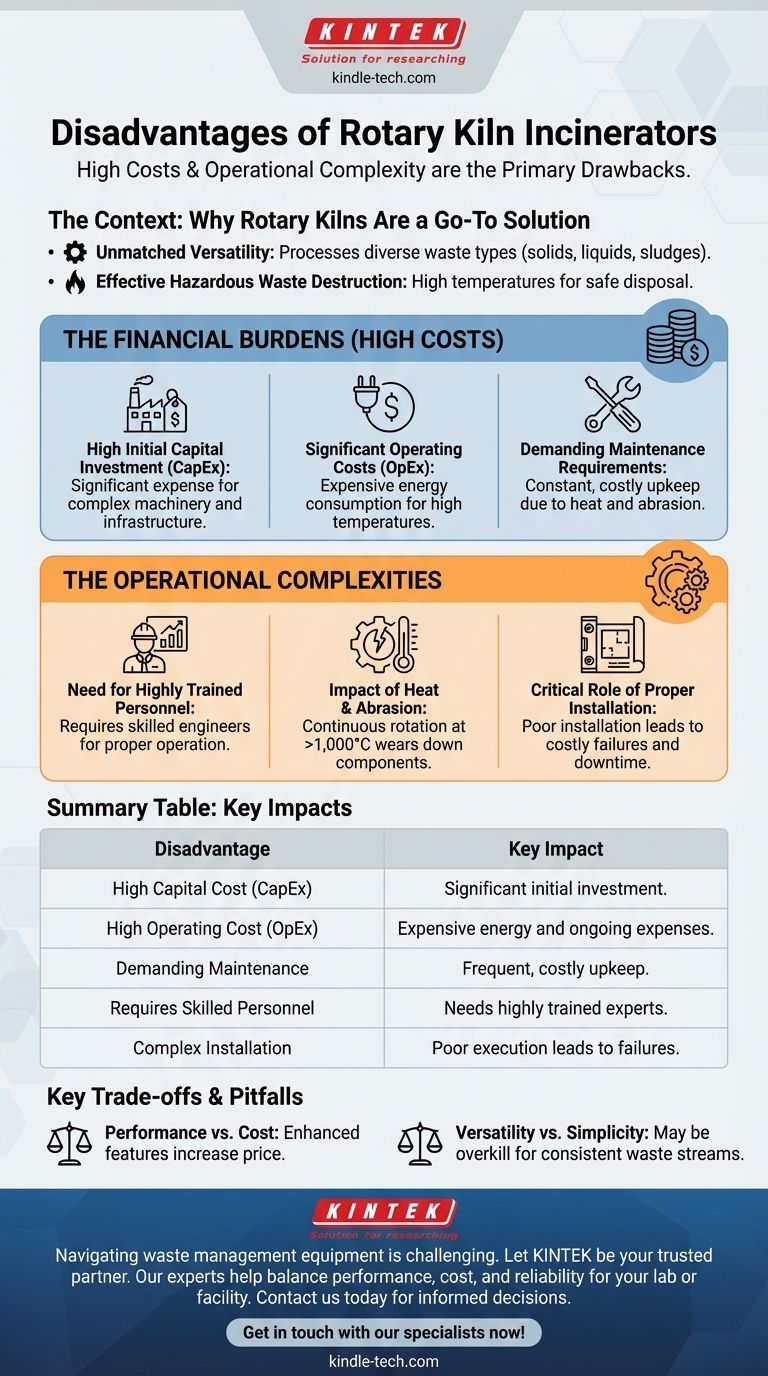
While incredibly effective, rotary kiln incinerators come with significant and unavoidable drawbacks. Their primary disadvantages are their extremely high costs—spanning initial capital, ongoing operations, and intensive maintenance—and the operational burden of requiring highly trained personnel to manage their complexity.
Rotary kilns are a premier technology for destroying a wide range of hazardous waste, but this versatility is not free. Decision-makers must understand that choosing a rotary kiln is a commitment to high long-term financial investment and specialized operational expertise.

The Context: Why Rotary Kilns Are a Go-To Solution
Before examining the disadvantages, it's important to understand why rotary kilns are often the preferred choice for complex waste management, which helps contextualize their trade-offs.
Unmatched Versatility
Rotary kilns are capable of processing a wide variety of waste types simultaneously, including solids, liquids, and sludges. This makes them vital for facilities that handle unpredictable or mixed waste streams.
Effective Hazardous Waste Destruction
These systems excel at the high-temperature, long-residence-time incineration required to safely destroy hazardous and toxic materials. This process significantly reduces waste volume while also allowing for energy recovery.
The Financial Burdens of Rotary Kiln Operation
The most significant barrier to adopting rotary kiln technology is financial. The costs are substantial and extend far beyond the initial purchase price.
High Initial Capital Investment (CapEx)
The design, manufacturing, and installation of a rotary kiln system represent a major capital expenditure. The machinery is large, complex, and requires a robust supporting infrastructure.
Significant Operating Costs (OpEx)
Day-to-day operation is expensive. The energy required to achieve and maintain high incineration temperatures is a primary driver of cost, whether using traditional fuels or electricity.
Demanding Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance is a constant and costly necessity. The combination of abrasive waste materials and extreme heat places immense stress on the kiln's mechanical components.
Understanding the Technical and Operational Complexities
Beyond the financial strain, rotary kilns present significant operational challenges that require dedicated resources and expertise.
The Need for Highly Trained Personnel
These are not "set it and forget it" machines. Proper operation requires a team of well-trained engineers and technicians to manage temperature profiles, waste feed rates, and emissions control systems.
The Impact of Heat and Abrasion
The continuous rotation of the kiln drum, combined with abrasive contents and temperatures exceeding 1,000°C, leads to predictable wear and tear. Refractory linings, seals, and moving parts like wheels and tires require regular inspection and replacement, driving up maintenance costs and downtime.
The Critical Role of Proper Installation
A poorly executed installation can lead to catastrophic and costly failures. Misalignment can damage the kiln's drum shell, support wheels, or drive system, leading to expensive rework and potentially voiding manufacturer warranties.
Key Trade-offs and Pitfalls to Avoid
Choosing a rotary kiln involves balancing its powerful capabilities against its inherent demands. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for a successful project.
Performance vs. Cost
Features that enhance performance—such as advanced air seals to ensure airtightness or specialized heater placement for even heat—also increase the initial cost and maintenance complexity. Every added capability comes with a price.
Versatility vs. Simplicity
While a rotary kiln can handle almost any waste stream, it may be overkill for a facility that only processes a single, consistent type of waste. Simpler, less expensive incineration technologies might be more appropriate in such cases.
The Installation Trap
Cutting corners on installation is a classic pitfall. Failing to adhere to the manufacturer's critical inspection points and alignment procedures is a false economy that almost always results in higher long-term costs and operational instability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by a clear-eyed assessment of your primary objectives, balanced against your budget and operational capacity.
- If your primary focus is managing diverse and hazardous waste streams: The rotary kiln is a superior technical solution, but you must budget for its high total cost of ownership and invest in a skilled team.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost and operational complexity: You should explore simpler, alternative incineration technologies that may be better suited for less complex or more uniform waste streams.
- If you are proceeding with a rotary kiln: Prioritize securing expert installation and committing to a dedicated, highly trained operational staff to protect your investment and ensure long-term reliability.
Ultimately, a successful rotary kiln implementation depends on acknowledging its costs and complexities from the very beginning.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Capital Cost (CapEx) | Significant initial investment for complex machinery and infrastructure. |
| High Operating Cost (OpEx) | Expensive energy consumption and ongoing operational expenses. |
| Demanding Maintenance | Frequent, costly upkeep due to heat and abrasion on components. |
| Requires Skilled Personnel | Needs highly trained engineers and technicians for proper operation. |
| Complex Installation | Poor installation can lead to failures and increased long-term costs. |
Navigating the complexities of waste management equipment is challenging. Let KINTEK be your trusted partner.
As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, we understand the critical balance between performance, cost, and reliability. If you're evaluating incineration technologies for your laboratory or facility, our experts can help you assess your specific needs and identify the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's expertise can ensure you make a well-informed investment decision.
Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4



















