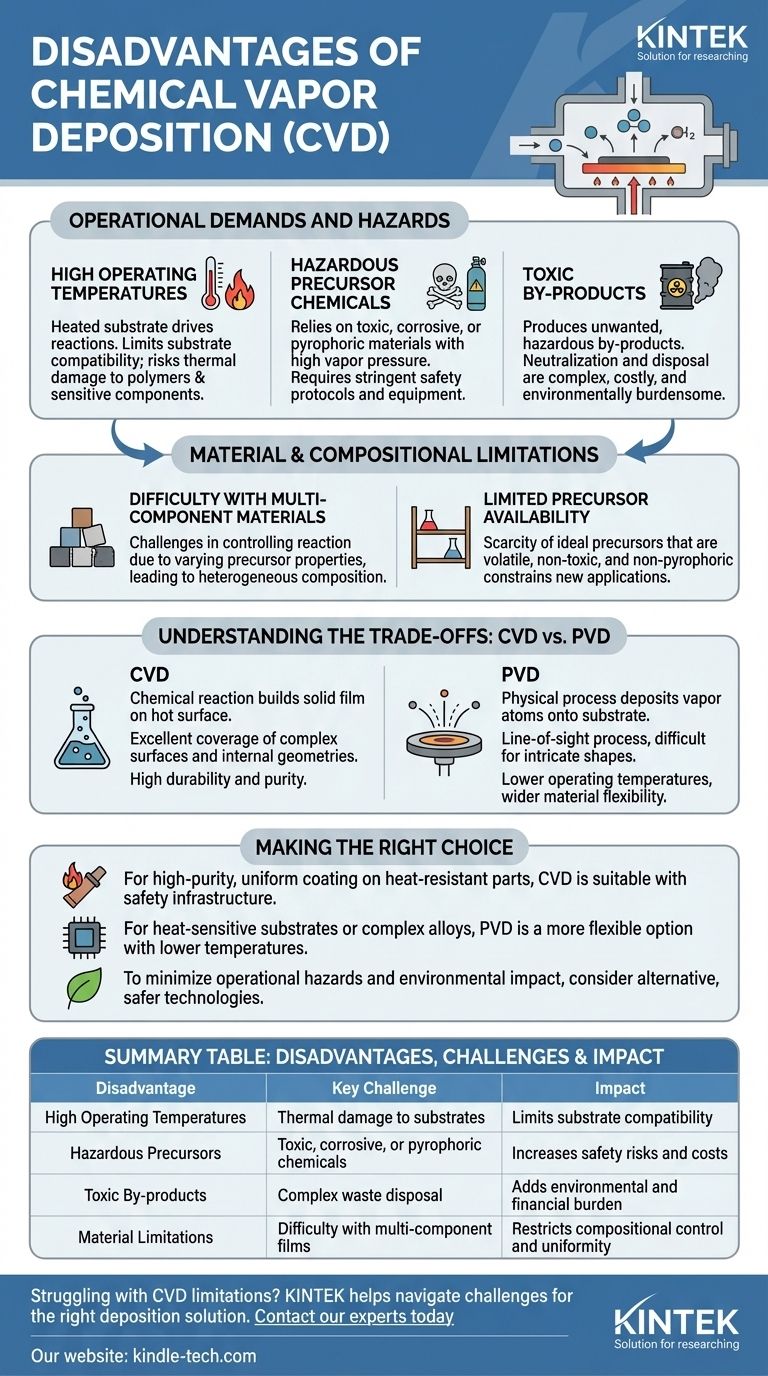
The primary disadvantages of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) are its high operating temperatures, reliance on hazardous precursor chemicals, and the creation of toxic, costly by-products. These factors introduce significant challenges related to substrate compatibility, operational safety, and environmental management.
While CVD is renowned for producing highly durable and uniform coatings, its core disadvantages stem from its demanding process chemistry. The method's effectiveness is often counterbalanced by risks and complexities involving heat, hazardous materials, and compositional control.

Operational Demands and Hazards
The fundamental nature of CVD—using a chemical reaction to build a film—introduces several operational hurdles that must be managed carefully.
High Operating Temperatures
CVD typically requires a heated substrate to drive the necessary chemical reactions. This high-temperature environment can cause thermal instability or damage to many materials.
This constraint limits the types of substrates that can be coated, excluding many polymers or sensitive electronic components that cannot withstand the heat.
Hazardous Precursor Chemicals
The process relies on chemical precursors with high vapor pressure, allowing them to exist in a gaseous state. Many of these chemicals are highly toxic, corrosive, or pyrophoric (igniting spontaneously in air).
Handling and storing these materials requires stringent safety protocols and specialized equipment, increasing both the risk and cost of the operation.
Toxic By-products
The chemical reactions that deposit the desired film also produce unwanted by-products. These substances are often as toxic and corrosive as the initial precursors.
Neutralizing and disposing of this hazardous waste is a complex and expensive problem, adding a significant environmental and financial burden to the process.
Material and Compositional Limitations
Beyond the operational hazards, CVD faces inherent limitations in the types of materials it can effectively create.
Difficulty with Multi-Component Materials
Synthesizing films made of multiple elements can be exceptionally difficult. Each precursor chemical has a different vapor pressure, nucleation rate, and growth rate.
These variations make it challenging to control the chemical reaction precisely, often resulting in a heterogeneous composition rather than a uniform, blended material.
Limited Precursor Availability
The universe of suitable precursor chemicals is limited. Finding a compound that is sufficiently volatile but also non-toxic and non-pyrophoric is a major challenge for many desired film materials.
This scarcity of ideal precursors can be a significant bottleneck in developing new coating applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: CVD vs. Other Methods
To fully appreciate CVD's disadvantages, it's useful to contrast it with its main alternative, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
The Chemical vs. Physical Core
CVD uses a chemical reaction between gaseous molecules and a hot surface to form a stable, solid film.
PVD, in contrast, is a physical process. It involves generating a vapor of atoms from a solid source (via heating or sputtering) and having them physically deposit onto the substrate's surface.
Coating Quality and Coverage
One of CVD's main advantages is its ability to coat complex surfaces and internal geometries uniformly because the precursor gas can reach all exposed areas. The resulting films are often highly durable and pure.
PVD is typically a line-of-sight process, making it difficult to coat intricate shapes evenly. Its films can also suffer from defects like "macros" (molten globules) depending on the specific technique used.
Process Constraints and Material Flexibility
CVD's disadvantages—high heat and reliance on specific, often hazardous, reactive gases—are its key constraints.
PVD processes often operate at lower temperatures and can be used to deposit a wider variety of materials, including conductive metals and complex alloys, without requiring a chemical reaction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition technology requires balancing the desired coating properties against the inherent limitations of the process.
- If your primary focus is a high-purity, uniform coating on a complex, heat-resistant part: CVD is an excellent choice, assuming you can invest in the necessary safety and waste-handling infrastructure.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive substrates or depositing complex alloys: A PVD method is likely a more suitable and flexible option due to its lower operating temperatures and simpler material sourcing.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational hazards and environmental impact: The high toxicity of CVD's chemicals and by-products necessitates exploring alternative technologies that offer a safer process profile.
Ultimately, an informed decision rests on weighing the superior coating conformity of CVD against its significant operational and material challenges.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High Operating Temperatures | Thermal damage to substrates | Limits substrate compatibility |
| Hazardous Precursors | Toxic, corrosive, or pyrophoric chemicals | Increases safety risks and costs |
| Toxic By-products | Complex waste disposal | Adds environmental and financial burden |
| Material Limitations | Difficulty with multi-component films | Restricts compositional control and uniformity |
Struggling with the limitations of Chemical Vapor Deposition?
At KINTEK, we understand that the high costs, safety hazards, and material constraints of CVD can be significant barriers for your laboratory. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables allows us to help you navigate these challenges and find the right deposition solution for your specific needs—whether it's a safer alternative or optimizing your current CVD process for better efficiency and control.
Let's find a safer, more efficient path forward for your coating applications. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs



















