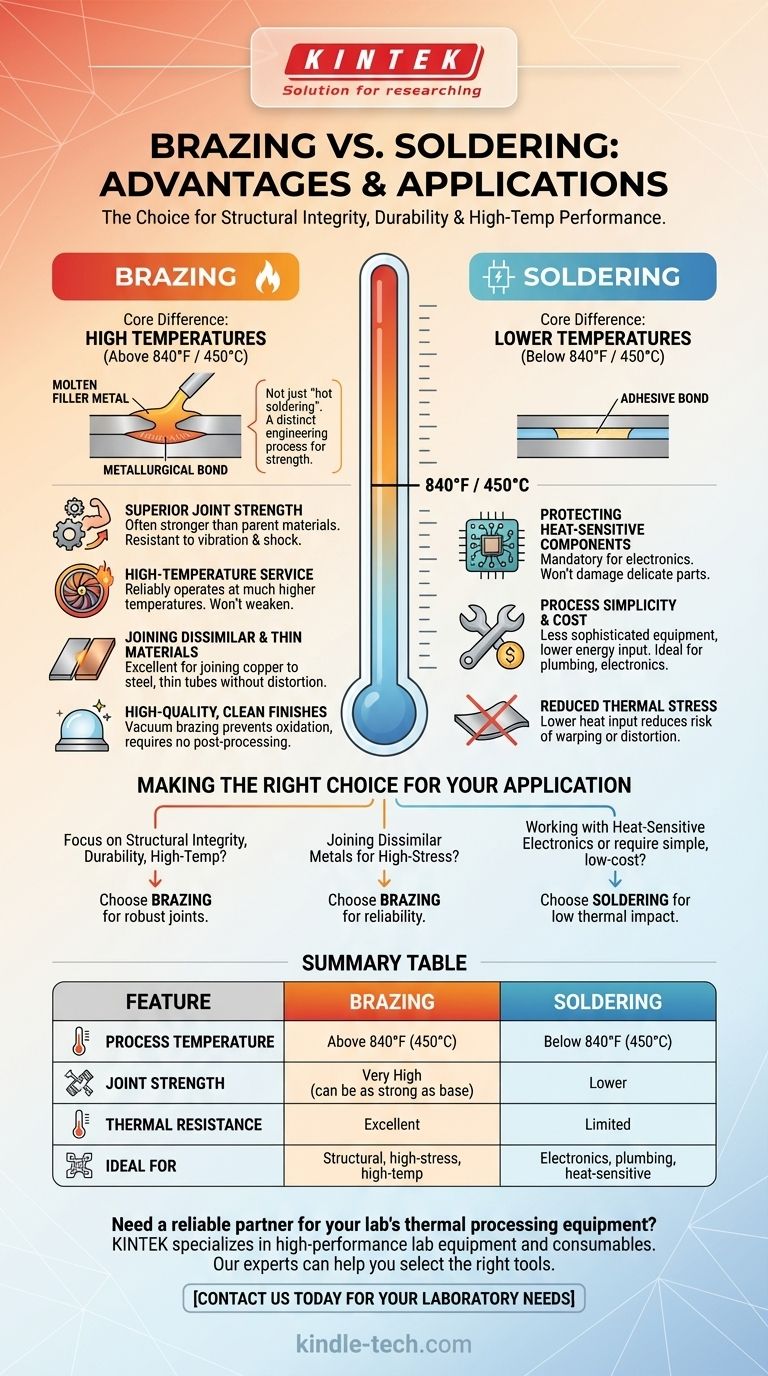
The primary advantages of brazing over soldering are significantly higher joint strength and greater thermal resistance. While both processes join materials using a filler metal without melting the base components, brazing uses higher temperatures (above 840°F / 450°C) to create a metallurgical bond that is often as strong as the parent materials themselves.
Brazing is not simply "hot soldering." It is a distinct engineering process chosen for applications where strength, durability, and performance under high temperatures are critical, while soldering is a lower-temperature process better suited for joining thermally sensitive or non-structural components.

The Core Difference: Temperature and Bond Formation
Defining the Temperature Threshold
Brazing is formally defined by the use of a filler metal that melts above 840°F (450°C). Soldering, by contrast, occurs below this temperature. This fundamental difference in thermal energy is the source of all other performance distinctions.
Creating a Stronger Metallurgical Bond
The higher temperatures used in brazing promote better wetting and diffusion of the filler metal into the surfaces of the base materials. This creates a true metallurgical bond, forming a strong, continuous connection between the components that is far more robust than the simpler adhesive bond of solder.
The Role of Capillary Action
Both processes rely on capillary action to draw molten filler metal into the tight gap between parts. However, the strength of a brazed joint is highly dependent on maintaining a precise, uniform gap, ensuring the filler metal creates a complete and powerful bond throughout the entire joint.
Key Advantages of Brazing
Superior Joint Strength
This is the most significant advantage. A properly brazed joint can be stronger than the base metals being joined, creating an assembly that is incredibly durable and resistant to vibration, shock, and mechanical stress. This is why it is used in critical automotive and aerospace applications.
High-Temperature Service
Because brazed joints are created at high temperatures, they can reliably operate at much higher service temperatures than soldered joints. A soldered joint would weaken and fail at temperatures that have no effect on a brazed connection.
Joining Dissimilar and Thin Materials
Brazing excels at joining dissimilar metals, such as copper to steel, which can be difficult or impossible to weld. It also distributes thermal stress gently, making it an excellent choice for joining thin-walled tubes or delicate parts without distortion or melting.
High-Quality, Clean Finishes
When performed in a controlled atmosphere (like vacuum brazing), the process prevents oxidation, resulting in a clean, strong joint with no need for post-processing or cleaning. This provides excellent consistency in high-volume production.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Choose Soldering
Protecting Heat-Sensitive Components
Soldering is the mandatory choice when working with electronics or other heat-sensitive components. The low temperatures used in soldering will not damage delicate parts, whereas the heat required for brazing would destroy them.
Process Simplicity and Cost
Soldering generally requires less sophisticated equipment and lower energy input, making it a simpler and more cost-effective process for many applications. It is ideal for plumbing, electronics assembly, and general repairs where structural strength is not the primary concern.
Reduced Thermal Stress
The lower heat input of soldering imparts less thermal stress on the base materials. This reduces the risk of warping or distortion, especially when working with large or complex assemblies that are not intended for high-stress environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct method is a critical engineering decision. Your final goal dictates the process.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity, durability, and high-temperature performance: Brazing is the superior choice, providing joints that are as strong as the parent materials.
- If you are working with heat-sensitive electronics or require a simple, low-cost joining method: Soldering offers the low thermal impact and ease of use necessary for these applications.
- If your goal is to join dissimilar metals for a high-stress application: Brazing provides a reliable and robust solution where other methods might fail.
Ultimately, selecting the right joining process ensures the integrity, safety, and longevity of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Above 840°F (450°C) | Below 840°F (450°C) |
| Joint Strength | Very High (can be as strong as base metals) | Lower |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent | Limited |
| Ideal For | Structural, high-stress, high-temperature applications | Electronics, plumbing, heat-sensitive components |
Need a reliable partner for your lab's thermal processing equipment? The choice between brazing and soldering is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the right tools for your specific joining applications, ensuring durability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques



















