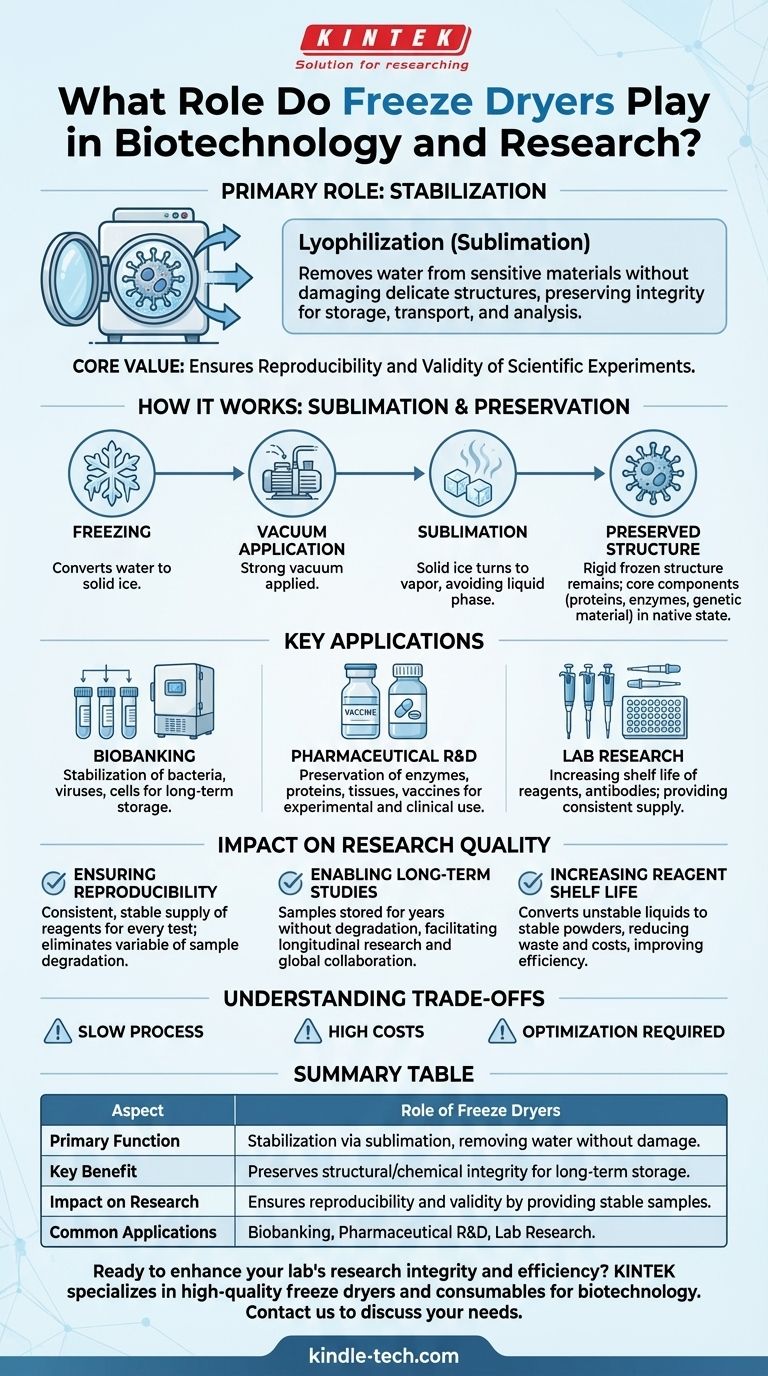
In biotechnology and research, the primary role of a freeze dryer is stabilization. This process, known as lyophilization, removes water from sensitive biological materials without damaging their delicate structures. By doing so, it preserves samples like cells, enzymes, and vaccines, ensuring their integrity for long-term storage, transport, and analysis.
The core value of freeze-drying extends beyond simple preservation. By maintaining the unaltered structural and chemical composition of a sample, it directly underpins the reproducibility and validity of scientific experiments, which is the foundation of credible research.

How Freeze-Drying Preserves Sample Integrity
Freeze-drying is not merely dehydration; it is a carefully controlled process designed to protect fragile biological structures that would be destroyed by conventional heating or air-drying methods.
The Principle of Sublimation
The process begins by freezing the material, converting all its water into ice. A strong vacuum is then applied, causing the ice to turn directly into vapor without first melting into a liquid.
This transition from solid to gas, called sublimation, is the key. It allows water to be removed while the rigid, frozen structure of the sample remains intact, preventing the collapse and damage that occurs when liquid water moves through and out of a cell.
Preserving Structural and Chemical Composition
Because sublimation avoids the destructive force of liquid water, the sample's core components—its proteins, enzymes, and genetic material—remain in their native state.
This ensures that a sample reconstituted months or years later is functionally identical to the original. The structural and chemical composition is left almost completely unaltered.
Key Applications in Biotechnology
Freeze-drying is essential for a wide range of sensitive materials common in research and development.
This includes the stabilization of bacteria, viruses, and cells for biobanking, as well as the preservation of enzymes, proteins, tissues, and vaccines for both experimental use and pharmaceutical formulation.
The Impact on Research Quality
The ability to perfectly preserve a sample has profound implications for the quality and reliability of scientific work. It removes variables that could otherwise compromise research findings.
Ensuring Experimental Reproducibility
Scientific discovery depends on reproducibility. Freeze-drying provides a consistent, stable supply of biological reagents and specimens for experiments.
By using identical starting materials for every test, researchers can be confident that observed differences are due to their experimental variables, not to the degradation of their samples.
Enabling Long-Term Studies and Collaboration
Many research projects, especially in genetics or drug efficacy, span years. Lyophilization allows samples to be stored for extended periods without degrading, making longitudinal studies possible.
It also facilitates collaboration between labs, as stabilized samples can be shipped globally without the need for complex cold-chain logistics, ensuring all teams are working with identical materials.
Increasing Reagent Shelf Life
Many critical lab reagents, particularly enzymes and antibodies, are highly unstable in liquid form and have a very short shelf life.
Freeze-drying converts them into a stable powder, dramatically increasing their usability over time. This reduces waste, lowers costs, and improves overall lab efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, freeze-drying is not without its challenges. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper application.
The Process Can Be Slow
Lyophilization is a time-intensive process. Depending on the sample volume and type, a single cycle can take anywhere from several hours to multiple days to complete.
High Initial and Operational Costs
Laboratory and production-scale freeze dryers represent a significant capital investment. They also consume a substantial amount of energy to maintain low temperatures and high vacuum levels over long cycles.
Not All Damage is Avoided
While sublimation is gentle, the initial freezing step and the final dry state can still induce stress on certain cellular structures. The process must be carefully optimized for each specific material to maximize viability and recovery.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific objective of your research will determine how you leverage freeze-drying technology.
- If your primary focus is long-term biobanking: Your goal is maximum stability to preserve the genetic and structural integrity of cells or tissues for decades.
- If your primary focus is pharmaceutical R&D: You will use freeze-drying to create stable, transportable formulations of biologics or vaccines that can be easily reconstituted in the clinic.
- If your primary focus is foundational lab research: Your objective is to guarantee the reproducibility of experiments by using consistently preserved enzymes, reagents, and cell lines.
Ultimately, understanding how to properly apply freeze-drying is fundamental to producing reliable, valid, and impactful scientific work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Freeze Dryers |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Stabilization via sublimation, removing water without damaging structures. |
| Key Benefit | Preserves structural/chemical integrity for long-term storage and transport. |
| Impact on Research | Ensures experimental reproducibility and validity by providing stable samples. |
| Common Applications | Biobanking (cells, bacteria), pharmaceutical R&D (vaccines), and lab research (enzymes, reagents). |
Ready to enhance your lab's research integrity and efficiency?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory freeze dryers and consumables tailored for biotechnology and research applications. Our equipment ensures the precise preservation of your sensitive biological samples—from cells and enzymes to vaccines—empowering you to achieve reproducible and valid results.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your specific needs. Let our experts help you select the perfect freeze-drying solution to stabilize your samples and advance your scientific work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- Where are evaporators used in food industry? Concentrate Products & Reduce Costs
- What physical property enhancements does freeze drying provide for pharmaceutical products? Achieve Superior Stability & Global Distribution
- How does freeze drying extend the shelf life of pharmaceutical products? Preserve Potency and Stability for Years
- Does THC evaporate over time? The Truth About Potency Loss and Preservation
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP



















