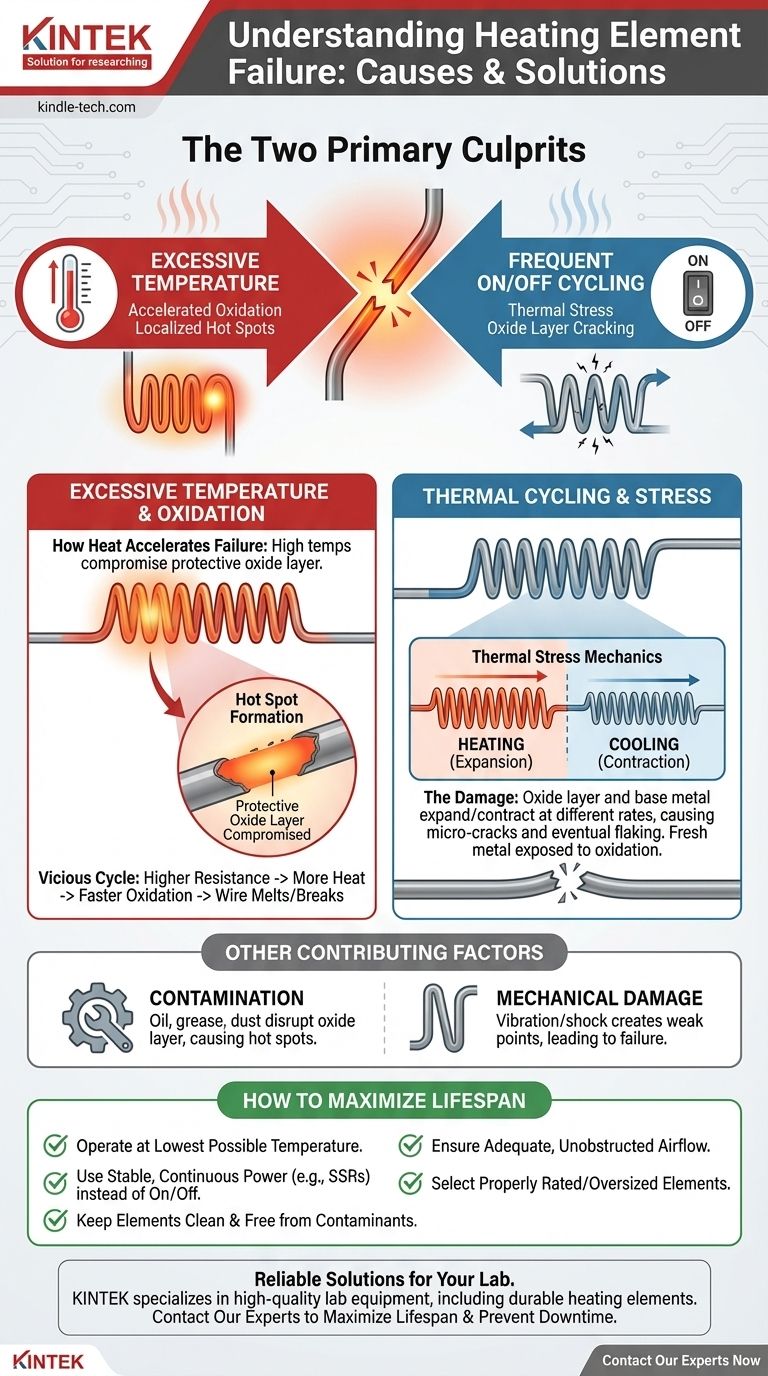
In short, heating element failures are almost always caused by two factors: running at too high a temperature and frequent on/off cycling. High temperatures accelerate a destructive process called oxidation, while cycling between hot and cold creates thermal stress that physically weakens the element over time until it breaks.
The lifespan of a heating element is not a matter of chance. It is a predictable outcome determined by the interplay between its operating temperature and the stress of its heating and cooling cycles.
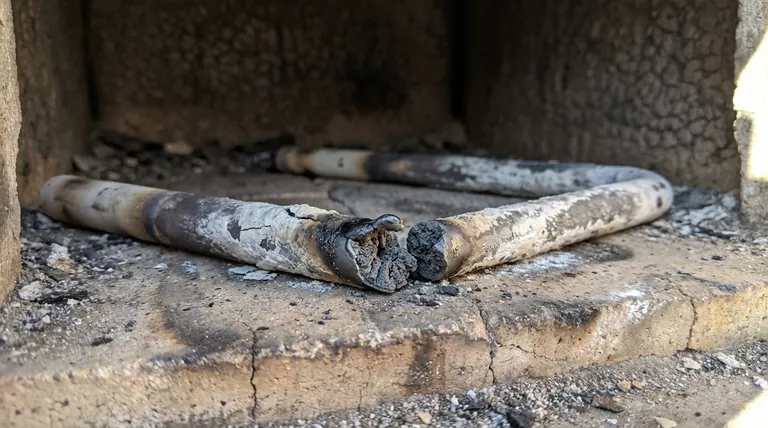

The Primary Culprit: Excessive Temperature and Oxidation
The single most significant factor in an element's life is its temperature. Even a small increase in operating temperature can dramatically shorten its lifespan.
How Heat Accelerates Failure
Every heating element alloy has a maximum recommended operating temperature. As the element approaches this limit, its rate of degradation increases exponentially. A wire that might last for years at a moderate temperature could fail in hours or days if run too hot.
Understanding Oxidation
At high temperatures, the metal alloy of the element reacts with oxygen in the air, forming a protective oxide layer on its surface. For common nichrome elements, this is a layer of chromium oxide. This layer is crucial because it resists further oxidation and has high electrical resistance.
However, if the temperature becomes excessive, this protective layer can be compromised, leading to rapid, uncontrolled oxidation of the parent metal underneath. This effectively "burns up" the element material.
The Vicious Cycle of "Hot Spots"
Failure often begins at a single, localized hot spot. This spot may be slightly hotter due to a restriction in airflow, a bend in the wire, or contamination. This hotter area oxidizes faster, which increases its electrical resistance.
Because the resistance is now higher at that one spot, it generates even more heat, which in turn causes even faster oxidation. This runaway cycle continues until the wire at the hot spot thins, weakens, and ultimately melts or breaks.
The Impact of Thermal Cycling
The second major cause of failure is the repeated stress from heating and cooling.
What is Thermal Cycling?
Thermal cycling is simply the process of turning the element on and off. Each time the element heats up, it expands. Each time it cools down, it contracts. This is the "intermittent operation" that causes significant wear.
The Mechanics of Thermal Stress
The protective oxide layer and the base metal underneath it expand and contract at slightly different rates. This mismatch creates mechanical stress with every cycle. Over time, this stress causes the brittle oxide layer to develop micro-cracks or even flake off entirely.
Why Cycling is More Damaging than Continuous Use
When the protective oxide layer flakes off, fresh, unprotected metal is exposed to the air. The next time the element heats up, a new oxide layer forms on this exposed metal.
This process repeats with every on/off cycle. Each time, a small amount of the element's core metal is consumed to form the new oxide layer. The wire becomes progressively thinner until it can no longer carry the current and breaks. An element run continuously at a stable temperature will often last much longer than one cycled frequently.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Other Factors
While temperature and cycling are the primary drivers, other real-world conditions contribute to failure.
Design vs. Operation
There is an inherent trade-off between performance and lifespan. An element must be hot enough to perform its function, but running it cooler will always extend its life. Proper system design ensures the element can do its job without constantly pushing its thermal limits.
The Role of Contamination
Foreign substances like oil, grease, dust, or manufacturing chemicals can be destructive. When heated, they can interfere with the protective oxide layer, causing chemical reactions that eat away at the element wire and create the initial hot spots that lead to failure.
Mechanical Damage
Vibration, physical shock during shipping, or improper installation can create weak points in the element. These nicks, scratches, or tight bends become stress concentration points where hot spots are likely to form, initiating the failure cycle.
How to Maximize Heating Element Lifespan
You can directly influence the lifespan of your elements by controlling their operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability: Operate the element at the lowest possible temperature that achieves your process goal and use power controllers (like phase-angle or zero-crossing SSRs) to provide stable, continuous power rather than crude on/off cycling.
- If your primary focus is extending the life of existing equipment: Ensure elements are kept clean and free from contaminants, and verify there is adequate, unobstructed airflow to prevent the formation of localized hot spots.
- If your primary focus is designing a new system: Select an element that is properly rated for the task. Oversizing it slightly ensures it can produce the required heat without operating near its maximum temperature limit.
By understanding that element failure is a predictable process of thermal and mechanical wear, you gain direct control over the reliability of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Cause of Failure | Primary Effect | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive Temperature | Accelerated oxidation | Hot spots form, wire weakens and breaks |
| Frequent On/Off Cycling | Thermal stress on oxide layer | Micro-cracks, flaking, and eventual breakage |
| Contamination | Disruption of protective oxide layer | Localized corrosion and hot spots |
| Mechanical Damage | Physical weak points | Stress concentration leading to failure |
Maximize the lifespan of your lab equipment and prevent costly downtime. Understanding the causes of heating element failure is the first step. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable heating elements designed for reliability. Our experts can help you select the right components and provide guidance on optimal operation to extend their life. Contact us today to ensure your lab runs smoothly and efficiently.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance









