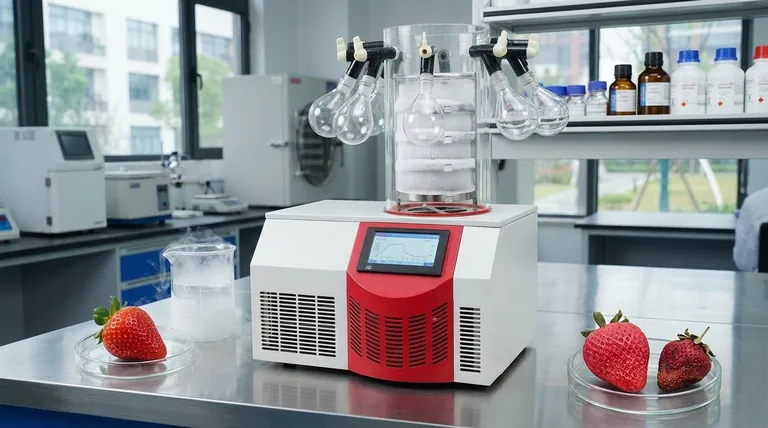
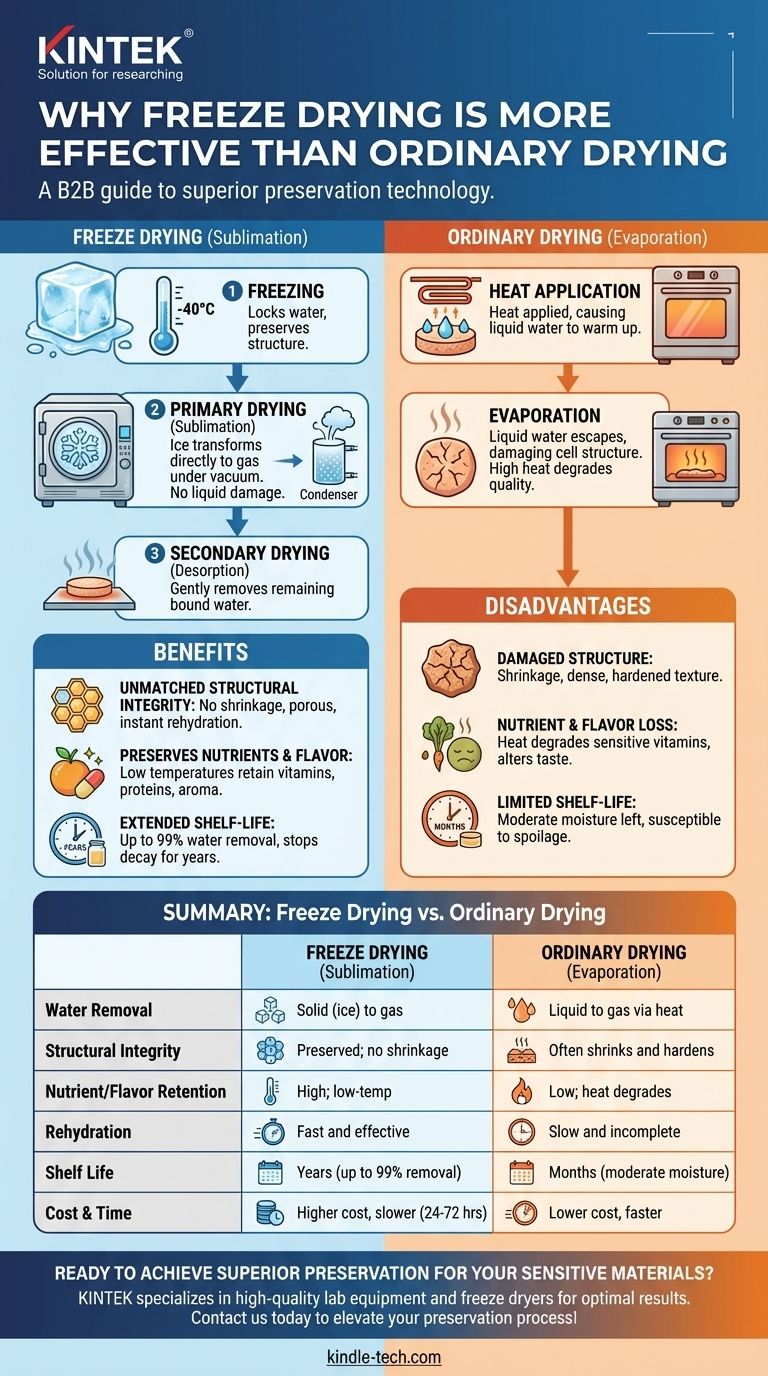
At a fundamental level, freeze drying is considered more effective than ordinary drying because it removes water by converting it from a solid (ice) directly into a gas (vapor), completely bypassing the destructive liquid phase. This process, called sublimation, preserves the product's original physical structure, chemical composition, and nutritional value in a way that conventional heat-based evaporation cannot.
While conventional drying uses heat to force liquid water out—damaging the product's structure and degrading its quality—freeze drying gently removes water from a frozen state. This fundamental difference is why freeze-dried products retain their original shape, flavor, and nutrients with unparalleled fidelity.

The Science of Preservation: Sublimation vs. Evaporation
To understand the effectiveness of freeze drying, you must first understand the core mechanisms of water removal and the impact each has on the material being dried.
How Conventional Drying Works
Conventional drying methods, such as using an oven or air dehydrator, rely on evaporation. Heat is applied to the product, causing the liquid water inside to warm up and turn into vapor.
This process is effective at removing water, but it comes at a cost. As liquid water moves through the product to escape, it can damage and collapse delicate cell structures, leading to shrinkage and a dense, hardened texture. The high heat also degrades heat-sensitive vitamins, alters flavors, and can change the product's color.
The Freeze-Drying Process: A Three-Step Journey
Freeze drying, also known as lyophilization, avoids these issues by keeping the water in a solid state throughout its removal. The process is a carefully controlled, low-temperature, low-pressure operation.
Step 1: Freezing
The product is first frozen solid, typically at very low temperatures (e.g., -40°C or colder). This step is critical because it locks the water molecules in place, preserving the product's physical structure before the drying begins.
Step 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
The frozen product is then placed under a deep vacuum. A small, controlled amount of heat is slowly introduced, providing just enough energy for the ice crystals to transform directly into water vapor.
This is sublimation. Because the water never becomes a liquid, the rigid structure of the frozen product remains intact. The water vapor is then drawn away and collected on an extremely cold condenser coil, turning back into ice.
Step 3: Secondary Drying (Desorption)
After the primary sublimation phase removes most of the ice, some water molecules remain bound to the product's surface. The temperature is gently raised further, still under vacuum, to break these bonds and remove the last traces of moisture.
The Tangible Benefits of Superior Preservation
The unique mechanism of sublimation translates directly into superior results across several key metrics.
Unmatched Structural and Textural Integrity
Because freeze drying preserves the product's cellular network, it does not shrink or toughen. The final product is highly porous and lightweight, retaining its original size and shape.
This porous structure allows for near-instantaneous rehydration. When water is added, it quickly fills the microscopic voids left behind by the sublimated ice crystals, returning the product to a state remarkably close to its fresh form.
Preservation of Nutrients and Flavor
The low temperatures used throughout the freeze-drying process minimize chemical reactions and degradation.
Heat-sensitive components like vitamins, proteins, and beneficial enzymes are largely retained. Volatile compounds responsible for aroma and flavor also remain, resulting in a product that tastes significantly better and is more nutritious than one dried with high heat.
Extended Shelf-Life Without Preservatives
By removing up to 99% of the water, freeze drying effectively halts the two main causes of decay: microbial growth (bacteria, mold) and enzymatic degradation.
When stored in an airtight, moisture-proof container, freeze-dried products can have a shelf life of many years, far exceeding that of conventionally dried goods, without requiring any chemical preservatives.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its clear advantages in quality, freeze drying is not the optimal choice for every situation. Its effectiveness comes with significant trade-offs.
The Cost of Quality: Time and Energy
Freeze drying is a slow, batch-based process. A typical cycle can take anywhere from 24 to 72 hours or longer, depending on the product and equipment.
The required machinery—powerful refrigeration systems and high-capacity vacuum pumps—is expensive to purchase and operate. This high energy consumption and long processing time are the primary reasons why freeze-dried products are significantly more expensive than their conventionally dried counterparts.
Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
The process must be carefully tailored to the specific product. Different materials require different freezing rates, vacuum levels, and temperature profiles to achieve optimal results without damaging the product.
While versatile, the method is best suited for high-value materials where the preservation of structure and biological activity is the highest priority, such as pharmaceuticals, lab samples, and premium food ingredients.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the "better" method depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is preserving high-value, sensitive materials: Freeze drying is the gold standard for pharmaceuticals, biological samples, and gourmet foods where quality is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is bulk reduction and moderate shelf-life: Conventional dehydration is a much more cost-effective and faster solution for many common foods like jerky or fruit leathers where some textural change is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is achieving the longest possible shelf-life with near-perfect rehydration: Freeze drying is unparalleled for creating emergency food supplies and ingredients that must perform like fresh.
Understanding the core mechanism of water removal—sublimation versus evaporation—is the key to selecting the right preservation technology for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Freeze Drying (Sublimation) | Ordinary Drying (Evaporation) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Removal | Solid (ice) to gas (vapor) | Liquid to gas via heat |
| Structural Integrity | Preserved; no shrinkage | Often shrinks and hardens |
| Nutrient/Flavor Retention | High; low-temperature process | Low; heat degrades components |
| Rehydration | Fast and effective | Slow and incomplete |
| Shelf Life | Years (up to 99% water removed) | Months (moderate moisture left) |
| Cost & Time | Higher cost, slower (24-72 hours) | Lower cost, faster |
Ready to achieve superior preservation for your sensitive materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including freeze dryers designed to preserve the structural integrity, nutritional value, and shelf life of your pharmaceuticals, biological samples, and premium food ingredients. Our solutions ensure precise temperature control and efficient sublimation for optimal results.
Contact us today to find the perfect freeze-drying system for your laboratory needs and elevate your preservation process!
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What are the key reasons to use a freeze dryer in laboratories? Preserve Sample Integrity for Reliable Research
- What makes freeze-dried products advantageous for transport? Drastically Reduce Shipping Costs & Simplify Logistics
- How does laboratory freeze drying work to preserve biological products? The Ultimate Guide to Lyophilization
- How are freeze dryers used in the pharmaceutical industry? Extend Drug Shelf Life & Stability
- What are amorphous materials in freeze drying? The Key to Preventing Product Collapse



















