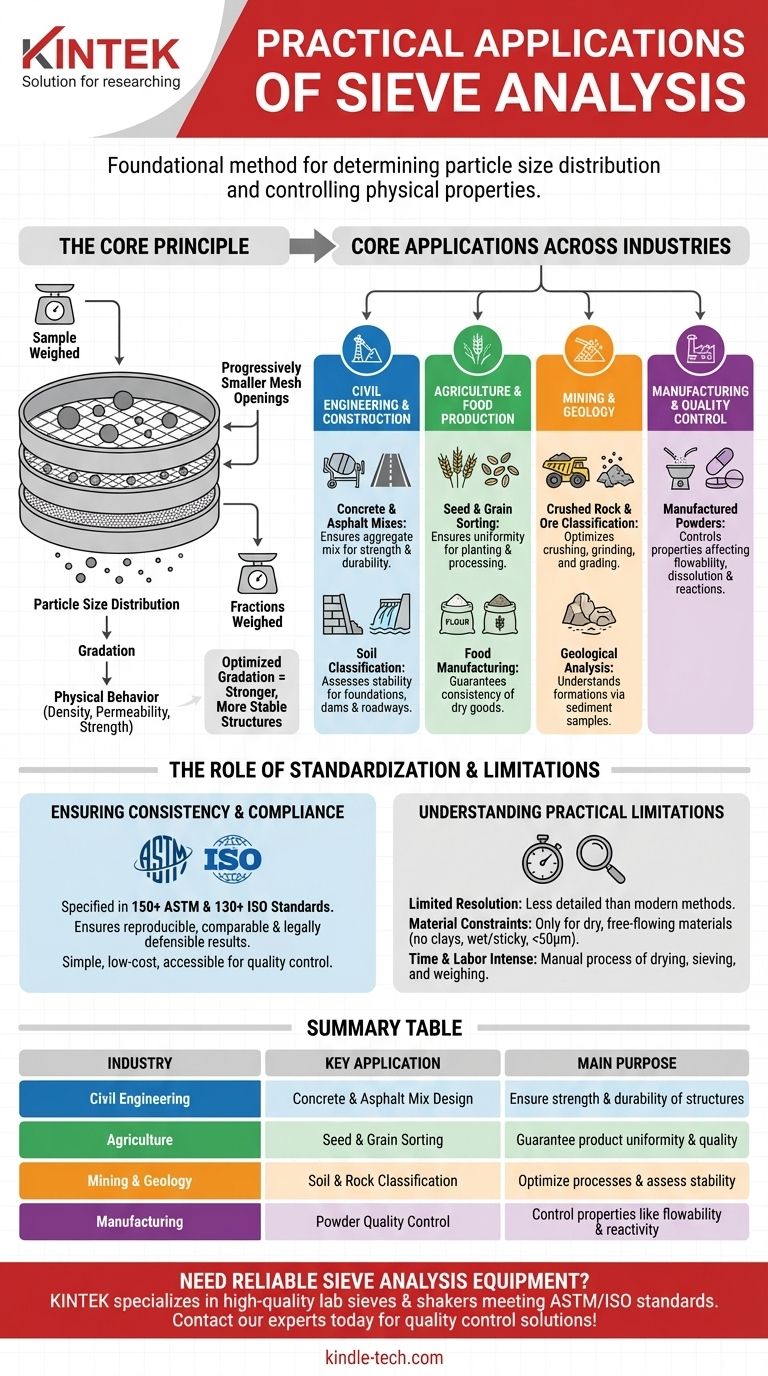
In practice, sieve analysis is the foundational method for determining the particle size distribution of granular materials. Its primary applications are in civil engineering to design durable concrete and asphalt mixes, in agriculture for sorting grains and seeds, and in geology to classify soils and rock aggregates. This simple, low-cost test provides the critical data needed to ensure materials meet the physical specifications required for their intended purpose.
Sieve analysis is not simply about measuring particles; it's about controlling a material's physical properties. The results directly inform decisions that guarantee the quality, safety, and performance of everything from highways and buildings to manufactured powders and food products.

Why Particle Size Distribution is a Critical Metric
The way particles of different sizes are mixed together—known as gradation—dictates the physical behavior of a bulk material. Sieve analysis is the classic, reliable method for quantifying this characteristic.
The Core Principle of Sieve Analysis
The process involves passing a weighed sample of material through a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings. Each sieve retains particles larger than its openings, effectively sorting the sample into different size fractions. By weighing the material left on each sieve, you can build a precise picture of the particle size distribution.
Linking Physical Properties to Performance
The mix of particle sizes determines critical properties like density, permeability, and strength. A well-graded material, with a good mix of large, medium, and small particles, will compact tightly, leaving fewer voids. This creates stronger, more stable structures, which is essential in construction materials.
Core Applications Across Major Industries
Sieve analysis is a cornerstone test because its results have direct and significant consequences on product quality and safety across numerous sectors.
Civil Engineering and Construction
This is the most common application. The strength and durability of concrete and asphalt depend entirely on the gradation of the sand and crushed rock (aggregates) used. Sieve analysis ensures the aggregate mix will pack correctly to minimize voids and create a strong, long-lasting final product.
It is also used in geotechnical engineering to classify soils. This information helps determine a soil's stability and suitability for building foundations, dams, and roadways.
Agriculture and Food Production
In agriculture, sieve analysis is used for quality control by sorting seeds and grains by size. This ensures uniformity for planting and processing. In food manufacturing, it guarantees the consistency of dry goods like flour, sugar, and spices.
Mining and Geology
The mining industry uses sieve analysis to classify crushed rock and ores. This is essential for optimizing crushing and grinding processes and for grading materials for sale. Geologists use it to analyze sediment samples and understand geological formations.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Many industrial processes rely on manufactured powders. Sieve analysis helps control the properties of these powders, which is critical in industries like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and metallurgy where particle size can affect dissolution rates, flowability, and chemical reactions.
The Critical Role of Standardization
The value of sieve analysis is magnified by its widespread standardization, making it a universally accepted and reliable testing method.
Ensuring Consistency and Compliance
Sieve analysis is specified in over 150 ASTM standards and over 130 ISO standards. These documents dictate the exact procedure, including sample size, sieving time, and acceptance criteria. Following these standards ensures that results are reproducible, comparable, and legally defensible for contractual or regulatory purposes.
A Reliable and Accessible Method
One of the key reasons for its widespread adoption is its simplicity and low cost. The equipment is inexpensive, the procedure is easy to learn, and the results are consistently accurate when performed correctly. This accessibility makes it a practical choice for quality control labs everywhere.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
While powerful, sieve analysis is not a universal solution. Understanding its trade-offs is key to using it appropriately.
Limited Resolution
A standard sieve stack typically uses a maximum of eight sieves. This means the resulting particle size distribution curve is based on a limited number of data points, offering a less detailed picture than modern methods like laser diffraction.
Material and Size Constraints
The method is only effective for dry, free-flowing granular materials. It cannot be used for clays that clump, materials that are wet or sticky, or particles that are electrostatically charged. Furthermore, standard sieving has a practical lower limit of around 50 micrometers (µm).
Time and Labor Intensity
The process of drying a sample, weighing, sieving (which can take considerable time on a shaker), and re-weighing each fraction is a manual and time-consuming task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sieve analysis is a tool, and its application should be guided by your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control in construction: Use sieve analysis to verify that your aggregates meet the specified gradation for concrete or asphalt mix designs.
- If your primary focus is agricultural grading: Employ sieves to sort products like seeds or grains by size, ensuring product uniformity and meeting quality standards.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance: Follow the exact ASTM or ISO standard method for your material to ensure your results are certifiable and contractually sound.
Ultimately, sieve analysis provides the essential data needed to control the physical properties of granular materials, turning them into reliable, predictable, and safe products.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Application | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Civil Engineering | Concrete & Asphalt Mix Design | Ensure strength & durability of structures |
| Agriculture | Seed & Grain Sorting | Guarantee product uniformity & quality |
| Mining & Geology | Soil & Rock Classification | Optimize processes & assess stability |
| Manufacturing | Powder Quality Control | Control properties like flowability & reactivity |
Need reliable sieve analysis equipment for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and shakers to ensure your particle size analysis meets ASTM and ISO standards. Whether you're in construction, agriculture, or manufacturing, our equipment delivers the accuracy you need for quality control and compliance.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieve analysis solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of the sieve method? Limitations in Accuracy and Efficiency
- How does the use of a 150 mesh sieve benefit polyimide precursor powders? Enhance Foam Structural Integrity
- What are the steps in sieving method? A Guide to Accurate Particle Size Separation
- What is the function of a sieve in a laboratory? Master Particle Size Analysis for Quality Control
- What is the function of stainless steel test sieves? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What is the purpose of using a 200-mesh sieve prior to the component analysis of biomass? Enhance Purity & Protect HPLC
- What determines the size of the sieve? A Guide to Industry Standards & Material Properties
- Why sieve analysis test is important for soils? Unlock Your Soil's Engineering Potential



















