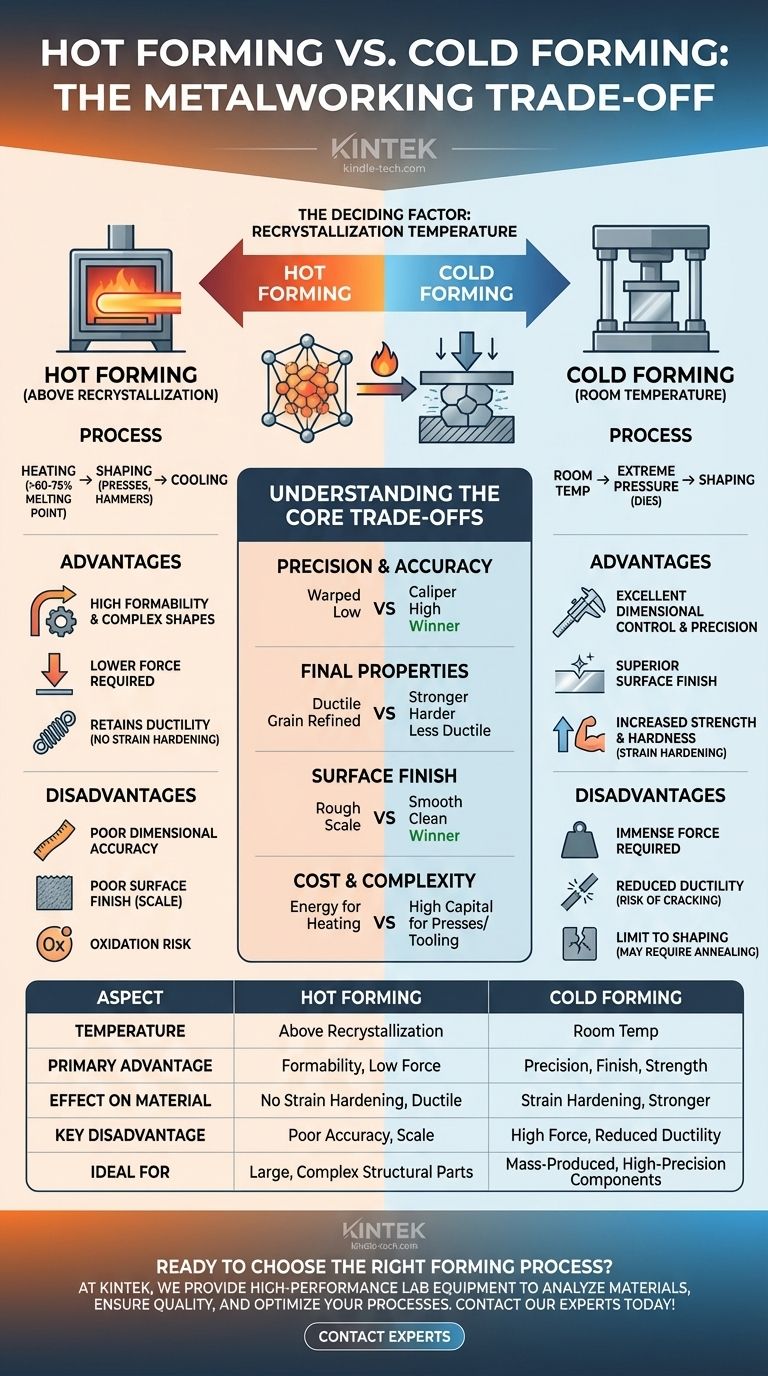
In metalworking, the fundamental choice between hot forming and cold forming comes down to a trade-off between formability and precision. Hot forming uses high temperatures to make metal easy to shape into complex forms, while cold forming uses immense pressure at room temperature to achieve superior dimensional accuracy and strength. Each method fundamentally alters the metal's properties in different ways, making them suitable for entirely different applications.
The decision hinges on a single, critical factor: the metal's recrystallization temperature. Working above this temperature (hot forming) prioritizes ease of shaping, while working below it (cold forming) prioritizes precision and strength in the final product.
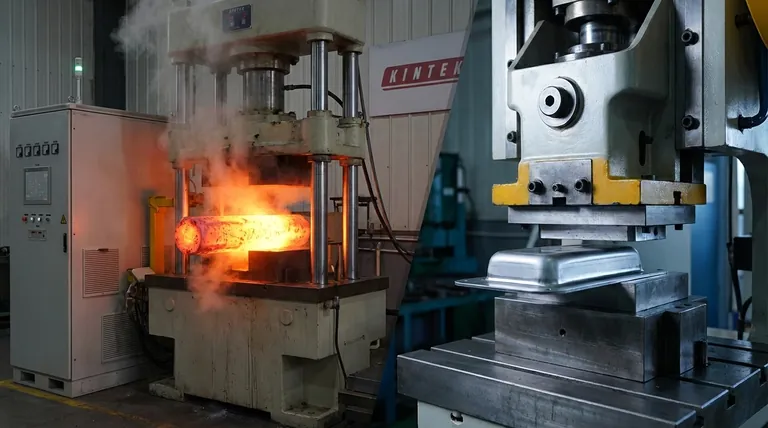

The Deciding Factor: Recrystallization Temperature
What is Recrystallization?
When a metal is deformed, its internal crystal structure, or "grains," become stretched and distorted. This is known as strain hardening.
Heating the metal above its recrystallization temperature triggers a crucial change. New, strain-free grains begin to form, effectively "resetting" the metal's internal structure and removing the effects of strain hardening.
This phenomenon is the scientific dividing line between the two processes. It explains why hot metal is soft and malleable, while cold metal becomes harder as you work it.
Hot Forming: Shaping with Heat
Hot forming involves deforming a metal at a temperature above its recrystallization point, typically ranging from 60% to 75% of its melting point.
The Process
The metal workpiece is heated in a furnace until it reaches the desired temperature, making it significantly more pliable. It is then quickly shaped using tools like presses, hammers, or rollers before it cools down.
Key Advantages
The primary advantage is a drastic reduction in the force needed to shape the material. This allows for the creation of large, complex components in a single operation.
Because the process occurs above the recrystallization temperature, the material does not strain harden. This means it retains its ductility, making it highly resistant to cracking during forming.
Inherent Disadvantages
As the metal cools from a high temperature, it shrinks and can warp unpredictably. This results in poor dimensional accuracy and tolerances compared to cold forming.
The high heat also causes oxidation on the metal's surface, forming a rough layer called "scale." This results in a poor surface finish that often requires secondary cleaning operations.
Cold Forming: Precision at Room Temperature
Cold forming, also known as cold working, involves shaping metal at or near room temperature. This process does not soften the material with heat; it relies purely on mechanical force.
The Process
Extreme pressure is applied to a metal workpiece using dies in a press. This forces the metal to flow into the desired shape. Common examples include forging, rolling, and drawing.
Key Advantages
Since there is no heating or cooling involved, thermal expansion and contraction are not factors. This allows for excellent dimensional control and high precision.
The process produces a smooth, clean surface, resulting in a superior surface finish that often requires no secondary treatment.
Cold working permanently distorts the metal's grain structure, a process called strain hardening. This increases the material's tensile strength and hardness, often making the final part stronger than the raw material it was made from.
Inherent Disadvantages
The primary drawback is the immense force required to shape the metal, which demands powerful and expensive machinery and robust tooling.
Strain hardening increases strength but reduces the metal's ductility, making it more brittle. There is a limit to how much a part can be shaped before it risks cracking, sometimes requiring an intermediate annealing (heating) step to soften it again.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
The choice between these methods is never arbitrary. It is a calculated decision based on the final requirements of the component.
Precision and Dimensional Accuracy
Cold forming is the clear winner. The absence of thermal warping allows for tight tolerances that are impossible to achieve consistently with hot forming.
Final Mechanical Properties
The results are fundamentally different. Cold forming produces a stronger, harder, but less ductile part. Hot forming retains the material's original ductility and can even refine the grain structure, improving toughness.
Surface Finish
Cold forming is superior. It produces a bright, smooth surface, whereas hot forming leaves a rough, scaled texture that must often be removed.
Cost and Complexity
The economics are complex. Hot forming requires significant energy for heating furnaces. Cold forming requires higher capital investment in powerful presses and durable tooling. For mass production of small, precise parts like screws and bolts, cold forming is often more economical per piece.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the ideal process is dictated by the goals of your specific project.
- If your primary focus is creating large or complex structural parts where ultimate precision is secondary: Hot forming is the superior choice due to its high formability and lower force requirements.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing smaller components with high dimensional accuracy and a superior surface finish: Cold forming provides unmatched precision and strengthens the material through work hardening.
- If your primary focus is enhancing the strength of a finished part without changing its shape: Cold forming techniques like shot peening are used to intentionally introduce beneficial strain hardening.
By aligning your project's goals with the fundamental principles of each process, you can select the most effective and economical path from raw material to finished part.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Forming | Cold Forming |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Above recrystallization temperature (60-75% of melting point) | Room temperature or near room temperature |
| Primary Advantage | High formability for complex shapes; lower force required | Superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish |
| Effect on Material | No strain hardening; retains ductility | Strain hardening increases strength and hardness |
| Key Disadvantage | Poor dimensional accuracy and surface finish (scale) | High force required; reduced ductility (risk of cracking) |
| Ideal For | Large, complex structural parts | Mass-produced, high-precision components |
Ready to Choose the Right Forming Process for Your Project?
The choice between hot and cold forming is critical to the success of your metal components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables needed to analyze material properties and ensure your forming processes are optimized for quality and efficiency.
We help our laboratory customers:
- Analyze Material Behavior: Test and understand how your metals respond to heat and pressure.
- Ensure Quality Control: Verify the dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties of your finished parts.
- Optimize Processes: Achieve the perfect balance of formability, strength, and precision.
Let's discuss your specific application needs. Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?
- What role does a high-temperature hot press play in the sintering of NITE-SiC? Optimize Your Densification Process
- What conditions does a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace provide for Copper-MoS2-Mo composites? Achieve Peak Densification



















