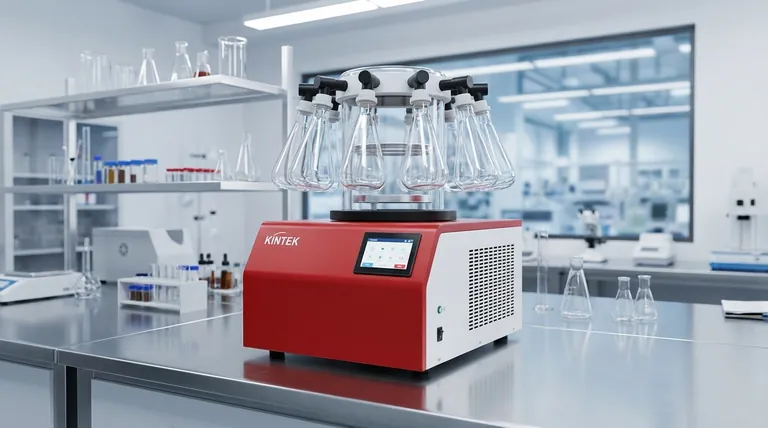
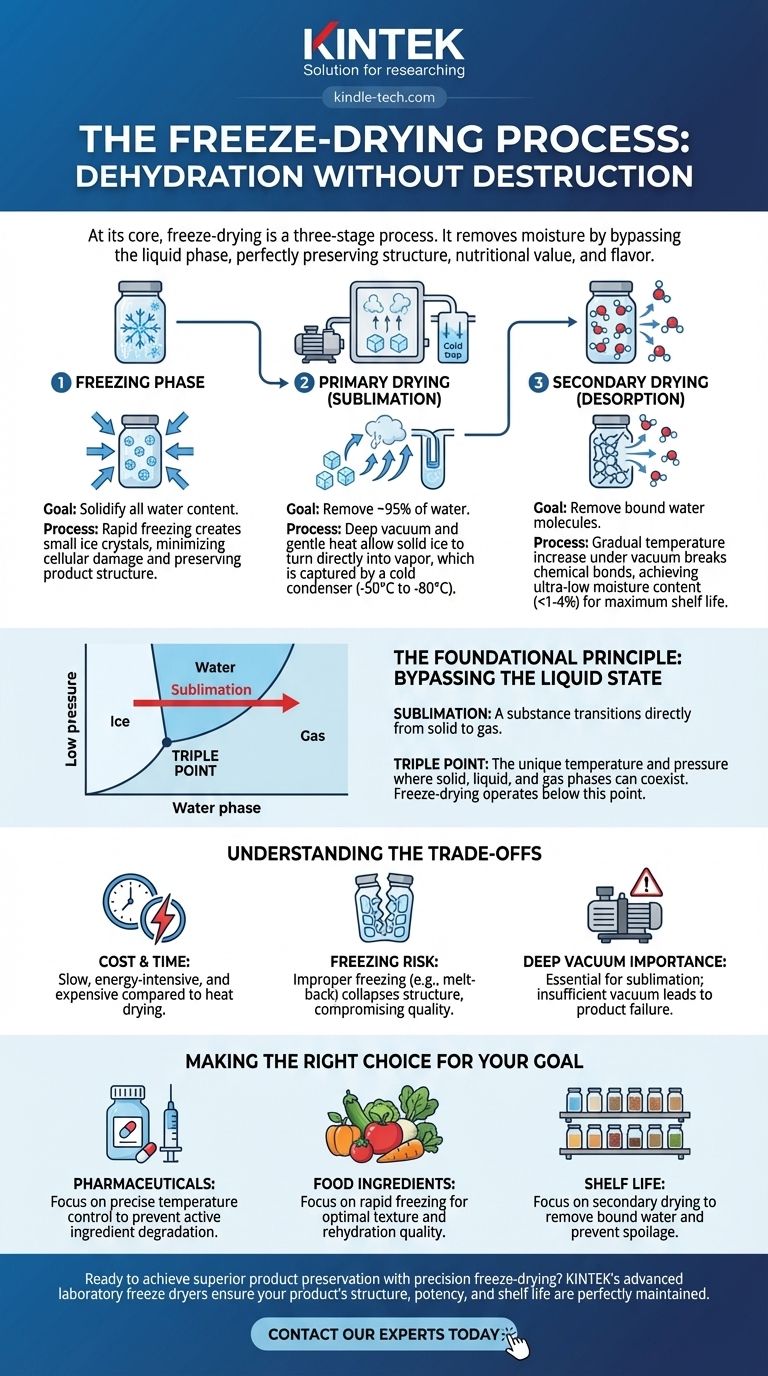
At its core, freeze-drying is a three-stage process. It begins with the Freezing Phase, where the material's water content is completely solidified. This is followed by Primary Drying, where a deep vacuum is applied to make the solid ice turn directly into vapor (sublimation). Finally, Secondary Drying removes the last traces of bound water molecules by gently raising the temperature, ensuring long-term stability.
The central principle of freeze-drying is dehydration without destruction. By skillfully manipulating temperature and pressure to bypass the liquid phase of water, the process removes moisture while perfectly preserving the product's original structure, nutritional value, and flavor.

The Foundational Principle: Bypassing the Liquid State
To truly understand freeze-drying, you must first grasp the concept of sublimation. This is the physical phenomenon where a substance transitions directly from a solid to a gas, completely skipping the liquid phase.
The Role of the "Triple Point"
Every substance has a unique temperature and pressure combination known as its triple point, where its solid, liquid, and gas phases can coexist.
By first freezing the water solid and then lowering the pressure below its triple point, we create an environment where adding a small amount of energy (heat) forces the ice to become vapor, not liquid water. This is the magic of freeze-drying.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
Each phase of the freeze-drying cycle is meticulously controlled to achieve a specific outcome, working together to produce a final product that is lightweight, stable, and high in quality.
Phase 1: The Freezing Stage
The goal of this initial phase is to convert all the water within the product into solid ice. The way this is done has a significant impact on the final product's quality.
Rapid freezing is typically preferred. This creates very small ice crystals, which cause minimal damage to the cellular structure of the material. Slow freezing creates large, disruptive crystals that can harm the texture and appearance of the final product.
Phase 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
This is the longest and most energy-intensive part of the cycle. Once the product is frozen solid, it is placed into the dryer, and a powerful vacuum pump creates a deep vacuum.
A component called a condenser (or "cold trap") is cooled to an extremely low temperature (e.g., -50°C to -80°C). Then, a small, controlled amount of heat is applied to the product shelves.
This combination of low pressure and gentle heat gives the ice molecules just enough energy to sublimate into water vapor. This vapor is immediately drawn away from the product and refrozen onto the extremely cold condenser surface, effectively removing it from the system. This stage removes roughly 95% of the water.
Phase 3: Secondary Drying (Desorption)
After all the ice has been sublimated, a small amount of water remains, chemically bound to the molecules of the product itself. Removing this water is crucial for achieving maximum shelf life.
During secondary drying, the vacuum is maintained, but the shelf temperature is gradually increased. This provides the energy needed to break the bonds holding these last water molecules, allowing them to be drawn away and captured by the condenser. The result is a product with extremely low moisture content, often less than 1-4%.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While freeze-drying offers superior results, it's essential to understand its limitations and the precision required to execute it properly.
The Cost of Quality
Freeze-drying is a slow and energy-intensive process. The equipment is expensive, and cycles can run from several hours to several days, making it significantly more costly than conventional heat-based drying methods.
The Risk of Improper Freezing
As mentioned, the freezing rate is critical. If a product is not frozen correctly or melts during the process (known as "melt-back"), its structure will collapse. This ruins the porous nature of the product, making it difficult to rehydrate and compromising its quality.
The Importance of a Deep Vacuum
The entire process hinges on maintaining a pressure level well below water's triple point. If the vacuum pump is not powerful enough or if there is a leak in the system, sublimation cannot occur efficiently. The ice will melt instead of sublimating, leading to product failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the three distinct phases allows you to appreciate why freeze-drying is chosen for specific applications and how to prioritize process parameters.
- If your primary focus is preserving sensitive pharmaceuticals or biologicals: Success depends on precise temperature control during all three phases to prevent degradation of active ingredients.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality food ingredients: Pay close attention to the initial freezing stage, as the rate of freezing directly controls the ice crystal size and, therefore, the final texture and rehydration quality.
- If your primary focus is extending shelf life: The secondary drying phase is most critical, as removing the final bound water molecules is the key to preventing chemical and biological spoilage over the long term.
By mastering the interplay of temperature and pressure, freeze-drying transforms perishable materials into stable, high-quality products that retain their most valuable characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Goal | Process Detail |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Freezing | Solidify all water content | Rapid freezing creates small ice crystals to preserve product structure. |
| 2. Primary Drying | Remove ~95% of water via sublimation | Vacuum and gentle heat turn solid ice directly into vapor, which is trapped. |
| 3. Secondary Drying | Remove bound water molecules | Increased temperature desorbs remaining water to achieve ultra-low moisture (<1-4%). |
Ready to achieve superior product preservation with precision freeze-drying?
KINTEK's advanced laboratory freeze dryers are engineered for reliability and exact control over every stage of the process—from rapid freezing to secondary drying. Whether you are preserving sensitive pharmaceuticals, high-value food ingredients, or biological samples, our equipment ensures your product's structure, potency, and shelf life are perfectly maintained.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment can meet your specific freeze-drying needs and enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures



















