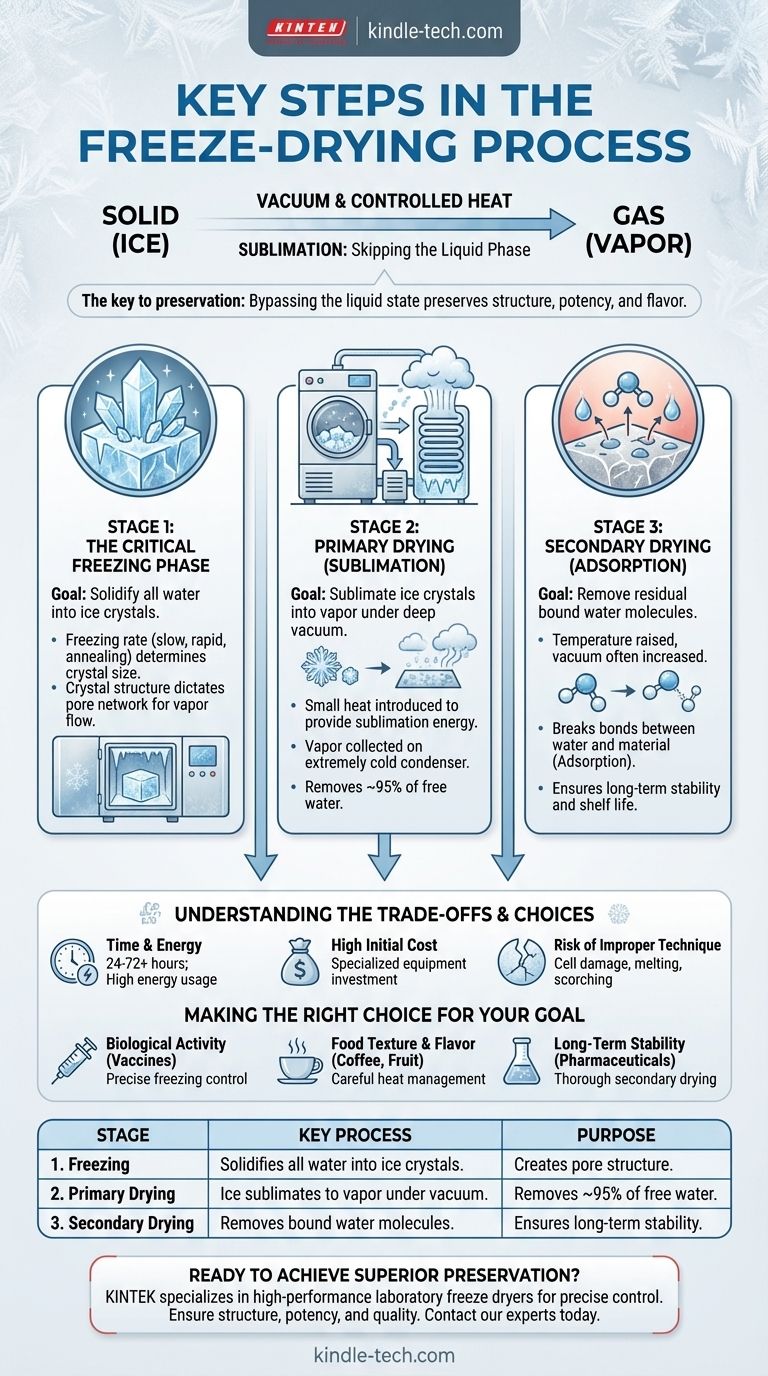
At its core, freeze-drying is a three-stage water removal process that preserves a material's structure and quality. Also known as lyophilisation, it involves first freezing the material solid, then placing it under a deep vacuum to turn the ice directly into vapor (sublimation), and finally, removing any remaining bound water molecules. This method avoids the damaging effects of liquid water and high-heat evaporation.
The crucial insight is that freeze-drying isn't just about removing water—it's about bypassing the liquid state entirely. By transforming ice directly into vapor, the process preserves a material's delicate structure, potency, and flavor with unmatched fidelity.

The Principle: Sublimation Over Evaporation
To understand freeze-drying, you must first understand sublimation. It is a phase transition where a substance goes directly from a solid to a gas, skipping the liquid phase entirely.
This is achieved by carefully controlling temperature and pressure. By freezing the material and then reducing the pressure below a specific threshold (the "triple point"), we create an environment where ice can no longer melt into water but will instead turn directly into vapor when minimal energy is added.
This is the key to preservation. The rigid structure of the frozen material is maintained throughout the process, preventing the shrinkage, chemical changes, and loss of quality common in conventional heat-based dehydration.
A Detailed Look at the Three Stages
Each stage of the freeze-drying process serves a distinct purpose, and mastering each one is critical for a successful outcome.
Stage 1: The Critical Freezing Phase
This is arguably the most important stage, as it sets the foundation for the entire process. The goal is to completely solidify all water within the material into ice crystals.
The method of freezing—whether it's done slowly, rapidly, or with an annealing step (cycling temperatures)—directly impacts the size of the ice crystals formed. This crystal structure dictates the pore network through which water vapor will travel during the subsequent drying stages, influencing the final speed and quality of the process.
Stage 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
With the material solidly frozen, the primary drying phase begins. The product is placed inside the freeze-dryer, and a powerful vacuum pump significantly lowers the pressure.
At this point, a small amount of heat is carefully introduced. This heat provides the energy the ice crystals need to sublimate into water vapor.
This vapor is then drawn away from the product and collected on an extremely cold condenser coil within the freeze-dryer, where it instantly turns back into ice. This phase is the longest, removing approximately 95% of the water from the material.
Stage 3: Secondary Drying (Adsorption)
After primary drying, a small amount of unfrozen water molecules remains bound to the surfaces of the material. The secondary drying stage is designed to remove this residual moisture.
During this final phase, the temperature is raised slightly higher and the vacuum level is often increased. This breaks the bonds between the water molecules and the material, a process known as adsorption, allowing the last traces of moisture to be removed. This step is essential for ensuring the long-term stability and shelf life of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While freeze-drying offers superior quality, it comes with practical considerations that must be weighed.
Time and Energy Consumption
Freeze-drying is a slow and methodical process. A typical cycle can take anywhere from 24 to 72 hours or more, depending on the material and volume. This long duration, combined with the energy required to maintain the vacuum and cold temperatures, makes it significantly more energy-intensive than other drying methods.
High Initial Cost
The specialized equipment required—a freeze-dryer with precise temperature controls, a deep vacuum system, and a robust condenser—represents a significant capital investment. This cost can be a barrier for smaller operations or applications where the premium quality of freeze-drying is not an absolute requirement.
The Risk of Improper Technique
The process is not foolproof. Using an incorrect freezing rate can damage cell structures, while applying too much heat during primary drying can cause the product to melt or scorch, negating the very benefits you seek to achieve. Success depends on developing a protocol tailored specifically to the material being processed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this process effectively, you must align your technique with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity (e.g., vaccines, probiotics): Emphasize precise control over the freezing rate to create an ice crystal structure that protects cellular integrity.
- If your primary focus is food texture and flavor (e.g., instant coffee, fruits): Prioritize careful heat management during primary drying to prevent scorching and preserve volatile aromatic compounds.
- If your primary focus is long-term shelf stability (e.g., pharmaceuticals, archival samples): Ensure the secondary drying phase is thorough and complete to remove all residual bound water.
Mastering these stages allows you to leverage freeze-drying not just as a preservation method, but as a tool for guaranteeing quality.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Freezing | Solidifies all water into ice crystals. | Creates the pore structure for vapor flow. |
| 2. Primary Drying | Ice sublimates to vapor under vacuum. | Removes ~95% of free water. |
| 3. Secondary Drying | Removes bound water molecules by adsorption. | Ensures long-term stability and shelf life. |
Ready to achieve superior preservation for your materials? The freeze-drying process is complex, but the right equipment makes it simple. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory freeze dryers designed for precise temperature and vacuum control, ensuring your products—from pharmaceuticals to food samples—retain their structure, potency, and quality. Contact our experts today to find the perfect lyophilization solution for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory freeze-drying system essential for fermentation biomass? Preserve Sample Integrity for Analysis
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance



















