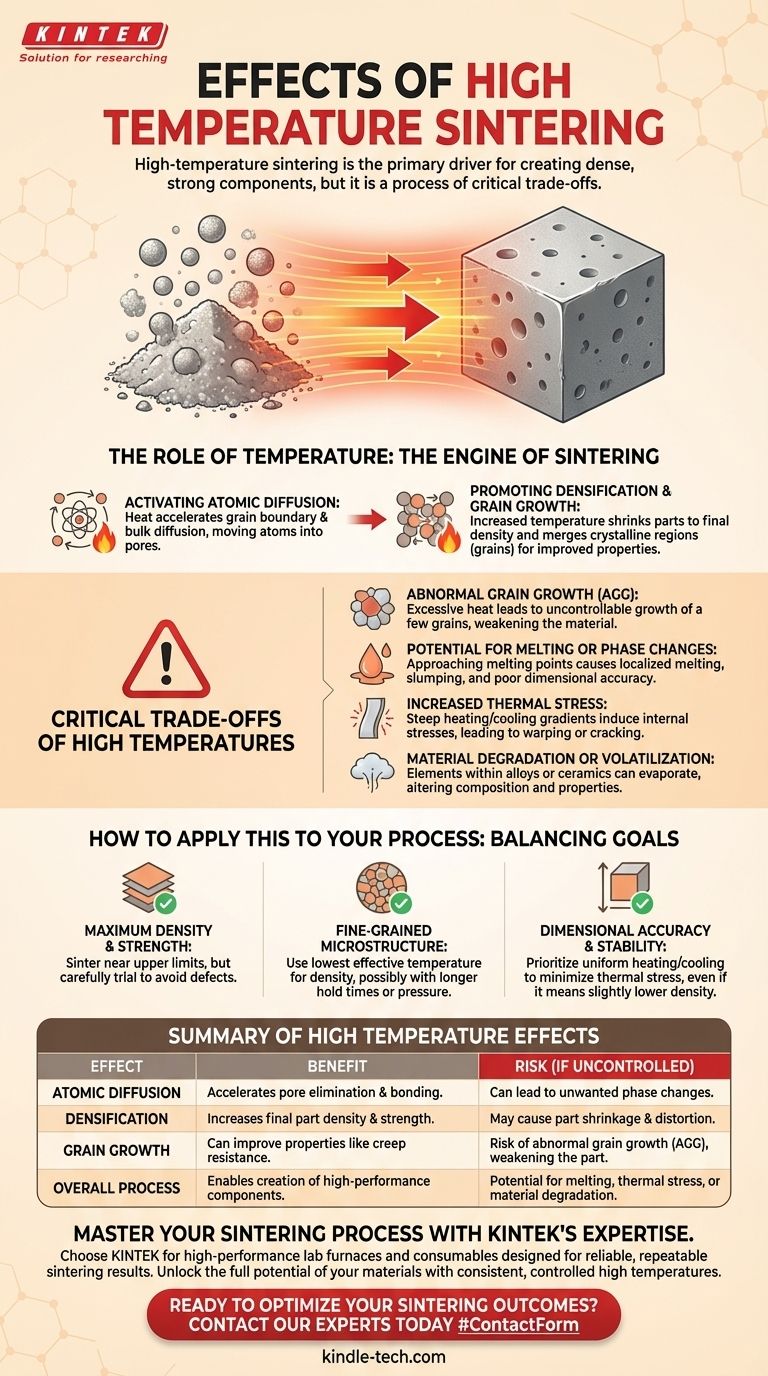
High-temperature sintering is the primary driver for creating dense, strong components, but it is a process of critical trade-offs. While elevated temperatures provide the necessary energy for particles to fuse together, exceeding the optimal temperature for a given material can introduce significant defects, such as abnormal grain growth, melting, or thermal stress, which severely compromise the final part's performance.
The core objective of sintering is not simply to apply high heat. It is to precisely control the temperature to activate the specific atomic diffusion mechanisms that eliminate porosity and build strength, without triggering detrimental effects that create a weak or unstable microstructure.

The Role of Temperature in Sintering Mechanisms
Temperature is the engine that drives the entire sintering process. It provides the thermal energy required for atoms to move, rearrange, and create a solid, coherent mass from loose powder.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
Sintering fundamentally relies on diffusion, the movement of atoms. Higher temperatures dramatically increase the rate of two key mechanisms: grain boundary diffusion and bulk diffusion. This atomic motion is what allows material to move into the empty spaces (pores) between particles.
Promoting Densification
As atoms diffuse and fill the pores, the component becomes denser. Increased temperature accelerates this process, reducing porosity and shrinking the part to its final, desired density. This is often the primary reason for using high sintering temperatures.
Driving Grain Growth
As particles bond and pores are eliminated, the individual crystalline regions, or grains, begin to merge and grow. This is a natural and often desirable consequence of sintering, as it can improve certain mechanical properties like creep resistance.
The Critical Trade-offs of High Temperatures
While heat is necessary, excessive temperature is one of the most common sources of failure in sintering. Pushing the temperature too high introduces a new set of problems that can negate any benefits.
The Risk of Abnormal Grain Growth (AGG)
If the temperature is too high or held for too long, a few grains can grow uncontrollably large by consuming their smaller neighbors. This creates a non-uniform microstructure with large, weak points that dramatically reduce the material's strength and reliability.
Potential for Melting or Phase Changes
Every material has a melting point. As the sintering temperature approaches this limit, you risk localized melting, also known as liquid phase formation. This can cause the component to slump, lose its shape, and have poor dimensional accuracy. It can also trigger unwanted changes in the material's crystalline structure.
Increased Thermal Stress
High temperatures require steeper heating and cooling ramps. This can create significant temperature gradients within the part, inducing internal stresses. These stresses can lead to warping or, in severe cases, cracking during or after the cooling cycle.
Material Degradation or Volatilization
Just as some organic compounds degrade with heat, elements within a metallic alloy or ceramic composite can begin to volatilize (evaporate) at excessively high temperatures. This changes the material's composition and can ruin its engineered properties.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing the right temperature is not a single decision; it is a balance dictated by your material and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength: You will likely need to sinter near the upper limit for your material, but must carefully conduct trials to identify the threshold where abnormal grain growth or melting begins.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a fine-grained microstructure (for high hardness or toughness): Your strategy should be to use the lowest possible temperature that achieves the necessary density, often requiring longer hold times or the use of pressure-assisted techniques.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy and stability: Prioritize uniform, controlled heating and cooling cycles to minimize thermal stress, even if it means accepting a slightly lower peak temperature and density.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control is the key to unlocking the full potential of your material through the sintering process.
Summary Table:
| Effect of High Temperature | Benefit | Risk (if Uncontrolled) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Diffusion | Accelerates pore elimination and bonding | Can lead to unwanted phase changes |
| Densification | Increases final part density and strength | May cause part shrinkage and distortion |
| Grain Growth | Can improve properties like creep resistance | Risk of abnormal grain growth (AGG), weakening the part |
| Overall Process | Enables creation of high-performance components | Potential for melting, thermal stress, or material degradation |
Master your sintering process with KINTEK's expertise.
Choosing the right sintering temperature is a delicate balance between achieving maximum density and avoiding defects like abnormal grain growth or thermal stress. Whether your goal is ultimate strength, a fine-grained microstructure, or superior dimensional accuracy, the precise control of your lab equipment is paramount.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed for reliable, repeatable sintering results. Our solutions help you unlock the full potential of your materials by providing the consistent, controlled high temperatures your process demands.
Ready to optimize your sintering outcomes? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's equipment can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure the integrity of your sintered components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















