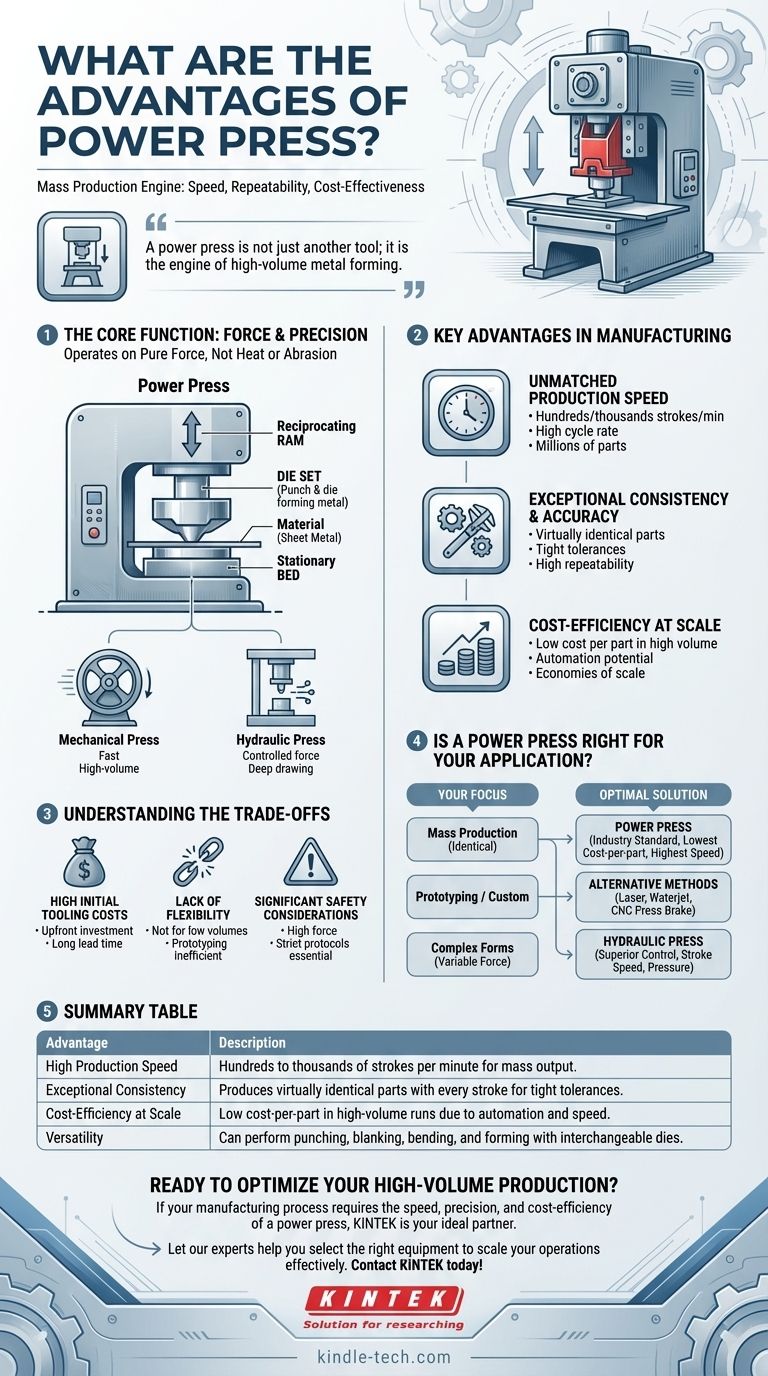
In essence, the primary advantages of a power press are its exceptional speed, high degree of repeatability, and unparalleled cost-effectiveness for mass production. This combination makes it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing for creating vast quantities of identical parts, from automotive components to electronic connectors. It achieves this by applying immense, controlled force to shape or cut material using a dedicated tool and die set.
A power press is not just another tool; it is the engine of high-volume metal forming. Its true value lies in its ability to transform raw metal into precise, identical components at a rate and cost that other manufacturing methods cannot match.

The Core Function: Force and Precision
To appreciate the advantages of a power press, it is critical to first understand its fundamental purpose. Unlike processes that rely on heat or abrasion, a power press operates on the principle of pure force.
What is a Power Press?
A power press is a machine that houses a stationary bed and a reciprocating ram. The ram moves up and down with immense force, pressing a tool or die set into material (typically sheet metal) placed on the bed.
This action allows the machine to perform a wide range of operations, including punching, blanking, bending, drawing, and forming.
The Role of the Die Set
The "brains" of the operation reside in the die set. This custom tooling, consisting of a punch (male part) and a die (female part), is what dictates the final shape of the component.
The versatility of a power press comes from its ability to use interchangeable die sets. The same press can produce entirely different parts simply by changing the tooling.
Mechanical vs. Hydraulic Presses
Power presses generally fall into two categories. Mechanical presses use a flywheel to generate very high speeds and are ideal for high-volume stamping and blanking. Hydraulic presses use fluid pressure to offer more control over force and stroke length, making them suitable for deep drawing or complex forming operations.
Key Advantages in Manufacturing
The unique operating principle of a power press delivers several key benefits that are essential for industrial-scale production.
Unmatched Production Speed
Mechanical power presses are incredibly fast, capable of running at hundreds or even thousands of strokes per minute. This high cycle rate makes them the undisputed choice for producing parts in the millions.
Exceptional Consistency and Accuracy
Once a die set is installed and calibrated, a power press produces a virtually identical part with every stroke. This high degree of repeatability is crucial for quality control in industries where tight tolerances are non-negotiable.
Cost-Efficiency at Scale
While the initial investment in a custom die set can be significant, the cost per part becomes extremely low during a high-volume production run. The speed of the press and the potential for full automation minimize labor costs and maximize output, leading to superior economies of scale.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging where a power press may not be the best fit.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The primary disadvantage is the high upfront cost and long lead time required to design and build a high-quality die set. This investment is only justifiable for large production volumes.
Lack of Flexibility for Low Volumes
Because of the reliance on custom tooling, power presses are not economical for prototyping or small-batch production. The setup time and tooling cost make it impractical for one-off parts or short runs.
Significant Safety Considerations
Power presses exert enormous force and move at high speeds, making them inherently dangerous. Strict safety protocols, guarding, and operator training are absolutely essential to prevent severe injury.
Is a Power Press Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific goals regarding volume, budget, and part complexity.
- If your primary focus is mass production of identical parts: A power press is the industry standard for achieving the lowest cost-per-part at the highest speed.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or custom fabrication: Consider alternative methods like laser cutting, waterjet cutting, or using a CNC press brake, as the tooling cost for a power press is prohibitive.
- If your primary focus is forming complex, deep shapes with variable force: A hydraulic press offers superior control over stroke speed and pressure compared to a faster mechanical press.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently determine if a power press is the optimal solution for your manufacturing goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Production Speed | Capable of hundreds to thousands of strokes per minute for mass output. |
| Exceptional Consistency | Produces virtually identical parts with every stroke for tight tolerances. |
| Cost-Efficiency at Scale | Low cost-per-part in high-volume runs due to automation and speed. |
| Versatility | Can perform punching, blanking, bending, and forming with interchangeable dies. |
Ready to Optimize Your High-Volume Production?
If your manufacturing process requires the speed, precision, and cost-efficiency of a power press, KINTEK is your ideal partner. We specialize in providing robust lab and pilot-scale equipment, including presses, that deliver the reliability and performance you need for R&D and small-batch production.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment to scale your operations effectively. Contact KINTELK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
People Also Ask
- How much pressure can a hydraulic press make? From 1 Ton to 75,000+ Tons of Force
- How fast is a hydraulic press? Understand the Critical Speed vs. Force Trade-off
- Can hydraulic systems that run too hot or too cold cause severe problems over time? Yes, and here's how to prevent it.
- What is the critical role of a pellet press in the fuel pretreatment of wheat straw lignin? Enhance Energy Efficiency
- What precautions should be taken during IR spectroscopy? Master Sample Prep for Accurate Results
- What is another name for a hydraulic press? The Bramah Press and Its Powerful Principle
- What is the primary purpose of a uniaxial hydraulic press for sulfide electrolytes? Optimize Ionic Conductivity Tests
- What is the use of potassium bromide KBr? From Historic Medicine to Modern Lab Essential



















