non-negotiable.
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment you need to master these processes. Our range of high-temperature furnaces, ovens, and quenching systems are engineered for the exacting control and uniformity required for hardening, tempering, annealing, normalizing, and case hardening applications.
Let us help you optimize your materials. Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific heat treatment challenges and find the perfect laboratory solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















