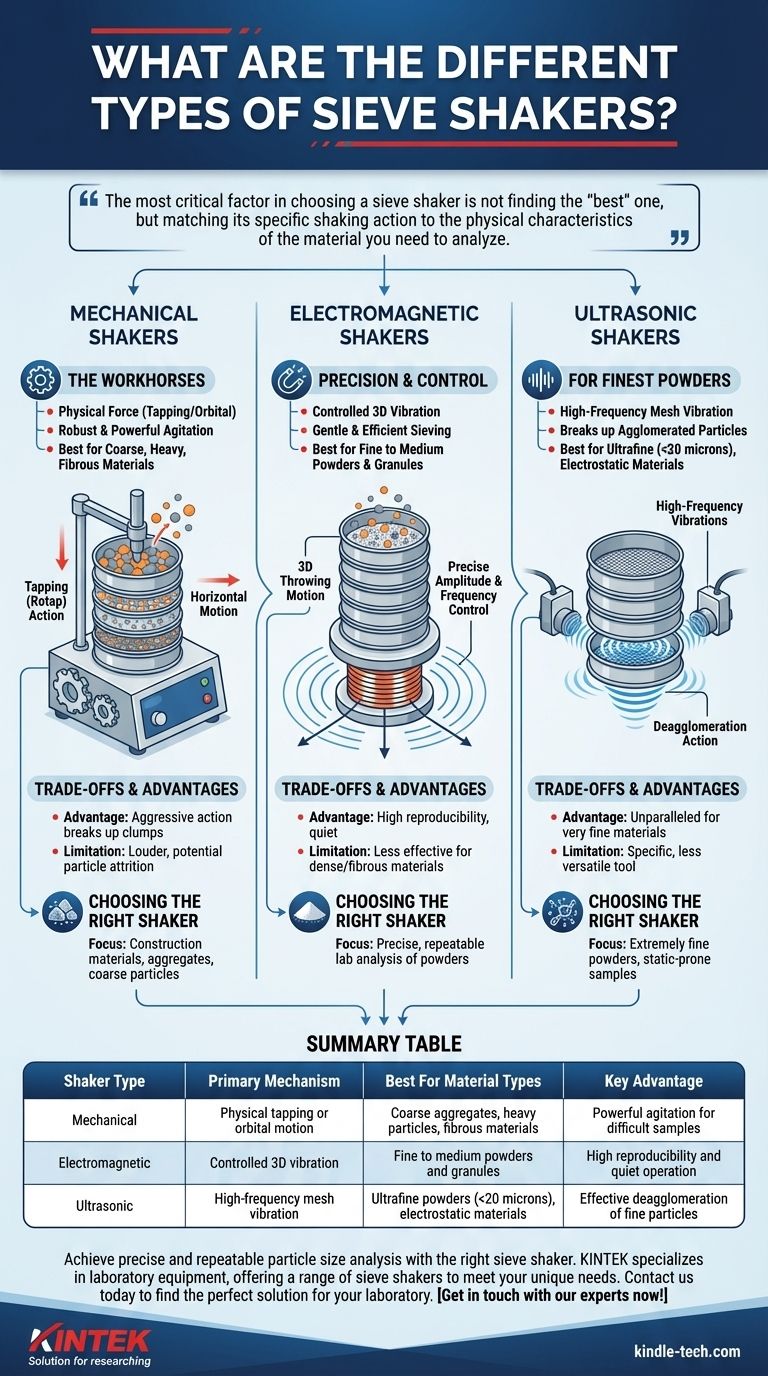
At their core, sieve shakers are categorized by the type of motion they use to agitate a stack of test sieves for particle size analysis. The two most common types are mechanical shakers, which use physical force like tapping or orbital movements, and electromagnetic shakers, which use a controlled 3D vibration. Specialized ultrasonic shakers also exist for very fine powders.
The most critical factor in choosing a sieve shaker is not finding the "best" one, but matching its specific shaking action to the physical characteristics of the material you need to analyze.

The Core Mechanisms: How Sieve Shakers Work
The effectiveness of a particle size analysis depends entirely on how well the shaker's motion separates the particles. Each mechanism is optimized for different particle shapes, sizes, and properties.
Mechanical Sieve Shakers: The Workhorses
Mechanical shakers generate movement through direct physical means. They are robust, established tools often favored for their powerful agitation.
The most common variant is the tapping shaker (often called a "Rotap" shaker). It combines a horizontal, circular motion with a vertical tapping action, which helps dislodge particles stuck in the sieve mesh and is effective for a wide range of materials.
Another type is the horizontal shaker. This machine moves the sieve stack in horizontal circles, which is the preferred method for needle-shaped, flat, long, or fibrous samples that might otherwise clog the mesh.
Electromagnetic Sieve Shakers: Precision and Control
Electromagnetic shakers use a powerful electromagnet to create a 3D throwing motion, moving particles up and across the sieve mesh simultaneously. This provides a gentle yet efficient sieving action.
Their primary advantage is reproducibility. The vibration intensity (amplitude) and frequency can be precisely controlled, often through digital interfaces and software, ensuring consistent test conditions every time. This makes them ideal for quality control and research environments.
Ultrasonic Sieve Shakers: For the Finest Powders
Ultrasonic shakers are a specialized category designed for particles that are extremely difficult to sieve, such as those under 20 microns. They use high-frequency vibrations generated directly at the sieve mesh.
This action is crucial for breaking up agglomerated particles or overcoming static charges that cause fine powders to cling to each other and the mesh, ensuring an accurate analysis of the finest materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each shaker type presents a distinct set of advantages and limitations. Selecting the correct one requires understanding these differences.
The Power of Mechanical Shakers
Mechanical shakers excel with larger, heavier, or irregularly shaped particles found in construction aggregates or mining. The aggressive tapping action is highly effective at breaking up clumps and forcing material through the sieves.
However, this same aggressive action can be a drawback. It can be significantly louder and may cause particle attrition, where brittle particles break down during sieving, skewing the results toward a finer distribution.
The Precision of Electromagnetic Shakers
Electromagnetic shakers are the standard for most laboratory analysis of fine to medium granules and powders. Their controlled, quiet operation and repeatable results are invaluable for R&D and quality control.
Their main limitation is with certain material types. The gentler 3D motion may be less effective for very dense aggregates or long, fibrous materials that benefit from the distinct tapping or horizontal action of a mechanical shaker.
The Specialty of Ultrasonic Shakers
Ultrasonic shakers are unparalleled for very fine, lightweight, or electrostatically charged powders. For these applications, other shaker types simply fail to deagglomerate the material effectively.
This high performance comes at the cost of versatility. They are not designed as general-purpose shakers and are a specific tool for a specific, and often difficult, problem.
Choosing the Right Shaker for Your Material
Your choice should be guided by the physical nature of your sample and the goal of your analysis.
- If your primary focus is construction materials, aggregates, or coarse particles: A mechanical shaker with a tapping or horizontal motion is the most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable analysis of powders and granules: An electromagnetic shaker provides the control and consistency required for laboratory environments.
- If your primary focus is extremely fine powders (<20 microns) prone to static or clumping: An ultrasonic shaker is the essential specialized tool for an accurate result.
Ultimately, matching the instrument's motion to the material's properties is the key to achieving a meaningful and accurate particle size analysis.
Summary Table:
| Shaker Type | Primary Mechanism | Best For Material Types | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Physical tapping or orbital motion | Coarse aggregates, heavy particles, fibrous materials | Powerful agitation for difficult samples |
| Electromagnetic | Controlled 3D vibration | Fine to medium powders and granules | High reproducibility and quiet operation |
| Ultrasonic | High-frequency mesh vibration | Ultrafine powders (<20 microns), electrostatic materials | Effective deagglomeration of fine particles |
Achieve precise and repeatable particle size analysis with the right sieve shaker. The accuracy of your results depends on matching the equipment to your specific materials. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, offering a range of sieve shakers to meet your lab's unique needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal shaker—whether mechanical, electromagnetic, or ultrasonic—to ensure your particle analysis is efficient, accurate, and reliable. Contact us today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Laboratory Oscillating Orbital Shaker
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the operating procedure of a sieve shaker? Master Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material
- What are the components of a sieving machine? Unlock the Anatomy of Precision Particle Separation
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- What is the speed of a sieving machine? Optimize Vibration for Maximum Efficiency and Accuracy



















