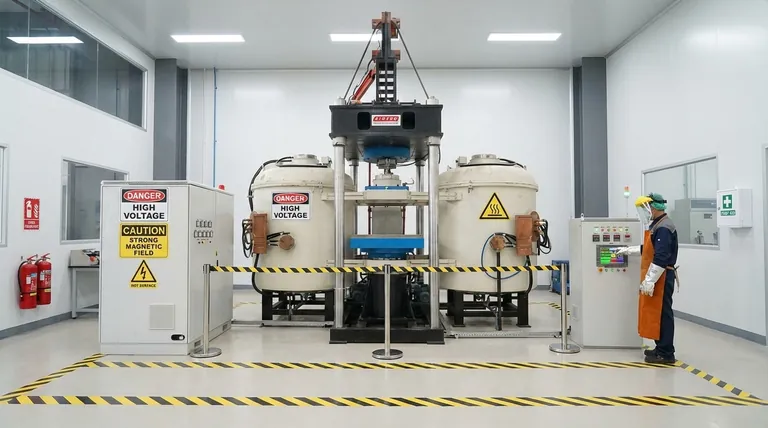
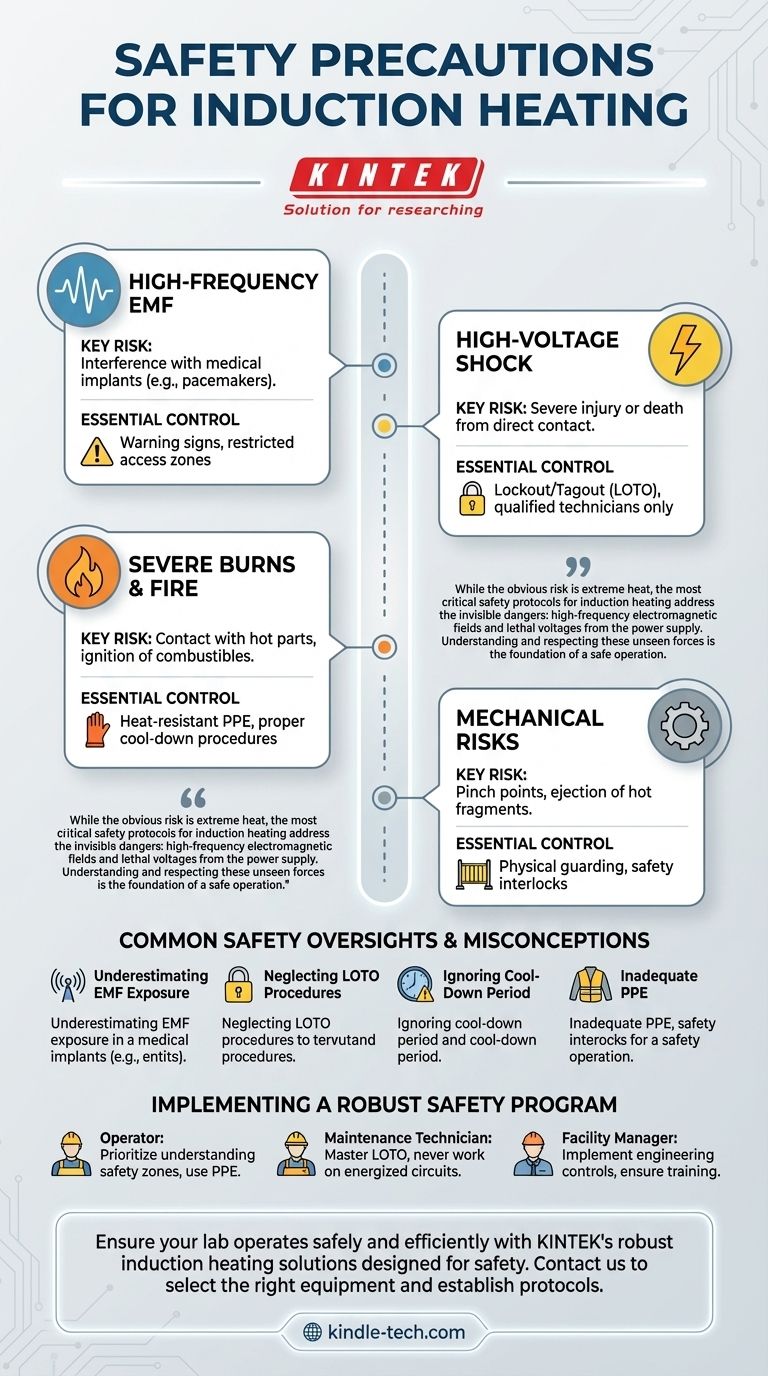
To operate induction heating systems safely, you must implement protections against its four primary hazards: high-frequency electromagnetic fields (EMF), high-voltage electrical shock, severe thermal burns, and mechanical risks. Effectively managing these requires a combination of engineering controls like shielding and interlocks, administrative controls like training and defined procedures, and the consistent use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
While the obvious risk is extreme heat, the most critical safety protocols for induction heating address the invisible dangers: high-frequency electromagnetic fields and lethal voltages from the power supply. Understanding and respecting these unseen forces is the foundation of a safe operation.

Deconstructing the Core Hazards
Induction heating is a highly efficient process, but its underlying principles create specific and serious risks. A comprehensive safety plan must address each one individually.
High-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields (EMF)
The very physics that makes induction heating work—a strong, alternating magnetic field—is a primary safety concern. This field extends into the area around the induction coil.
The most acute danger is to personnel with active medical implants, such as pacemakers or insulin pumps. The EMF can interfere with or completely disable these life-sustaining devices, creating a medical emergency.
For this reason, clear warning signs and restricted access zones are non-negotiable. All personnel and visitors must be made aware of this risk before entering the area.
High-Voltage Electrical Shock
Induction heaters require a high-power electrical supply to generate the strong magnetic fields. The power supply, transmission lines, and the coil itself operate at lethal voltages and currents.
Direct contact with any energized component can cause severe injury or instant death. Cabinet doors must have safety interlocks that de-energize the system when opened.
Only qualified and authorized technicians should ever perform maintenance or repair. Standard electrical safety protocols, especially Lockout/Tagout (LOTO), are mandatory before any service work begins.
Severe Burns and Fire Risk
The intended output of the process is intense heat, which is also a significant hazard. Workpieces can reach hundreds or thousands of degrees in mere seconds.
Accidental contact with a heated part, the induction coil, or adjacent fixtures can cause deep and severe thermal burns. Even after the power is off, the workpiece remains dangerously hot for a significant cool-down period.
Furthermore, the intense radiant heat can ignite any nearby combustible materials, such as oily rags, cardboard, or wooden structures, creating a substantial fire risk.
Mechanical and Ancillary Risks
Many induction systems are integrated into automated production lines, introducing mechanical hazards like pinch points from robotic arms or conveyor systems.
In the event of a workpiece failing under thermal stress, there is also a risk of hot metal fragments being ejected at high velocity.
Common Safety Oversights and Misconceptions
Complacency is the greatest threat in any industrial environment. With induction heating, this often manifests in overlooking the less obvious dangers.
Underestimating EMF Exposure
Because you cannot see or feel the magnetic field, it is easy to become complacent about its presence. The "it won't affect me" mindset is dangerous.
Safety zones must be strictly enforced. Personnel with medical implants must be prohibited from the area entirely, without exception.
Neglecting Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures
Failing to properly de-energize and lock out the power supply before service is a leading cause of electrical fatalities.
Simply turning a switch to the "off" position is not sufficient. The energy source must be physically isolated and locked to prevent accidental re-energization while a technician is working on the equipment.
Ignoring the "Cool-Down" Period
A workpiece that is no longer glowing red can still be hot enough to cause a third-degree burn instantly.
Operators must be trained to respect the required cool-down time and always handle recently heated parts with appropriate thermal gloves and tongs.
Inadequate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Standard work gloves offer zero protection from the extreme temperatures involved. Similarly, everyday safety glasses may not be adequate for the potential impact from a fractured workpiece.
PPE must be selected specifically for the hazards present: heat-resistant gloves, aprons, and face shields are often necessary, in addition to standard safety glasses.
Implementing a Robust Safety Program
Your safety strategy should be tailored to your specific role and environment. The goal is to create multiple layers of protection.
- If your primary focus is as an operator: Prioritize understanding safety zones, consistently using your assigned PPE, and never bypassing a safety guard or interlock.
- If your primary focus is as a maintenance technician: Master the LOTO procedure and never work on an energized circuit; you must be formally qualified to service the specific equipment.
- If your primary focus is as a facility manager or designer: Implement engineering controls like physical guarding and EMF shielding, enforce strict access control, and ensure comprehensive training for all personnel.
A systematic approach to safety transforms induction heating from a potential hazard into a powerful and predictable manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Hazard | Key Risk | Essential Control |
|---|---|---|
| High-Frequency EMF | Interference with medical implants | Warning signs, restricted access zones |
| High-Voltage Shock | Severe injury or death from contact | Lockout/Tagout (LOTO), qualified technicians only |
| Severe Burns & Fire | Contact with hot parts, ignition of combustibles | Heat-resistant PPE, proper cool-down procedures |
| Mechanical Risks | Pinch points, ejection of hot fragments | Physical guarding, safety interlocks |
Ensure your lab operates safely and efficiently. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, offering robust induction heating solutions designed with safety as a priority. Our experts can help you select the right equipment and establish the necessary safety protocols for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your lab's needs and how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- Why is high-precision temperature control at 630°C necessary for Al-Sc vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Alloy Stability
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- How does a high-precision temperature control heating system facilitate the study of stainless steel corrosion?
- Why is a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace required for Ni-Cr-Co-Ti-V alloys? Achieve High Density & Purity

















