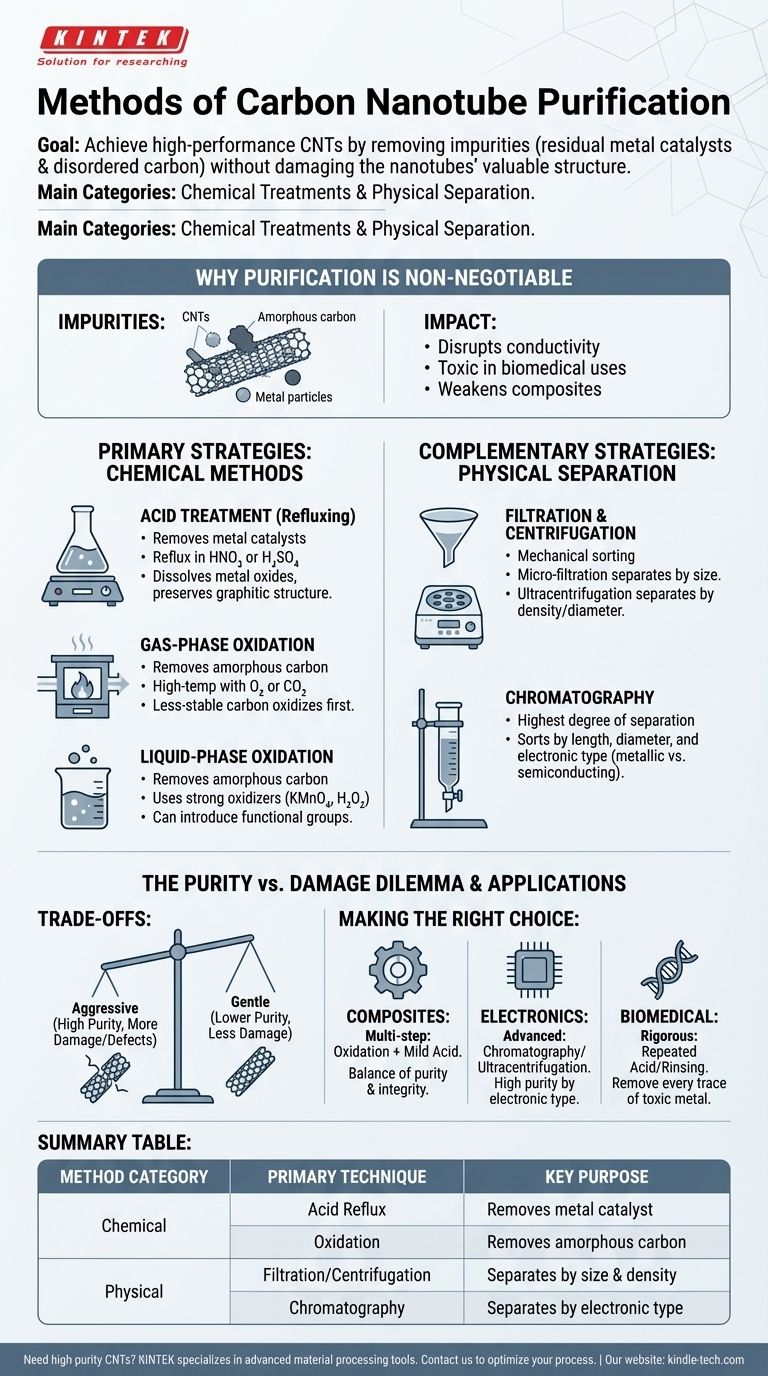
To achieve high-performance results with carbon nanotubes (CNTs), a purification step is almost always required. As-synthesized CNTs are contaminated with residual metal catalysts and non-nanotube carbon forms, which must be removed. The primary methods for purification fall into two main categories: chemical treatments that selectively attack impurities, and physical separation techniques that sort materials based on their physical properties.
The central challenge of CNT purification is not merely the removal of impurities, but doing so without introducing significant damage to the nanotubes' valuable atomic structure. Therefore, the choice of method is a critical trade-off between achieving high purity and preserving the inherent properties of the CNTs.

Why Purification is a Non-Negotiable Step
Before exploring the methods, it's essential to understand what needs to be removed and why. The raw output from any synthesis process is a heterogeneous mix that compromises the final material's performance.
The Problem of Impurities
As-synthesized CNTs are typically contaminated with two main types of materials: residual metal catalysts (like iron, cobalt, or nickel) used to grow the tubes, and other forms of disordered carbon (such as amorphous carbon or fullerenes).
Impact on Performance
These impurities can severely degrade the exceptional properties of CNTs. Metal particles disrupt electrical and thermal conductivity and can be toxic in biomedical applications. Amorphous carbon acts as an insulating barrier and a point of mechanical failure in composites.
Primary Purification Strategies: Chemical Methods
Chemical methods are the most common approach for bulk purification. They leverage the different chemical reactivities of CNTs versus the impurities.
Acid Treatment (Refluxing)
This is the most widely used technique for removing metallic catalyst particles. It involves refluxing the raw CNT material in strong acids, such as nitric acid (HNO₃) or sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), which dissolve the metal oxides without significantly affecting the graphitic CNT structure.
Gas-Phase Oxidation
To remove amorphous carbon, high-temperature oxidation is often employed. The material is heated in the presence of a gas like air, oxygen (O₂), or carbon dioxide (CO₂). The less-stable, disordered carbon oxidizes and burns off at a lower temperature than the more crystalline CNTs.
Liquid-Phase Oxidation
This approach uses strong oxidizing agents in a solution to attack amorphous carbon. Common agents include potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) or hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂). This method can also introduce functional groups onto the CNT surface.
Complementary Strategies: Physical Separation
Physical methods are often used in combination with chemical treatments to further refine the CNTs or to separate them based on their specific characteristics.
Filtration and Centrifugation
These are straightforward mechanical techniques. Micro-filtration can separate CNTs from larger particulate impurities. Ultracentrifugation, particularly density gradient ultracentrifugation, can separate CNTs based on their density, which correlates with their diameter or wall number.
Chromatography
For highly specialized applications, chromatography offers the highest degree of separation. This technique can sort CNTs by their length, diameter, and even their electronic type (separating metallic from semiconducting tubes), which is critical for electronics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a purification method is a balancing act. An aggressive approach may yield high purity but at the cost of the very properties you seek to leverage.
The Purity vs. Damage Dilemma
The primary trade-off is between removing impurities and damaging the CNTs. Harsh acid treatments or high-temperature oxidation can introduce defects (like holes or functional groups) into the nanotube walls, which can degrade their mechanical strength and electrical conductivity.
Scalability and Cost
Simple, one-pot methods like acid reflux are relatively inexpensive and easy to scale for industrial production. In contrast, advanced techniques like chromatography are complex, low-yield, and far too costly for anything other than high-value research or microelectronic applications.
Multi-Step Necessity
No single method is perfect. Effective purification almost always requires a multi-step process. A typical sequence might involve gas-phase oxidation to remove amorphous carbon, followed by an acid wash to dissolve catalyst particles, and a final filtration step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal purification strategy is dictated entirely by the end-use of the carbon nanotubes.
- If your primary focus is bulk composite materials: A cost-effective, multi-step process combining oxidation and a mild acid wash often provides the best balance of purity and preserved mechanical integrity.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: Advanced, less-damaging techniques like chromatography or ultracentrifugation are necessary to achieve the required purity and separation by electronic type.
- If your primary focus is biomedical applications: Rigorous and repeated purification is paramount to remove every trace of toxic metal catalyst, often involving multiple acid treatments and extensive rinsing.
Ultimately, the optimal purification strategy is the one that achieves the necessary purity level while preserving the critical properties required for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Method Category | Primary Technique | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Acid Reflux (HNO₃, H₂SO₄) | Removes metal catalyst particles |
| Chemical | Gas/Liquid-Phase Oxidation | Removes amorphous carbon |
| Physical | Filtration & Centrifugation | Separates by size and density |
| Physical | Chromatography | Separates by electronic type (metallic/semiconducting) |
Need high-purity carbon nanotubes for your research or product development? The right purification strategy is critical for performance. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing. Our experts can help you select the right tools to achieve the purity level your application demands while preserving the valuable properties of your CNTs. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and optimize your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the cons of sputtering? Key Limitations in Thin Film Deposition
- What are the steps of MOCVD process? A Guide to High-Quality Semiconductor Film Growth
- How are high-temperature reaction furnaces used in the coating of regenerated graphite for improved anode performance?
- What is the atmospheric pressure CVD process? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What are the examples of CVD techniques? Compare APCVD, LPCVD, PECVD, and MOCVD
- What is deposition gas examples? Discover Key Gases That Turn Directly to Solid
- What are the benefits of physical vapour deposition? Achieve Superior Thin Film Coatings
- What is the difference between PVD and CVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















