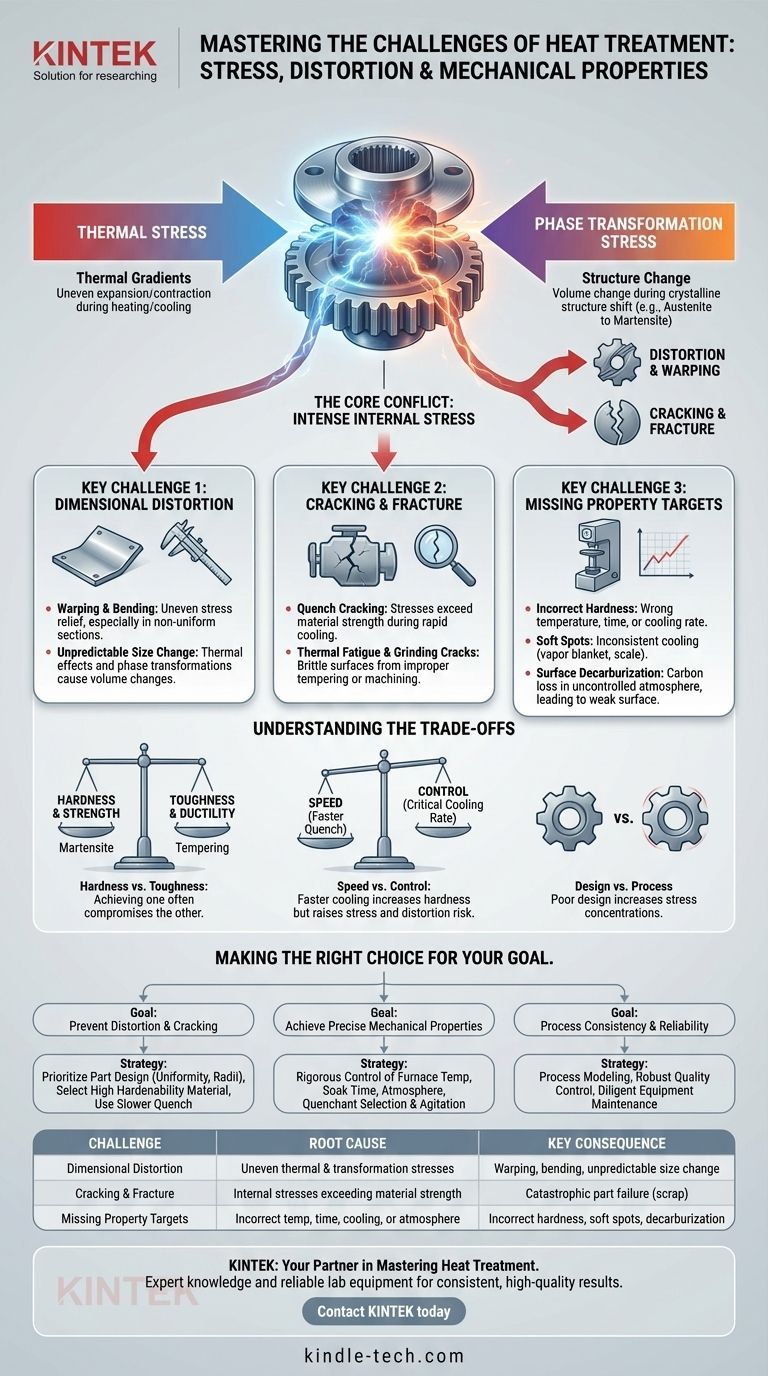
In essence, the primary challenges of heat treatment are controlling dimensional distortion and preventing cracks while simultaneously achieving the desired mechanical properties, such as hardness and toughness. These issues arise from the immense internal stresses generated by rapid temperature changes and the material's own structural transformations during the process. Successfully navigating these challenges requires a deep understanding of metallurgy, thermodynamics, and part design.
The core challenge of heat treatment is not just about heating and cooling metal; it's about managing the intense internal war between thermal stress and metallurgical transformation. Winning this war means achieving the target properties without the part warping, cracking, or failing.
The Core Conflict: Thermal Stress vs. Metallurgical Transformation
Nearly every significant heat treatment problem can be traced back to the stresses induced within the material. These stresses come from two distinct but simultaneous sources.
Thermal Gradients and Stress
When a part is heated or cooled, different sections change temperature at different rates. A thick section will lag behind a thin section, creating a thermal gradient.
This temperature difference causes sections to expand or contract against each other, generating powerful internal forces known as thermal stress.
Phase Transformation Stress
Heat treatment is designed to change the material's crystalline structure, or phase. For steel, this often means transforming the high-temperature austenite phase into the hard martensite phase upon cooling.
This phase transformation is accompanied by a change in volume. Martensite, for example, is less dense and occupies more volume than the austenite it forms from. This expansion creates another layer of intense internal stress.
The Combined Effect
During a rapid quench, thermal stress (from cooling) and transformation stress (from phase change) are combined. If their sum exceeds the material's strength at that temperature, the part will either permanently deform (distortion) or fracture (cracking).
Key Challenge 1: Dimensional and Shape Distortion
Distortion is a change in the size or shape of a part. It is one of the most common and costly challenges, often rendering a precisely machined component useless.
Warping and Bending
Warping occurs when internal stresses are relieved unevenly, causing the part to bend or twist. This is especially problematic in parts with non-uniform cross-sections, where thin areas cool and transform much faster than thick areas.
Unpredictable Size Change
All parts change size during heat treatment due to thermal effects and phase transformations. While some of this is predictable and can be accounted for in initial machining, non-uniform stress relief can lead to unpredictable and unacceptable dimensional changes.
Key Challenge 2: Cracking and Fracture
Cracking is the most catastrophic failure in heat treatment. A cracked part is scrap, and the failure often points to a fundamental issue in the material selection or process control.
Quench Cracking
Quench cracking is the classic example. It occurs during rapid cooling when internal stresses become so high they literally pull the material apart.
This is most common in high-carbon steels or complex geometries with sharp internal corners, which act as stress risers. The crack often initiates once the surface is cold and brittle while the core is still hot and contracting.
Thermal Fatigue and Grinding Cracks
Parts that are improperly tempered can be excessively brittle. Subsequent manufacturing steps like grinding can easily introduce micro-cracks on the surface, which can grow into catastrophic failures when the part is put into service.
Key Challenge 3: Missing the Mechanical Property Target
The entire purpose of heat treatment is to achieve a specific set of mechanical properties. Failing to do so negates the entire process.
Incorrect Hardness
Achieving the correct hardness requires precise control over temperature, time, and cooling rate. Quenching too slowly results in a part that is too soft; quenching too aggressively (or using the wrong steel) can lead to excessive hardness and brittleness.
Soft Spots
Inconsistent cooling across a surface can lead to soft spots. This is often caused by a vapor blanket (the Leidenfrost effect) that insulates the part from the quenchant, or by surface scale that interferes with heat transfer.
Surface Decarburization
In an uncontrolled furnace atmosphere, carbon can diffuse out of the steel's surface. This decarburization creates a soft, weak outer layer that compromises wear resistance and fatigue life, even if the core hardness is correct.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Solving one challenge can often create another. Effective heat treatment is a balancing act.
Hardness vs. Toughness
This is the most fundamental trade-off in metallurgy. The process of quenching to create hard martensite also creates a very brittle material. Tempering is a subsequent heating step used to relieve stress and increase toughness, but it always comes at the expense of some hardness and strength.
Speed vs. Control
A faster quench generally produces higher hardness. However, it also generates much higher thermal stress, dramatically increasing the risk of distortion and cracking. The challenge is to cool just fast enough to get the required properties—a concept known as the critical cooling rate—but no faster.
Design vs. Process
A poorly designed part is difficult to heat treat successfully. Sharp internal corners, drastic changes in section thickness, and unnecessary complexity all create stress concentrations. Often, the best way to solve a heat treatment problem is to redesign the part to be more "heat-treat-friendly."
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these challenges is the first step to mitigating them. Your focus will determine your primary strategy.
- If your primary focus is preventing distortion and cracking: Prioritize part design with uniform sections and generous radii, and select a material with higher hardenability that allows for a slower, less stressful quench.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise mechanical properties: Emphasize rigorous control over furnace temperature, soak time, furnace atmosphere, and the selection and agitation of your quenchant.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and reliability: Invest in process modeling, robust quality control with 100% inspection for critical parts, and diligent equipment maintenance to prevent issues like decarburization and inconsistent quenching.
Mastering heat treatment comes from controlling the variables that generate stress while achieving the transformations that deliver strength.

Summary Table:
| Challenge | Root Cause | Key Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Distortion | Uneven thermal & transformation stresses | Warping, bending, unpredictable size change |
| Cracking & Fracture | Internal stresses exceeding material strength | Catastrophic part failure (scrap) |
| Missing Property Targets | Incorrect temp, time, cooling, or atmosphere | Incorrect hardness, soft spots, decarburization |
Achieve precise mechanical properties without the risk of distortion or cracking. The challenges of heat treatment require expert knowledge and high-quality equipment. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable ovens, furnaces, and quenchant systems you need for consistent, high-quality results. Let our expertise help you master the balance between strength and stress. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and find the right solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation



















