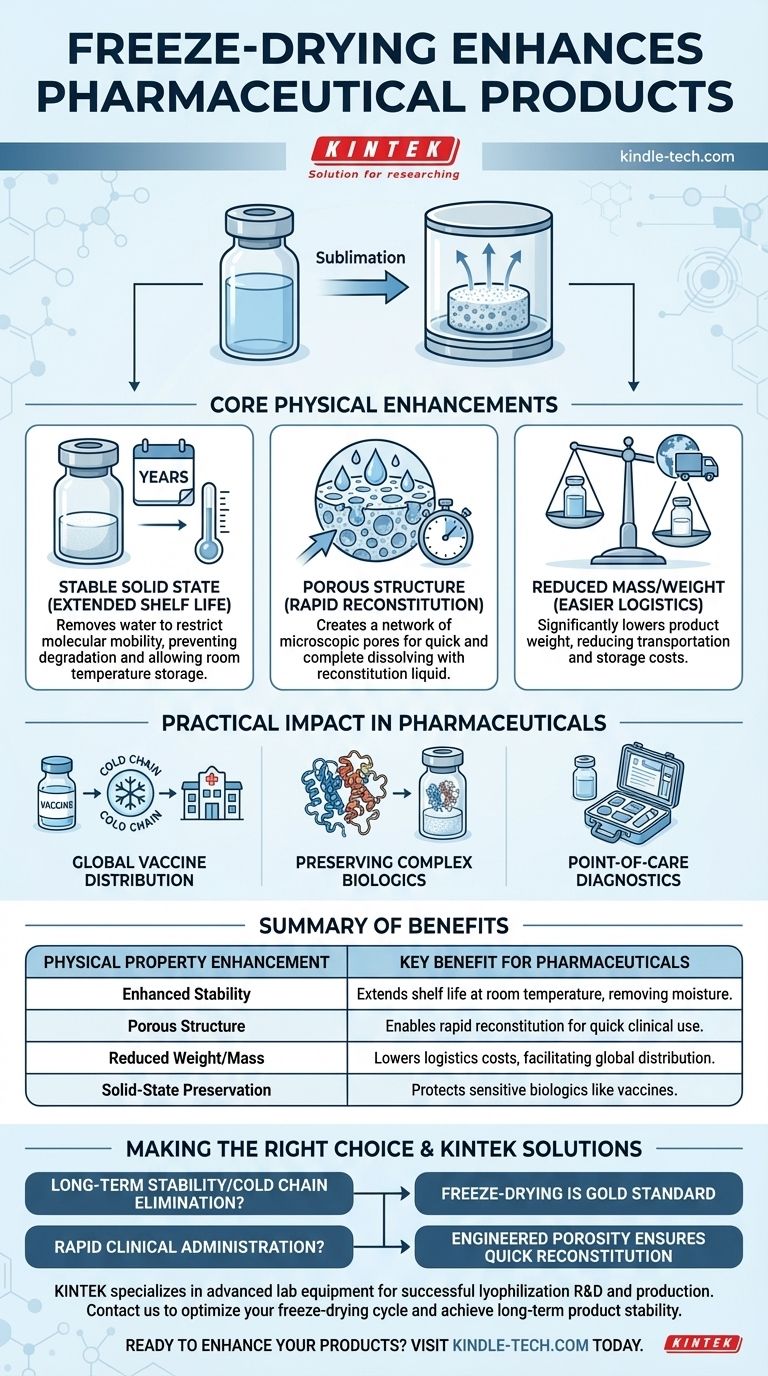
Freeze-drying fundamentally alters a pharmaceutical product's physical state to achieve specific, highly desirable outcomes. The process enhances stability by removing moisture, creates a porous structure for rapid reconstitution, reduces the product's overall weight, and dramatically extends its viable shelf life, often for many years at room temperature.
By transforming an unstable liquid into a stable, lightweight solid, freeze-drying addresses the core challenges of preservation and distribution. This isn't just a drying technique; it's a method for engineering a product's physical properties to make sensitive medicines practical for global use.

The Core Physical Enhancements
Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is a multi-step process involving freezing, a primary drying phase (sublimation), and a secondary drying phase. Each step contributes to the final product's enhanced physical characteristics.
Creating a Stable, Solid State
The primary goal of freeze-drying is to remove water, which is often a key driver of chemical and biological degradation.
By locking the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and excipients into a solid "cake," the process severely restricts molecular mobility. This prevents degradation reactions and preserves the delicate structure of sensitive biologics like vaccines and proteins.
This enhanced stability is what allows for a significantly extended shelf life, removing the need for constant refrigeration or freezing.
Engineering a Porous Structure
As ice crystals are removed from the frozen product via sublimation, they leave behind a network of microscopic pores.
This resulting porous structure dramatically increases the surface area of the solid product. When it's time for use, this allows the reconstitution liquid (like sterile water) to penetrate the cake quickly and evenly.
The outcome is rapid and complete reconstitution, a critical feature for medicines that need to be prepared swiftly in a clinical setting.
Reducing Mass and Weight
Water is dense and heavy. Removing it from the formulation significantly reduces the final product's weight.
This makes the product far easier and cheaper to transport and store. A lightweight product reduces logistical burdens, a crucial factor in distributing vaccines or treatments to remote locations.
The Practical Impact in Pharmaceuticals
These physical enhancements are not just theoretical advantages; they directly enable the development and use of critical medical products.
Enabling Global Vaccine Distribution
Many modern vaccines are based on biologics that are inherently unstable in liquid form.
Freeze-drying removes the dependence on a continuous "cold chain" (unbroken refrigeration), which is a major logistical and financial hurdle for global health initiatives. This allows stable vaccines to be stockpiled and distributed worldwide.
Preserving Complex Biologics
Heat- and moisture-sensitive ingredients, especially large-molecule drugs, are prime candidates for lyophilization. The process preserves their complex three-dimensional structures, which are essential for their therapeutic efficacy.
Facilitating Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Freeze-drying is also essential for creating portable diagnostic kits. Reagents can be pre-measured and lyophilized in vials or cartridges, remaining stable for long periods at room temperature until they are needed for a test.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, freeze-drying is not a universal solution. It involves a series of complex and resource-intensive steps.
High Process Cost
Lyophilization is a slow, energy-intensive process that requires specialized, expensive equipment. The long cycle times can create bottlenecks in manufacturing, increasing the final cost of the drug product.
Potential for Molecular Stress
Both the freezing and drying stages can introduce physical stresses. If the process is not carefully optimized for a specific molecule, it can lead to aggregation or denaturation, compromising the product's effectiveness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use freeze-drying depends entirely on the specific challenges your product faces.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability and eliminating the cold chain: Freeze-drying is the gold standard for preserving sensitive biologics and vaccines.
- If your primary focus is rapid administration in a clinical setting: The engineered porosity of a lyophilized product ensures it can be reconstituted quickly and reliably.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective manufacturing for a robust molecule: A simpler liquid formulation or traditional solid-dose form may be a more practical alternative.
Ultimately, freeze-drying provides a powerful solution for transforming otherwise fragile and impractical molecules into robust and effective pharmaceutical products.
Summary Table:
| Physical Property Enhancement | Key Benefit for Pharmaceuticals |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Stability | Extends shelf life, often at room temperature, by removing moisture and preventing degradation. |
| Porous Structure | Enables rapid and complete reconstitution with water for quick clinical use. |
| Reduced Weight/Mass | Lowers transportation and storage costs, facilitating global distribution. |
| Solid-State Preservation | Protects the delicate structure of sensitive biologics like vaccines and proteins. |
Ready to enhance the stability and efficacy of your pharmaceutical products?
Freeze-drying is a complex but transformative process. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for successful lyophilization R&D and production. Our expertise can help you optimize your freeze-drying cycle to preserve sensitive biologics, ensure rapid reconstitution, and achieve the long-term stability your product demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your pharmaceutical development goals with reliable, high-performance solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using freeze drying for phase change materials with biopolymer shells? Optimize Stability
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- Why is a laboratory freeze-drying system essential for fermentation biomass? Preserve Sample Integrity for Analysis



















