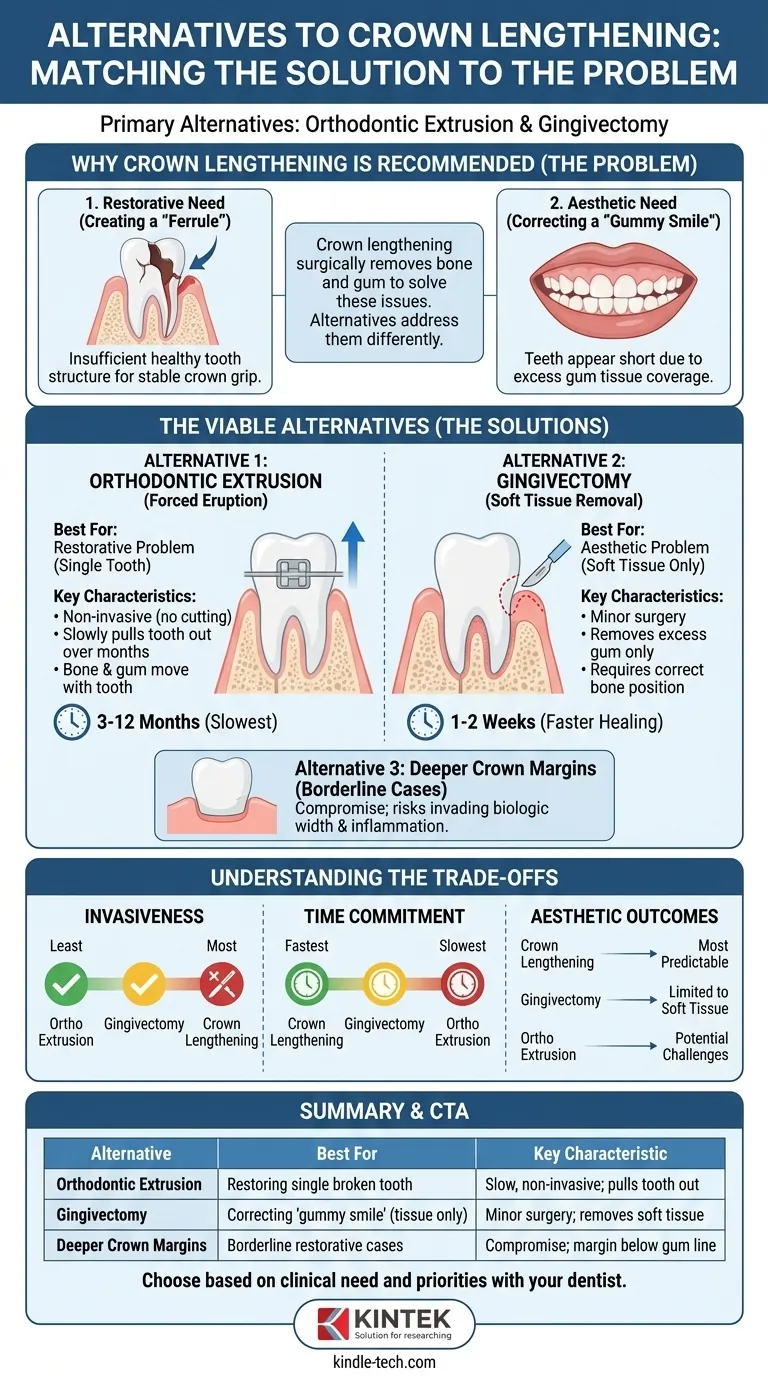
In many cases, the primary alternatives to surgical crown lengthening are orthodontic extrusion and gingivectomy. Orthodontic extrusion, also known as forced eruption, slowly pulls a tooth out to expose more of its structure, while a gingivectomy is a less invasive procedure that removes only excess gum tissue. The best alternative depends entirely on the clinical reason crown lengthening was recommended in the first place, such as restoring a broken tooth or correcting a "gummy smile."
The choice is not about finding a "better" procedure, but about matching the right solution to the specific problem. Crown lengthening solves the problem of insufficient tooth structure by removing bone and gum, while its alternatives address more specific scenarios, often in a less invasive but slower manner.

Why Crown Lengthening is Recommended
To understand the alternatives, we must first understand the two core problems that crown lengthening is designed to solve. Almost every case falls into one of these two categories.
The Restorative Need: Creating a "Ferrule"
A dental crown needs to grip onto a certain amount of healthy tooth structure to be stable for the long term. This gripping area is called the ferrule.
When a tooth breaks or has a deep cavity near the gum line, there isn't enough tooth structure left above the gums for the crown to hold onto securely.
Crown lengthening surgically lowers the gum and bone levels around that tooth, intentionally exposing more of the tooth to create the necessary ferrule for a durable restoration.
The Aesthetic Need: Correcting a "Gummy Smile"
Sometimes, the teeth are perfectly healthy but appear short because they are covered by too much gum tissue. This is often referred to as a "gummy smile" or altered passive eruption.
In this situation, aesthetic crown lengthening is performed to remove the excess gum tissue and reshape the underlying bone, revealing the proper length and shape of the teeth for a more balanced, harmonious smile.
The Viable Alternatives, Explained
If you are looking for an alternative, it's critical to know which of the above problems you are trying to solve.
Alternative 1: Orthodontic Extrusion (Forced Eruption)
This is the most common alternative for a restorative problem on a single tooth. Instead of cutting gum and bone away, this technique pulls the tooth out slightly.
An orthodontist attaches a bracket to the damaged tooth and uses light, continuous pressure to slowly erupt or "extrude" it over several months. As the tooth moves, the bone and gum tissue move with it.
Once enough tooth structure is exposed, the tooth is stabilized, and the dentist can proceed with creating a permanent crown.
Alternative 2: Gingivectomy or Gingivoplasty
This is a viable alternative for a purely aesthetic problem where the issue is excess soft tissue only.
A gingivectomy is a minor surgical procedure that removes a small amount of gum tissue (the "gingiva") from around the teeth. A gingivoplasty is the reshaping of that tissue.
This is only an option when the underlying bone is already in the correct position and doesn't need to be altered. If bone removal is required to get a stable result, a gingivectomy alone is not sufficient.
Alternative 3: Deeper Crown Margins
In some borderline restorative cases, a dentist might be able to place the edge, or margin, of the crown slightly below the gum line without formal surgery.
This is highly dependent on the specific location and the health of the gums. Pushing a margin too deep can invade the biologic width—the natural seal of tissue around the tooth—causing chronic inflammation, bleeding, and bone loss.
For this reason, it is often considered a compromise rather than an ideal long-term solution.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each approach has a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed for your specific situation.
Invasiveness and Healing
Crown lengthening is the most invasive procedure, as it involves reshaping both soft tissue and bone. It requires a healing period of several weeks before a final crown can be made.
Gingivectomy is less invasive, involving only soft tissue removal. Healing is typically faster, often within one to two weeks.
Orthodontic extrusion is the least invasive of all. It involves no cutting of tissue, but it does require wearing an orthodontic appliance.
Time Commitment
Crown lengthening provides the fastest definitive result. The procedure itself is relatively quick, and after the 6-8 week healing period, the tooth is ready for restoration.
Orthodontic extrusion is by far the slowest option. The process of erupting the tooth can take anywhere from 3 to 12 months, followed by a stabilization period.
Aesthetic Outcomes
For correcting a "gummy smile" across multiple teeth, crown lengthening offers the most predictable and comprehensive aesthetic results.
Orthodontic extrusion can sometimes lead to aesthetic challenges with the gum line or create a "black triangle" between the teeth, which may require further minor contouring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be made after a thorough discussion with your dental provider, weighing the pros and cons as they apply to your specific tooth and overall health.
- If your primary focus is restoring a single broken tooth while avoiding bone surgery: Orthodontic extrusion is the most conservative and effective alternative to explore.
- If your primary focus is making your teeth look longer due to excess gums: A gingivectomy is a potential solution, but only if your dentist confirms no bone reshaping is necessary.
- If your primary focus is speed and predictability for a long-term restoration: Surgical crown lengthening often remains the clinical standard of care for creating a durable result.
Understanding these pathways empowers you to have a more informed discussion with your dentist about the solution that best fits your clinical needs and personal priorities.
Summary Table:
| Alternative | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Orthodontic Extrusion | Restoring a single broken tooth | Slow, non-invasive; pulls tooth out to expose structure |
| Gingivectomy | Correcting a 'gummy smile' due to excess gum tissue | Minor surgery; removes soft tissue only |
| Deeper Crown Margins | Borderline restorative cases | Compromise; places crown margin below gum line |
Need precision tools for dental procedures like crown lengthening or its alternatives? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for dental laboratories and clinics, ensuring accuracy and reliability in restorative and aesthetic workflows. Contact us today to discuss how our products can support your practice's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?

















