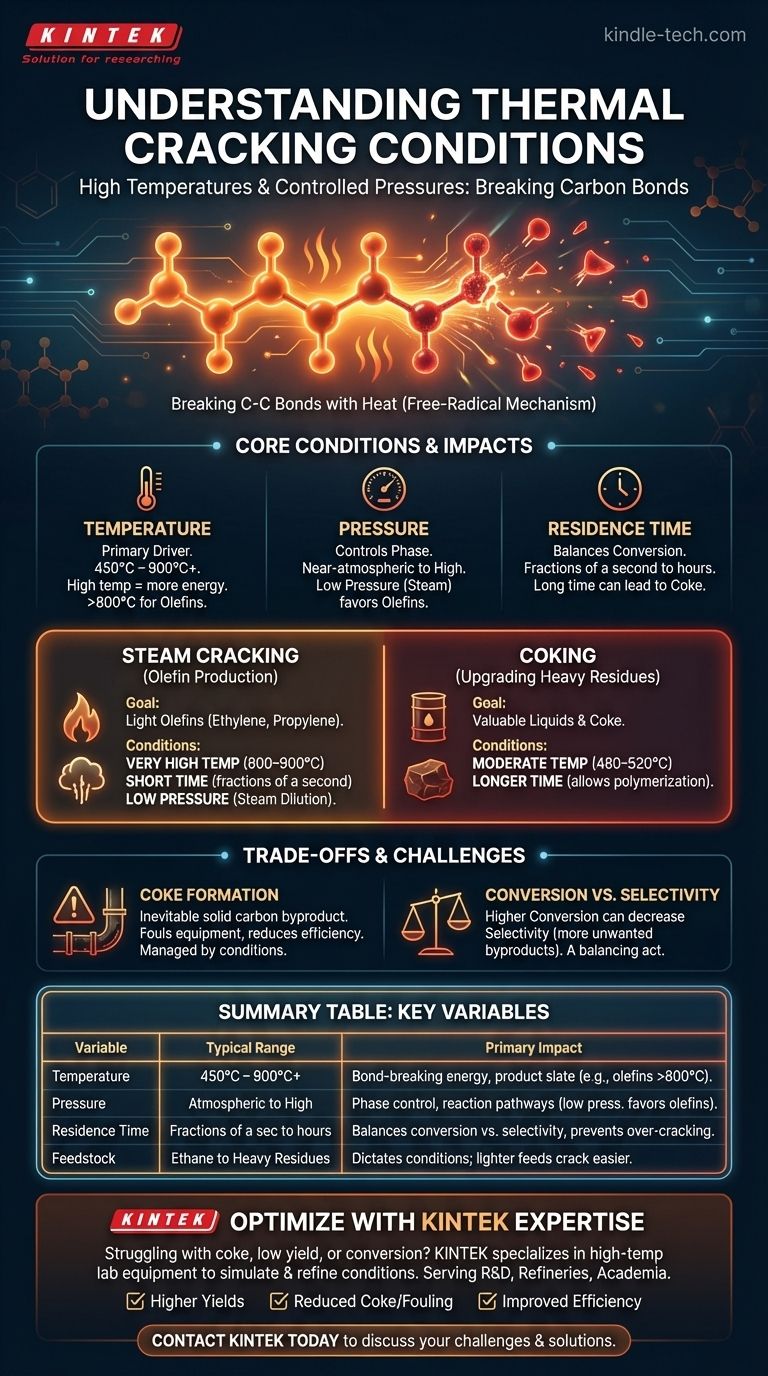
In short, thermal cracking requires high temperatures and controlled pressures. The process operates by subjecting large hydrocarbon molecules to enough thermal energy to break them apart. Typical conditions range from 450°C to over 900°C (840°F to 1650°F), with pressures varying from near-atmospheric to high, depending on the specific goal of the cracking process.
The core principle is not just about heat, but about control. Thermal cracking is the precise application of thermal energy to sever carbon-carbon bonds, transforming low-value, large hydrocarbons into smaller, higher-value products like gasoline components and light olefins. The exact conditions are a carefully calibrated function of the feedstock and the desired output.

The Fundamental Principle: Breaking Carbon Bonds with Heat
Thermal cracking is one of the oldest and most fundamental processes in petroleum refining. It works without catalysts, relying solely on thermal energy to initiate the chemical breakdown of molecules.
What is Thermal Cracking?
Thermal cracking is a process that decomposes large, complex hydrocarbon molecules found in crude oil into smaller, more useful ones. This happens when the feedstock is heated to a temperature high enough to cause the carbon-carbon bonds to rupture.
The process follows a free-radical mechanism. The initial heat provides the activation energy needed to break a bond, creating highly reactive free radicals. These radicals then trigger a chain reaction, propagating through the feedstock until smaller, stable molecules are formed.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary driver of thermal cracking. It directly provides the energy needed to break strong C-C and C-H bonds.
Different temperature ranges yield different results. Moderate temperatures (450–750°C) are often used in processes like visbreaking or coking, while much higher temperatures (above 800°C) are necessary to produce light olefins like ethene.
The Influence of Pressure
Pressure determines the phase of the hydrocarbons (liquid or vapor) and influences the rate and type of reactions that occur.
High pressures can keep the feedstock in a liquid phase and are used in older thermal cracking methods to produce gasoline. Conversely, low hydrocarbon pressures, often achieved by diluting the feedstock with steam, are used to maximize the yield of valuable gases like ethylene and propylene by suppressing secondary reactions.
The Impact of Residence Time
Residence time is the duration the feedstock is held at the cracking temperature. It is a critical variable that works in tandem with temperature.
A longer residence time increases the overall conversion of the feedstock. However, if it's too long, it can lead to "over-cracking," where even the desired small molecules are broken down further, forming excessive coke and light gases.
Key Industrial Thermal Cracking Processes
The general principles of thermal cracking are applied in several distinct industrial processes, each with finely tuned conditions to achieve a specific outcome.
Steam Cracking: The Heart of Olefin Production
The goal of steam cracking is to produce light olefins (alkenes), primarily ethylene and propylene, which are the building blocks for plastics and other chemicals.
The conditions are extreme: very high temperatures of 800–900°C (1470–1650°F), very short residence times (fractions of a second), and low hydrocarbon partial pressure. This low pressure is achieved by mixing the feedstock (like naphtha or ethane) with steam before it enters the furnace.
Coking: Upgrading Heavy Residues
Coking processes take the heaviest, lowest-value residue from the distillation process and convert it into more valuable liquid products and solid petroleum coke.
The conditions are less severe than steam cracking. Temperatures are lower, around 480–520°C (900–970°F), but the residence time is much longer, allowing the complex cracking and polymerization reactions to proceed, ultimately forming coke.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Optimizing a thermal cracking process requires balancing competing factors. Success is measured not just by what is produced, but also by what is avoided.
The Inevitability of Coke Formation
Coke, a hard, solid, carbon-rich deposit, is an unavoidable byproduct of thermal cracking. It forms from complex side reactions and coats the inside of reactor tubes and equipment.
This fouling reduces heat transfer efficiency and can eventually plug the reactor, forcing a costly shutdown for cleaning or "decoking." The conditions in steam cracking (high temperature, low pressure) are specifically designed to minimize this effect.
Product Selectivity vs. Conversion
A classic engineering trade-off exists between conversion and selectivity.
- Conversion is the percentage of the feedstock that is successfully broken down.
- Selectivity is the percentage of the converted feedstock that becomes the desired product.
Pushing for higher conversion by increasing temperature or residence time often decreases selectivity, as desirable products may be cracked further into less valuable light gases and coke.
Feedstock Flexibility and its Impact
The ideal cracking conditions are highly dependent on the feedstock. Lighter feedstocks like ethane crack easily to produce a high yield of ethylene.
Heavier feedstocks like gas oil or atmospheric residue are more complex. They require different conditions and produce a much wider slate of products, making the process more challenging to control and optimize.
Matching Cracking Conditions to Your Goal
The optimal conditions for thermal cracking are not a single set of numbers but a strategy tailored to a specific economic and chemical objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing light olefins (ethylene, propylene): You need the extreme conditions of steam cracking—very high temperatures (800°C+), low hydrocarbon partial pressures, and extremely short residence times.
- If your primary focus is upgrading heavy, low-value residues: You need the moderate temperature and longer residence time conditions of a coking process to allow for the controlled thermal breakdown into valuable liquids and solid coke.
- If your primary focus is minimizing unwanted byproducts: Careful control over residence time and the use of steam dilution are critical to suppress secondary reactions that lead to excessive coke formation.
Ultimately, the conditions for thermal cracking are a precise balancing act between temperature, pressure, and time, engineered to break down specific molecules into the most valuable products possible.
Summary Table:
| Variable | Typical Range | Primary Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 450°C – 900°C+ | Determines bond-breaking energy and product slate (e.g., olefins require >800°C) |
| Pressure | Near-atmospheric to High | Controls phase (liquid/vapor) and reaction pathways; low pressure favors olefins |
| Residence Time | Fractions of a second to hours | Balances conversion vs. selectivity; prevents over-cracking and coke formation |
| Feedstock | Ethane to Heavy Residues | Dictates required conditions; lighter feeds crack easier to target products |
Optimize Your Thermal Cracking Process with KINTEK's Expertise
Struggling with coke formation, low yield, or inefficient hydrocarbon conversion? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature laboratory equipment and consumables designed to simulate and refine thermal cracking conditions. Our reactors, furnaces, and analytical tools help you precisely control temperature, pressure, and residence time—enabling you to maximize product selectivity and minimize downtime.
We serve:
- R&D labs developing new cracking catalysts or processes
- Refineries optimizing existing thermal cracking operations
- Academic institutions researching hydrocarbon conversion
Let us help you achieve:
✅ Higher yields of valuable products (e.g., ethylene, gasoline)
✅ Reduced coke formation and equipment fouling
✅ Improved process efficiency and cost savings
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your thermal cracking challenges and discover how our solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of furnace in semiconductor? Master Thermal Oxidation, Diffusion & Annealing
- What are the advantages of using a Hastelloy (HC-276) tubular reactor for studying FeS deposition mechanisms?
- Why are high-precision tube furnaces necessary for photoelectrocatalytic materials? Achieve Atomic Synthesis Precision
- How do industrial-grade box or tube furnaces optimize material properties? Master Zirconium Alloy Heat Treatment
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Purity
- What critical conditions does a high-temperature tube furnace provide? Optimize Melt-Casting for Solid-State Batteries
- What is the primary industrial objective of utilizing a high-temperature drop tube furnace (HDTF)?
- What role does a cylindrical horizontal quartz tube furnace play in manganese coatings? Master Thermal Oxidation



















