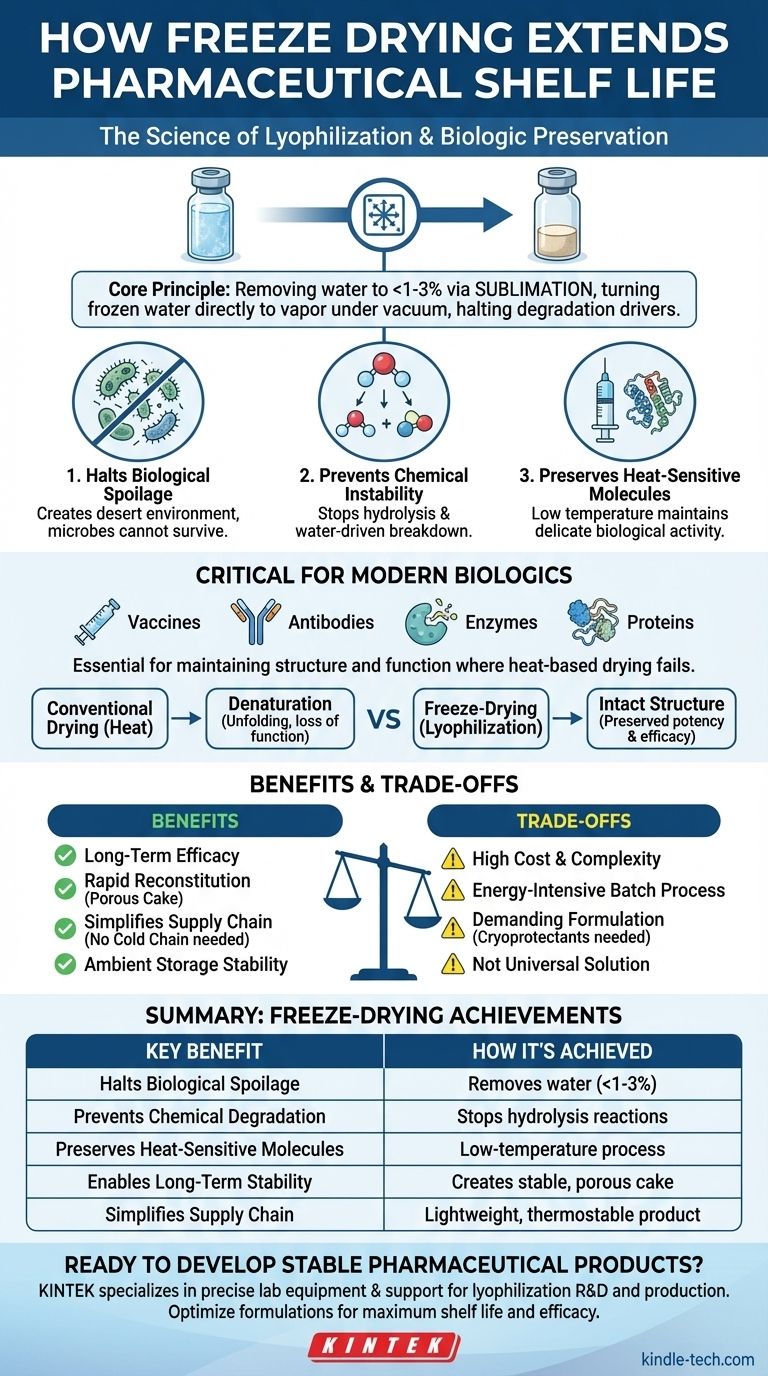
At its core, freeze-drying, or lyophilization, extends the shelf life of pharmaceutical products by removing water content to a very low level. This is achieved through sublimation—turning frozen water directly into vapor under a vacuum—which halts the two primary drivers of degradation: biological growth and chemical reactions.
The central advantage of freeze-drying isn't just the removal of water; it's the ability to do so at low temperatures. This preserves the delicate molecular structure and biological activity of modern, heat-sensitive drugs like vaccines and antibodies, which would be destroyed by conventional heat-based drying.

The Core Principle: Arresting Degradation at the Molecular Level
To understand why lyophilization is so effective, we must look at how it neutralizes the key threats to a drug's stability.
Removing Water via Sublimation
Freeze-drying is a multi-stage process. First, the product is completely frozen. Then, it's placed under a deep vacuum, and a small amount of heat is introduced.
Under these conditions, the frozen water doesn't melt into a liquid. Instead, it sublimates—transforming directly into a gas, which is then drawn out of the product. This avoids the structural damage that occurs when water moves through and evaporates from a product in its liquid state.
Halting Biological Spoilage
Microorganisms like bacteria and mold are a primary cause of spoilage. They require water to live, grow, and multiply.
By reducing the water content to negligible levels (often less than 1-3%), freeze-drying effectively creates a desert environment where these microbes cannot survive. This arrests all biological degradation processes.
Preventing Chemical Instability
Water is not just a medium for life; it's also a highly reactive chemical solvent. Many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are degraded through chemical reactions like hydrolysis, where water molecules break down the drug's structure.
Removing water molecules physically separates the reactants, stopping these degradation pathways and preserving the drug's chemical integrity and potency for years.
Why Lyophilization is Critical for Modern Biologics
For simple, stable molecules, basic drying might suffice. But for complex biologics, lyophilization is often the only viable option for creating a shelf-stable product.
Preserving Temperature-Sensitive Molecules
Many modern drugs, including vaccines, antibodies, enzymes, and proteins, are extremely sensitive to heat. Their medicinal function depends on a precise, complex three-dimensional structure.
Heat-based drying would denature these molecules, causing them to unfold and lose their function—similar to how cooking transforms an egg white. Because lyophilization occurs at low temperatures, it keeps these fragile structures intact.
Ensuring Long-Term Efficacy and Potency
By preserving the drug's physical structure and chemical integrity, freeze-drying ensures the product remains potent and effective until it reaches the patient. The drug that is reconstituted for injection years after manufacturing is virtually identical to the one that was first formulated.
Enabling Rapid Reconstitution
The sublimation process creates a porous, sponge-like structure in the final dried product, often called a "cake." This high surface area allows sterile water or a diluent to quickly and completely re-dissolve the drug, making it ready for administration in seconds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, lyophilization is not a universal solution. It involves specific challenges that must be considered.
High Cost and Complexity
Freeze-drying is a slow, energy-intensive batch process that can take several days to complete. The equipment is expensive to acquire, operate, and maintain, making it one of the most costly unit operations in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Demanding Formulation Development
You cannot simply freeze-dry any liquid formulation. The process requires specialized formulations containing cryoprotectants and lyoprotectants (like specific sugars) to protect the active drug molecule from the stresses of freezing and drying.
Not Always Necessary
For robust, heat-stable small molecules, simpler and cheaper drying methods may be perfectly adequate. Lyophilization is a targeted technology reserved for products whose stability and value justify the significant investment in time and resources.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
The decision to use lyophilization should be driven by the nature of your product and your strategic goals.
- If your primary focus is preserving biologics (vaccines, proteins, antibodies): Lyophilization is the gold standard for maintaining the structural integrity and biological activity required for efficacy.
- If your primary focus is simplifying the supply chain: Lyophilization creates lightweight, thermostable products that eliminate the need for a costly and complex cold chain for storage and transport.
- If your primary focus is long-term stockpiling or strategic reserve: This process is unmatched for producing pharmaceuticals that remain stable and potent for many years at ambient temperatures.
Ultimately, leveraging freeze-drying is a strategic decision to transform a fragile, unstable liquid drug into a robust, stable product ready for global distribution and long-term storage.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | How Freeze-Drying Achieves It |
|---|---|
| Halts Biological Spoilage | Removes water (<1-3%), creating an environment where microbes cannot survive. |
| Prevents Chemical Degradation | Stops hydrolysis and other water-driven reactions that break down the drug. |
| Preserves Heat-Sensitive Molecules | Low-temperature process maintains the structure of vaccines, antibodies, and proteins. |
| Enables Long-Term Stability | Creates a solid, porous "cake" that remains potent for years at ambient temperatures. |
| Simplifies Supply Chain | Produces lightweight, thermostable products that don't require a cold chain. |
Ready to develop a stable, long-lasting pharmaceutical product?
Freeze-drying is a complex but essential process for preserving the potency of sensitive biologics. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and expert support needed for successful lyophilization R&D and production.
Our team can help you select the right technology and optimize your formulation to ensure your vaccines, proteins, or other temperature-sensitive drugs achieve maximum shelf life and efficacy.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your project and discover how our expertise in lab equipment can support your pharmaceutical development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory freeze-drying system essential for fermentation biomass? Preserve Sample Integrity for Analysis
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for drying nickel nanoparticle precursors? Prevent Hard Agglomeration Now
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling



















