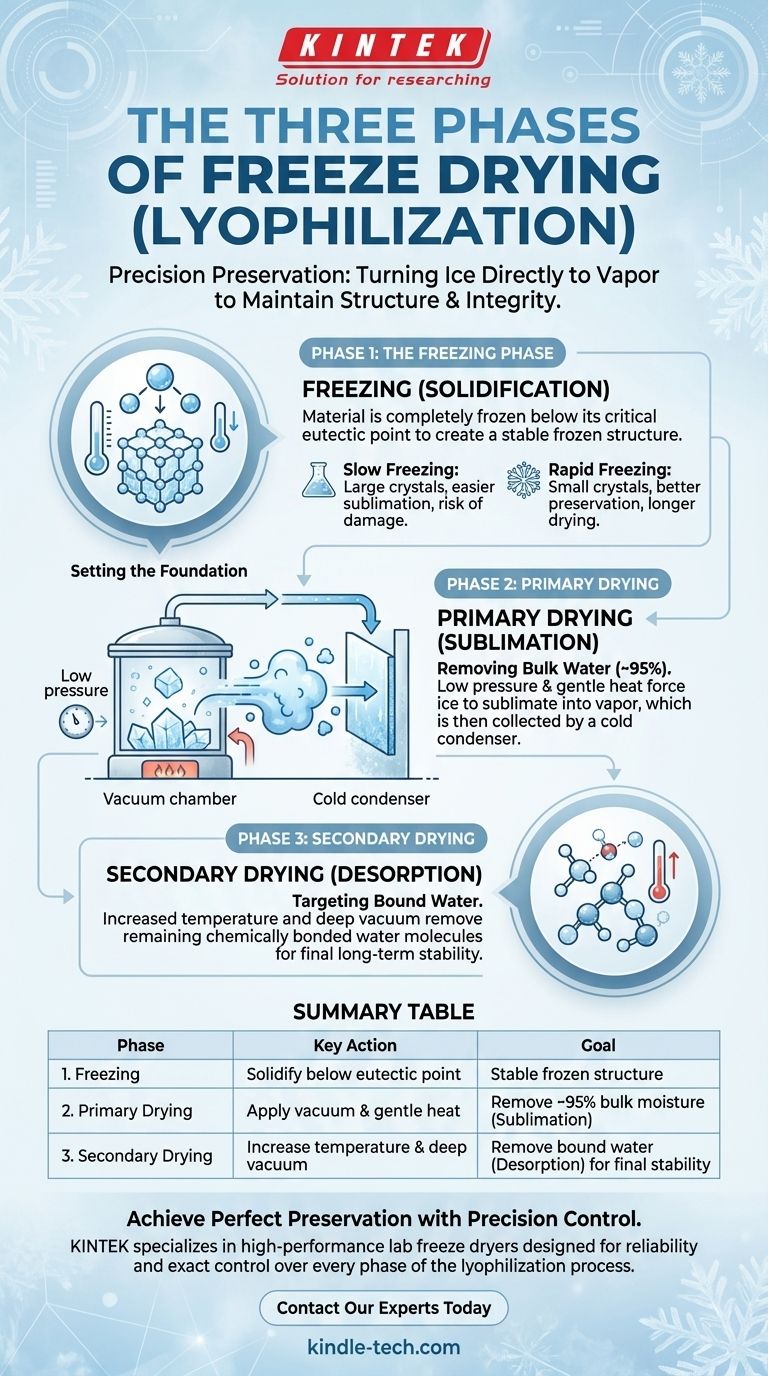
The process of freeze drying, or lyophilization, is a precise preservation technique executed in three distinct phases. These are the Freezing Phase, where the material is solidified; the Primary Drying Phase, where frozen water is removed through sublimation; and the Secondary Drying Phase, where remaining bound water molecules are removed to ensure final stability.
Freeze drying is not simply freezing and then drying. It is a controlled, three-stage process that leverages the principle of sublimation—turning ice directly into vapor—to remove water while perfectly preserving the material's original structure and chemical integrity.

How Freeze Drying Works: The Science of Preservation
The Goal: Bypassing the Liquid Phase
The fundamental goal of freeze drying is to dry a material without ever letting the water pass through its liquid phase.
Liquid water is the primary enabler of microbial growth and the chemical reactions that cause degradation. By removing it, you can achieve remarkable long-term preservation.
The Key Concept: Sublimation
Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from a solid to a gas, skipping the liquid state entirely.
Freeze drying manipulates temperature and pressure to force the solid ice in a product to sublimate into water vapor, which is then removed. This is why the physical structure of the original material remains intact.
Phase 1: The Freezing Phase
Setting the Foundation
This initial phase is the most critical step in the entire process. The material must be cooled until it is completely frozen, well below a critical temperature known as its triple point or eutectic point.
Failing to freeze the material adequately will cause it to melt instead of sublimate during the drying phase, destroying the product's structure.
The Importance of Freezing Speed
The rate of freezing determines the size of the ice crystals that form.
Slow freezing creates large ice crystals, which are easier to sublimate but can damage delicate cellular structures. Rapid freezing creates small ice crystals that better preserve cell walls but make the subsequent drying phases longer. The correct method depends entirely on the product being preserved.
Phase 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
Removing the Bulk Water
Once the product is properly frozen, the pressure inside the freeze dryer chamber is dramatically lowered to create a deep vacuum. Then, a small, controlled amount of heat is applied.
This combination of low pressure and gentle heat gives the frozen water molecules enough energy to sublimate directly into vapor. This phase removes approximately 95% of the water content.
The Role of the Vacuum and Condenser
The vacuum pump in a freeze dryer not only reduces the pressure but also helps pull the water vapor away from the product.
This vapor is then collected and re-frozen onto an extremely cold surface within the machine called the condenser, effectively trapping it and preventing it from re-entering the product chamber.
Phase 3: Secondary Drying (Desorption)
Targeting Bound Water
After primary drying, a small amount of "bound" water remains, with molecules chemically adhered to the product itself.
This phase targets this stubborn residual moisture, which can still compromise long-term stability if not removed.
Achieving Final Stability
To remove the bound water, the temperature is raised slightly higher than in the primary phase, and the vacuum is often pulled even deeper.
This gives the remaining water molecules enough energy to break their bonds and leave the product, a process known as desorption. The result is a product with extremely low moisture content, ready for long-term, shelf-stable storage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
The Risk of Collapse or "Melt-Back"
The single biggest risk during drying is providing too much heat. If the product temperature rises above its critical eutectic point, the frozen structure will melt and collapse.
This "melt-back" is irreversible and results in a failed batch with poor structure and compromised stability.
The Slow and Energy-Intensive Nature
While highly effective, freeze drying is a slow process, often taking days to complete.
The combination of deep vacuum and temperature control also makes it significantly more energy-intensive and expensive than other dehydration methods. This is a primary trade-off for its superior preservation quality.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding these phases allows for the precise control needed to achieve a specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is preserving delicate biological structures: You must master the freezing phase, likely using rapid freezing to create small, non-damaging ice crystals.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and speed: You must optimize the heat input during primary drying to the absolute maximum without causing melt-back.
- If your primary focus is maximum long-term shelf stability: You must ensure the secondary drying phase is run to completion to remove all residual bound water.
By controlling the physics of each phase, you can transform a wet, perishable material into a perfectly preserved, shelf-stable product.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Action | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Freezing | Solidify material below its eutectic point | Create a stable frozen structure for sublimation |
| 2. Primary Drying | Apply vacuum & gentle heat for sublimation | Remove ~95% of frozen water (bulk moisture) |
| 3. Secondary Drying | Increase temperature for desorption | Remove bound water molecules for final stability |
Ready to achieve perfect preservation for your samples?
Understanding the three phases of freeze drying is the first step. Implementing them with precision requires the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab freeze dryers designed for reliability and exact control over every phase of the lyophilization process. Whether you are preserving delicate biologicals, pharmaceuticals, or food products, our solutions help you maximize shelf life and maintain structural integrity.
Contact our experts today to find the ideal freeze drying system for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Does THC evaporate over time? The Truth About Potency Loss and Preservation
- What is the principle behind the process of extraction? Mastering Selective Solubility for Efficient Separation
- What role do freeze dryers play in biotechnology and research? Ensure Sample Integrity and Reproducibility
- What are the three main stages of the freeze-drying process? Master Sublimation and Desorption
- What are the primary benefits of using a lab freeze dryer in pharmaceutical applications? Enhance Drug Stability and Shelf Life



















