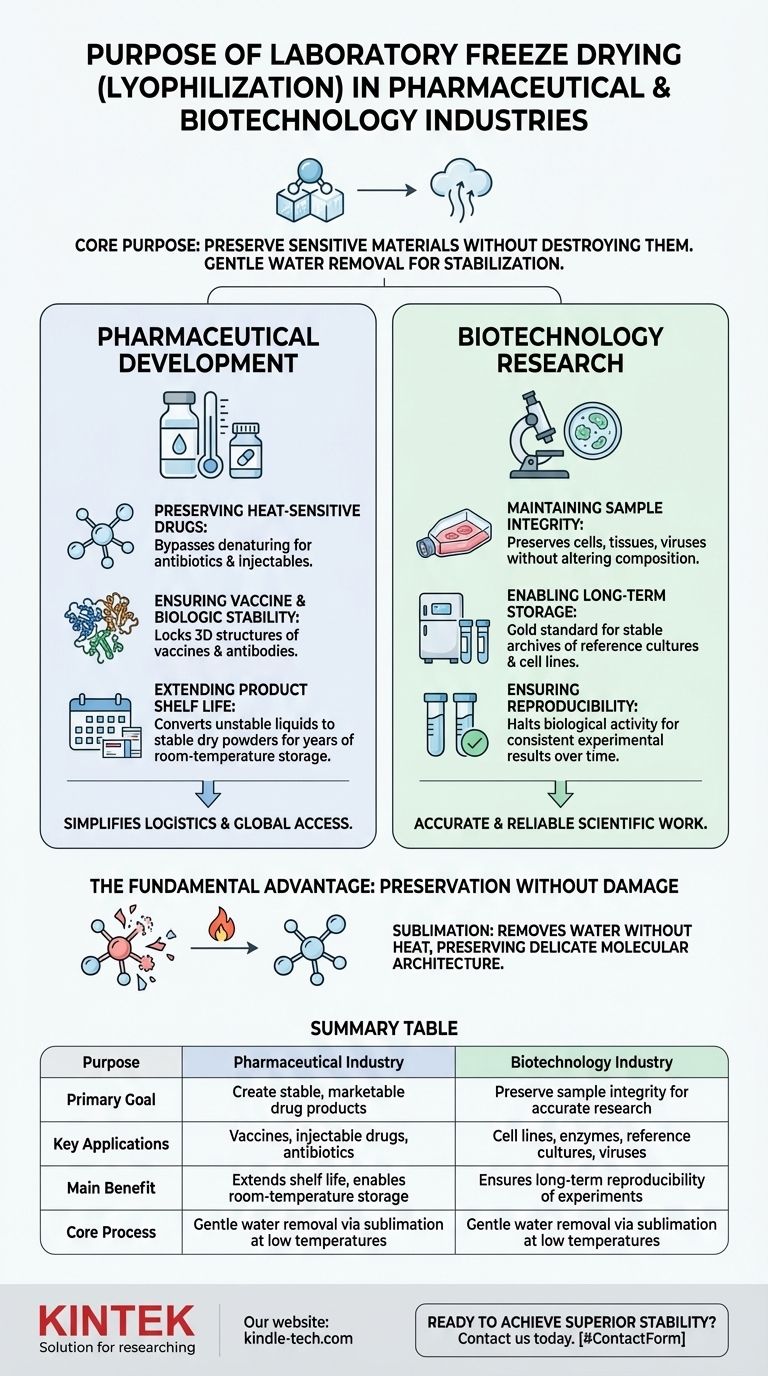
At its core, laboratory freeze drying serves one critical purpose in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries: to preserve sensitive materials without destroying them. This process, also known as lyophilization, gently removes water at low temperatures, which stabilizes delicate biological and chemical compounds, dramatically extends their shelf life, and maintains their essential properties for storage and transport.
The fundamental value of freeze drying is its ability to dehydrate heat-sensitive products like vaccines, enzymes, and cells. It ensures their structural integrity and biological activity remain intact, a feat impossible with conventional heat-based drying methods.

The Role in Pharmaceutical Development
In the pharmaceutical sector, freeze drying is not just a preservation technique; it is an enabling technology. It allows for the creation and distribution of advanced drugs that would otherwise be too unstable to exist as viable products.
Preserving Heat-Sensitive Drugs
Many modern medications, especially biologic drugs, are incredibly sensitive to heat. Applying conventional drying methods would denature them, rendering them ineffective and unsafe.
Freeze drying bypasses this issue by operating at very low temperatures and pressures. This is crucial for producing stable formulations of antibiotics, injectable drugs, and other temperature-sensitive Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API).
Ensuring Vaccine and Biologic Stability
Vaccines, enzymes, and antibodies are complex biological structures. Their effectiveness depends entirely on maintaining a precise three-dimensional shape.
Lyophilization locks this structure in place by removing water, which is often a key factor in degradation. This ensures the vaccine or biologic remains potent from the point of manufacture to the moment of administration.
Extending Product Shelf Life
Freeze drying converts unstable liquid formulations into stable, dry powders. This transformation dramatically increases the shelf life of products, allowing them to be stored for years at room temperature instead of weeks or months under refrigeration.
This stability simplifies logistics, reduces waste, and makes critical medicines accessible in regions without consistent cold-chain infrastructure.
The Role in Biotechnology and Research
For biotechnology labs, the integrity of biological samples is paramount. Freeze drying provides a reliable method for long-term storage and analysis, ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of scientific work.
Maintaining Sample Integrity
Research often relies on the analysis of cells, tissues, viruses, and bacteria. Freeze drying preserves these specimens without altering their chemical or structural composition.
This ensures that the material being studied is in the same state as when it was collected, which is essential for accurate experimental results.
Enabling Long-Term Storage
Biotechnology requires the long-term storage of reference cultures, cell lines, and other biological materials. Lyophilization is the gold standard for creating stable archives of these assets.
By halting biological activity without causing damage, freeze drying allows researchers to store valuable materials for future analysis, ensuring the reproducibility of experiments over time.
The Fundamental Advantage: Preservation Without Damage
The core challenge with many biologicals is their fragility. Traditional drying uses heat, which can break chemical bonds and destroy the very properties that make a drug or sample useful.
Freeze drying works through sublimation—turning solid ice directly into water vapor, skipping the liquid phase entirely. This gentle process removes water without the destructive force of heat, preserving the delicate molecular architecture of the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of freeze drying is tailored to the specific outcome required by each industry.
- If your primary focus is product delivery and stability (Pharmaceuticals): Freeze drying is the key to creating a marketable, stable drug or vaccine that can be stored and transported effectively.
- If your primary focus is research integrity (Biotechnology): Freeze drying is the essential tool for preserving biological samples to ensure accurate, reproducible, and reliable scientific results over the long term.
Ultimately, freeze drying empowers scientists and manufacturers to work with and distribute sensitive biological materials that would otherwise be too fragile to handle.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Pharmaceutical Industry | Biotechnology Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Create stable, marketable drug products | Preserve sample integrity for accurate research |
| Key Applications | Vaccines, injectable drugs, antibiotics | Cell lines, enzymes, reference cultures, viruses |
| Main Benefit | Extends shelf life, enables room-temperature storage | Ensures long-term reproducibility of experiments |
| Core Process | Gentle water removal via sublimation at low temperatures | Gentle water removal via sublimation at low temperatures |
Ready to achieve superior stability for your sensitive materials?
KINTEK's laboratory freeze dryers are engineered to meet the precise demands of pharmaceutical development and biotechnology research. Our solutions ensure your vital drugs, vaccines, and biological samples maintain their potency and integrity.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how we can support your specific lyophilization challenges and help you preserve what matters most.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing



















