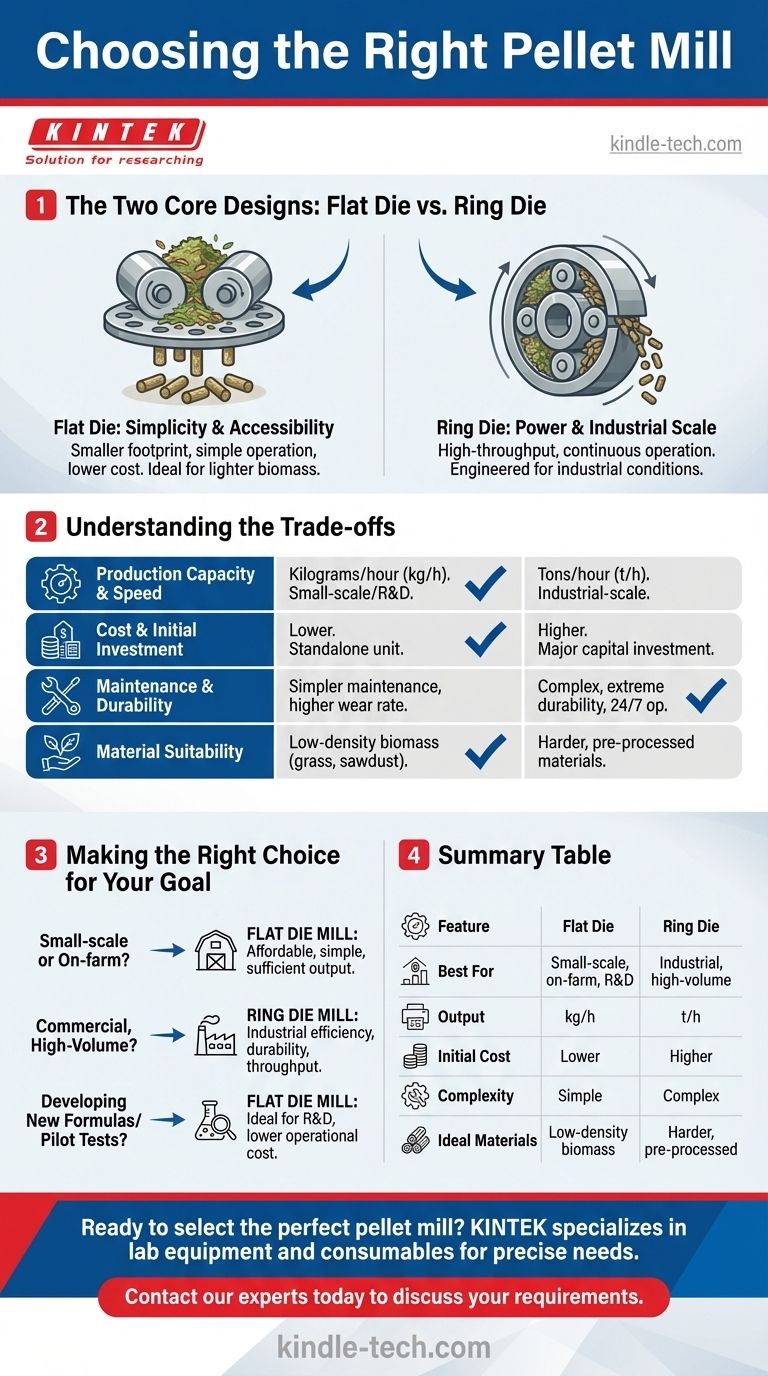
When evaluating pellet mills, the industry is dominated by two primary designs: the flat die pellet mill and the ring die pellet mill. The fundamental difference between them is not just their shape, but their operational principle, which directly dictates their suitability for different production scales. Flat die mills are designed for smaller, less intensive applications, while ring die mills are built for high-volume, industrial manufacturing.
The choice between a flat die and a ring die pellet mill is a strategic decision about scale. Flat die mills serve small-scale needs with simplicity and lower cost, whereas ring die mills are the standard for high-throughput, continuous commercial production.

The Two Core Designs: Flat Die vs. Ring Die
To select the right equipment, you must first understand how each design works. The mechanical difference is the primary driver of their distinct advantages and applications.
The Flat Die Pellet Mill: Simplicity and Accessibility
A flat die pellet mill operates on a straightforward principle. A flat, circular, perforated plate (the die) sits horizontally. One or more rollers press down on raw material, forcing it through the holes in the die to form pellets.
This design is mechanically simple, often compared to a meat grinder. Its vertical feeding and direct pressure make it highly effective for lighter, fluffier biomass that might not feed as easily in other systems.
These machines are the entry point for pellet production due to their smaller footprint, simpler operation, and significantly lower initial cost.
The Ring Die Pellet Mill: Power and Industrial Scale
In a ring die pellet mill, the die is a thick-walled ring or cylinder that rotates at high speed, typically on a vertical or horizontal axis. Rollers located on the inside of the ring press the raw material outwards.
Centrifugal force flings the material against the inner surface of the rotating ring, where the rollers create immense pressure to extrude it through the die holes. This process is highly efficient and allows for a much greater throughput.
Ring die mills are the workhorses of the commercial pelleting industry, designed for continuous, high-volume operation in settings like large-scale wood pellet plants and industrial feed mills.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two types involves a clear set of trade-offs related to output, cost, and operational demands. There is no single "best" type; there is only the best fit for a specific goal.
Production Capacity and Speed
A flat die mill's output is measured in kilograms or pounds per hour. It is perfectly suited for on-farm use, laboratory testing, or small business ventures.
A ring die mill's output is measured in tons per hour. Its design is inherently built for speed and efficiency, making it the only choice for industrial-scale production where downtime is costly.
Cost and Initial Investment
The initial investment for a flat die mill is relatively low. The machine is often a standalone unit and requires less supporting infrastructure, making it accessible for smaller operators.
A ring die mill represents a major capital investment. It is rarely a standalone machine but rather a key component in a larger, automated production line, requiring significant upfront cost and facility planning.
Maintenance and Durability
Flat die mills are simpler to maintain, and replacing the die and rollers is a more straightforward process. However, these components may experience a higher wear rate under constant, heavy use compared to their industrial counterparts.
Ring die mills are engineered for extreme durability and 24/7 operation. While maintenance procedures are more complex and parts are more expensive, they are designed for longevity under punishing industrial conditions.
Material Suitability
Due to their direct downward pressure, flat die mills often excel with low-density, soft materials like grass, alfalfa, and sawdust that can be difficult to feed into a ring die system.
Ring die mills can handle a wider range of material hardness and density, including hard woods, due to the high pressure and speed generated within the pelleting chamber. The high efficiency makes them ideal for uniform, pre-processed feedstock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by a clear assessment of your production volume, budget, and long-term operational plans.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or on-farm production: A flat die mill offers the best balance of affordability, simplicity, and sufficient output for your needs.
- If your primary focus is commercial, high-volume manufacturing: A ring die mill is the necessary investment for achieving industrial-level efficiency, durability, and throughput.
- If you are developing new formulas or running pilot tests: The smaller scale and lower operational cost of a flat die mill make it the ideal and most practical choice.
Understanding this fundamental distinction between scale and design empowers you to select the right tool for your specific production objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Flat Die Pellet Mill | Ring Die Pellet Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Small-scale, on-farm, R&D | Industrial, high-volume production |
| Output Capacity | Kilograms per hour (kg/h) | Tons per hour (t/h) |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher (major capital investment) |
| Operational Complexity | Simple | Complex, requires automated line |
| Ideal Materials | Low-density biomass (e.g., grass, sawdust) | Harder, pre-processed materials (e.g., hard woods) |
Ready to select the perfect pellet mill for your operation?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and small-to-medium production facilities. Whether you need a reliable flat die mill for R&D and pilot testing or are planning to scale up your production, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for optimal performance and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and find the ideal pellet mill solution for your laboratory or production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- What advantages does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) offer for solid-state batteries? Superior Density & Uniformity
- How does a cold isostatic press improve microhardness uniformity? Achieving Consistency in TiC10/Cu-Al2O3 Composites
- What advantages does Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) offer for nickel-alumina composites? Enhance Density & Strength
- How does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) contribute to the fabrication of HE-O-MIEC and LLZTO? Expert Densification Guide
- What are the advantages of using a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP)? Achieve High Density in Ceramic Pellets



















