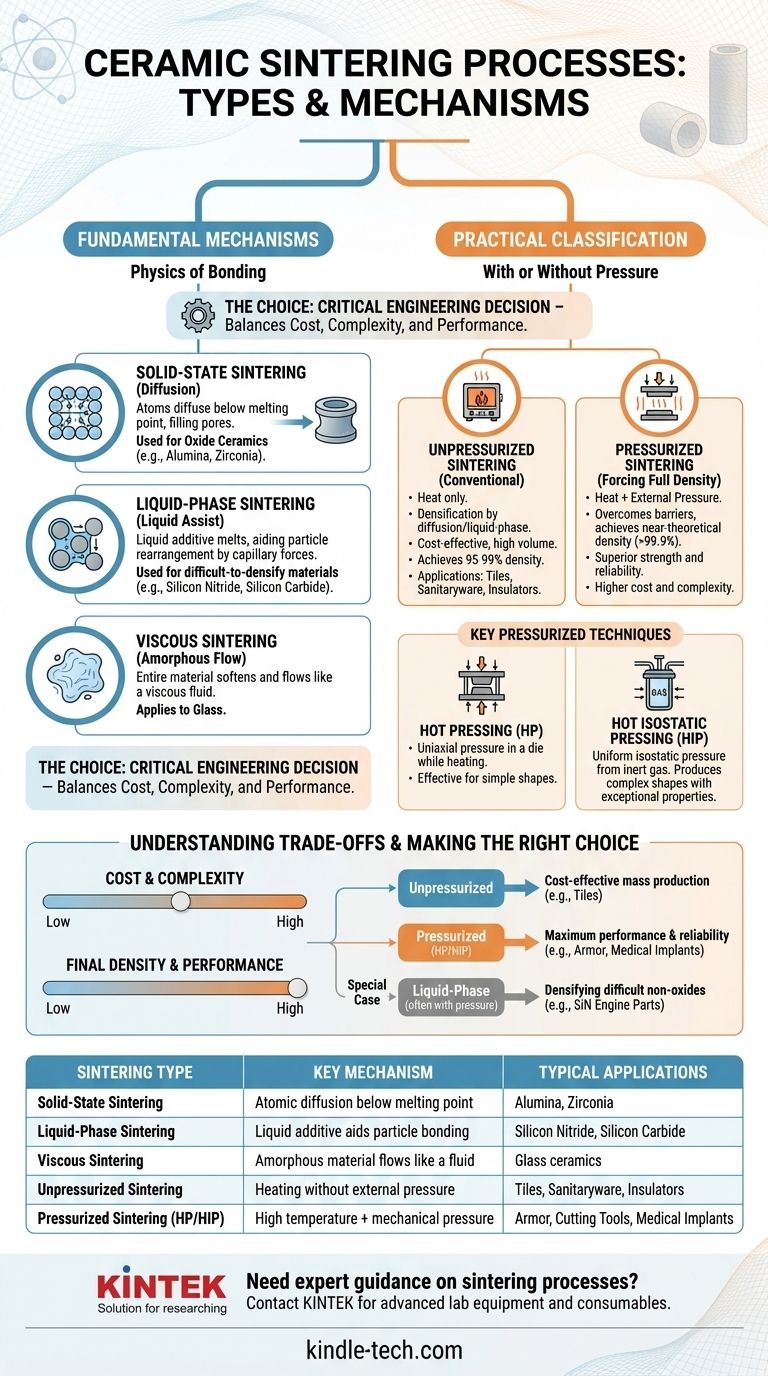
At its core, ceramic sintering processes are primarily categorized in two ways: by the physical mechanism that drives densification and by the processing conditions used. The fundamental mechanisms are solid-state sintering, where atoms diffuse through a solid, and liquid-phase sintering, where a liquid additive aids particle rearrangement. These are applied using either unpressurized (conventional) methods or pressurized techniques to achieve the desired final properties.
The choice of a sintering process is not arbitrary; it is a critical engineering decision. It represents a trade-off between manufacturing cost, processing complexity, and the final performance requirements—such as density and mechanical strength—demanded by the ceramic's specific application.

The Fundamental Mechanisms of Sintering
To understand the different processes, you must first grasp the underlying physics of how individual ceramic particles bond together to form a dense, solid object. The primary mechanisms are distinguished by the state of matter involved during heating.
Solid-State Sintering: Diffusion in Action
Solid-state sintering, also called solid-phase sintering, is a process where a ceramic powder compact is heated to a high temperature, typically below its melting point.
At this temperature, atoms gain enough energy to diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This atomic movement gradually fills the pores between particles, causing the component to shrink and densify. This is the primary method used for many oxide ceramics like alumina and zirconia.
Liquid-Phase Sintering: A Liquid Assist
Liquid-phase sintering is used for materials that are very difficult to densify using diffusion alone, such as silicon nitride and silicon carbide.
In this process, small amounts of an additive are mixed with the ceramic powder. At sintering temperature, this additive melts and forms a liquid phase that wets the solid ceramic particles. Capillary forces from this liquid pull the particles together, dramatically accelerating rearrangement and densification.
Viscous Sintering: The Flow of Amorphous Materials
A third, less common mechanism is viscous sintering, which applies to amorphous materials like glass.
Instead of distinct particles diffusing, the entire material softens and behaves like a highly viscous fluid. Under the force of surface tension, the material slowly flows to minimize its surface area, which naturally eliminates pores and leads to densification.
Practical Classification: With or Without Pressure
Beyond the atomic mechanism, the most significant practical distinction between sintering processes is the use of external pressure. This choice directly impacts the final density, mechanical properties, and cost of the ceramic part.
Unpressurized Sintering: The Conventional Path
Unpressurized sintering, often called conventional or pressureless sintering, is the most common and cost-effective method.
A green body (a pressed powder compact) is simply heated in a furnace. Densification occurs solely through the mechanisms of diffusion or liquid-phase formation described earlier. While effective for many applications like tiles and sanitaryware, it can leave behind some residual porosity.
Pressurized Sintering: Forcing Full Density
Pressurized sintering combines high temperature with the simultaneous application of external mechanical pressure. This pressure physically forces particles together, overcoming barriers to densification and enabling the creation of nearly pore-free ceramics.
This approach is essential for high-performance applications where maximum strength and reliability are non-negotiable.
Key Pressurized Techniques
Several specialized techniques fall under the pressurized sintering umbrella:
- Hot Pressing (HP): Powder is placed in a die and uniaxially pressed while being heated. It is highly effective but generally limited to simple shapes.
- Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): A component is heated in a high-pressure vessel, where an inert gas applies uniform, isostatic (equal from all directions) pressure. This can produce complex shapes with exceptionally high density and superior mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering process requires a clear understanding of its inherent advantages and limitations. The "best" method is entirely dependent on the material and the goal.
Cost and Complexity
Unpressurized sintering is relatively simple and utilizes standard furnace equipment, making it ideal for high-volume, low-cost production. Pressurized methods like HIP require highly specialized, expensive equipment and significantly increase processing costs and complexity.
Final Density and Performance
Pressurized sintering is unmatched for achieving near-theoretical density (>99.9%). This absence of porosity leads to a dramatic improvement in mechanical properties like strength, hardness, and fracture toughness. Conventional sintering often results in densities between 95-99%, which is sufficient for many but not all applications.
Material Constraints
Some high-covalency ceramics, like silicon carbide, resist solid-state diffusion. For these materials, densification is nearly impossible without the aid of liquid-phase formers or the driving force of external pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of sintering process must be aligned with your material properties and end-use requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production (e.g., ceramic tiles, insulators): Conventional, unpressurized sintering is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and reliability (e.g., armor, cutting tools, medical implants): Pressure-assisted methods like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) are required to achieve near-full density.
- If your primary focus is densifying difficult non-oxide ceramics (e.g., silicon nitride engine parts): Liquid-phase sintering, often combined with a pressurized technique, is the most effective approach.
Understanding these fundamental distinctions empowers you to select the precise manufacturing path required to achieve your material's target performance.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Type | Key Mechanism | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Atomic diffusion below melting point | Alumina, Zirconia |
| Liquid-Phase Sintering | Liquid additive aids particle bonding | Silicon Nitride, Silicon Carbide |
| Viscous Sintering | Amorphous material flows like a fluid | Glass ceramics |
| Unpressurized Sintering | Heating without external pressure | Tiles, Sanitaryware, Insulators |
| Pressurized Sintering (HP/HIP) | High temperature + mechanical pressure | Armor, Cutting Tools, Medical Implants |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right sintering process for your ceramic components? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're developing high-performance ceramics for medical implants or optimizing cost-effective mass production, our team can help you choose the right sintering furnaces and accessories to achieve your target density and mechanical properties. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your ceramic sintering outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















