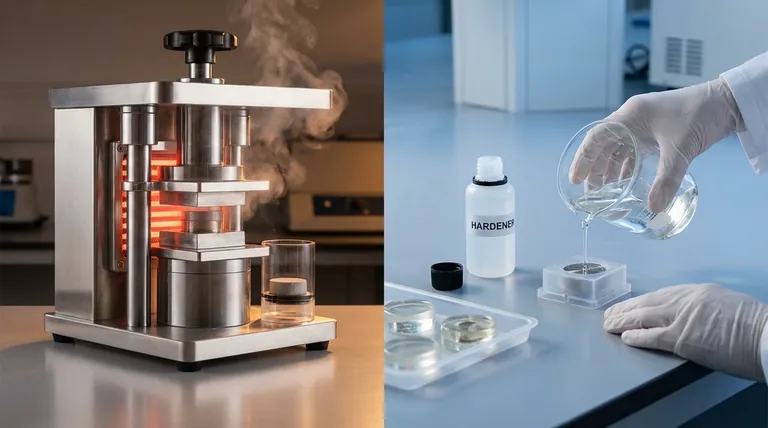
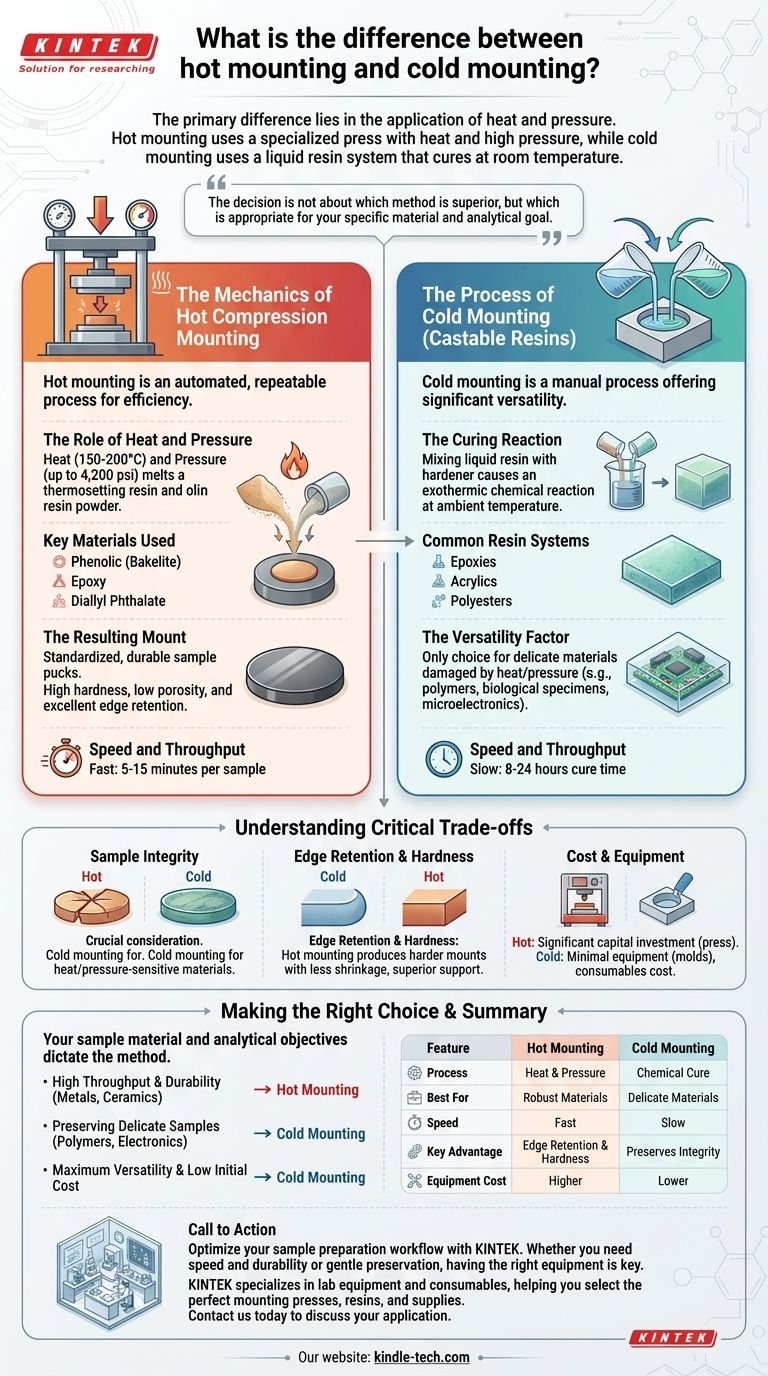
The primary difference between hot and cold mounting lies in the application of heat and pressure. Hot mounting, also known as compression mounting, uses a specialized press to encase a sample in a polymer resin under elevated temperature and high pressure. In contrast, cold mounting uses a multi-part liquid resin system that cures at room temperature through a chemical reaction, requiring no external pressure.
The decision between hot and cold mounting is not about which method is superior, but which one is appropriate for your specific material and analytical goal. Hot mounting prioritizes speed and mount quality for robust samples, while cold mounting prioritizes the preservation of delicate, heat-sensitive, or pressure-sensitive materials.

The Mechanics of Hot Compression Mounting
Hot mounting is an automated and highly repeatable process designed for efficiency and consistency in a laboratory setting. It produces standardized, durable sample pucks ideal for subsequent grinding and polishing.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
The process uses a mounting press that simultaneously applies heat (typically 150-200°C) and pressure (up to 4,200 psi). This combination melts a thermosetting or thermoplastic resin powder, allowing it to flow around the sample and solidify into a dense, hard mount as it cures or cools.
Key Materials Used
The most common resins for hot mounting are phenolic (Bakelite), which is cost-effective for routine work, and epoxy or diallyl phthalate compounds, which offer superior hardness and edge retention for more demanding applications.
The Resulting Mount
Hot mounting creates a sample puck of a standardized size and shape. These mounts are known for their high hardness, low porosity, and excellent edge retention, which is critical for accurately examining the surface or coatings on a material.
The Process of Cold Mounting (Castable Resins)
Cold mounting is a manual process that offers significant versatility, especially for samples that cannot withstand the conditions of a hot press.
The Curing Reaction
This method involves mixing a liquid resin with a hardener. The subsequent chemical reaction, which is an exothermic process, causes the mixture to cure into a solid block at ambient temperature over a period of several hours to a full day.
Common Resin Systems
The primary systems used are epoxies, acrylics, and polyesters. Epoxies are favored for their low shrinkage, excellent adhesion, and clarity, making them ideal for delicate electronics or porous samples. Acrylics cure much faster but have higher shrinkage and a stronger odor.
The Versatility Factor
The key advantage of cold mounting is its ability to handle nearly any type of sample. It is the only choice for materials that would be damaged or structurally altered by heat and pressure, such as polymers, biological specimens, or microelectronics.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing the correct method requires a clear understanding of the trade-offs between speed, sample integrity, and cost.
Speed and Throughput
Hot mounting is significantly faster, with cycle times typically ranging from 5 to 15 minutes per sample. Cold mounting is a much slower process, with cure times often requiring 8 to 24 hours before the sample is ready for preparation.
Sample Integrity
This is the most crucial consideration. If your material is heat-sensitive or pressure-sensitive, you must use cold mounting. The high temperatures and pressures of hot mounting can warp, melt, fracture, or otherwise alter the microstructure of delicate specimens.
Edge Retention and Hardness
Hot mounting generally produces a harder mount with less shrinkage, resulting in a tighter fit around the sample. This provides superior support during grinding and polishing, minimizing the rounding of edges that can obscure important surface features.
Cost and Equipment
Hot mounting requires a significant initial capital investment in a compression press. In contrast, cold mounting requires minimal equipment—primarily molds and mixing supplies—making the consumables the main recurring cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your sample material and analytical objectives should always dictate your mounting method.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and durability: Hot mounting is the ideal choice for routine analysis of robust materials like metals, alloys, and many ceramics.
- If your primary focus is preserving delicate or heat-sensitive samples: Cold mounting is the only safe option for polymers, circuit boards, soft metals, or any material whose microstructure could be altered by heat.
- If your primary focus is maximum versatility and low initial cost: Cold mounting allows a lab to handle the widest variety of sample types and shapes without a large capital investment.
By understanding these core differences, you can select the mounting process that best protects your sample's integrity and serves your analytical goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Mounting | Cold Mounting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heat (150-200°C) & Pressure (up to 4,200 psi) | Chemical cure at room temperature |
| Best For | Robust materials (metals, ceramics) | Delicate, heat-sensitive materials (polymers, electronics) |
| Speed | Fast (5-15 minutes) | Slow (8-24 hours) |
| Key Advantage | Superior edge retention & hardness | Preserves delicate sample integrity |
| Equipment Cost | Higher (requires a press) | Lower (molds & consumables) |
Optimize your sample preparation workflow with KINTEK.
Choosing the correct mounting method is critical for accurate material analysis. Whether you need the speed and durability of hot mounting for metals or the gentle preservation of cold mounting for delicate samples, having the right equipment is key.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect mounting presses, resins, and supplies to ensure your samples are prepared perfectly for analysis, protecting your investment in research and quality control.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal solution for your lab. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- How should an RVC sheet be handled and set up during an experiment? Ensure Precision and Data Integrity
- What is the process of mounting in metallurgy? A Guide to Perfect Specimen Preparation
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to MIC testing? Ensure Precision in Stainless Steel Specimens
- What is the purpose of using epoxy resin and laboratory mounting equipment? Precision in U71Mn Weld Area Analysis
- What is a hot mounting press machine? Precision Control for Metallurgy & Electronics Assembly



















