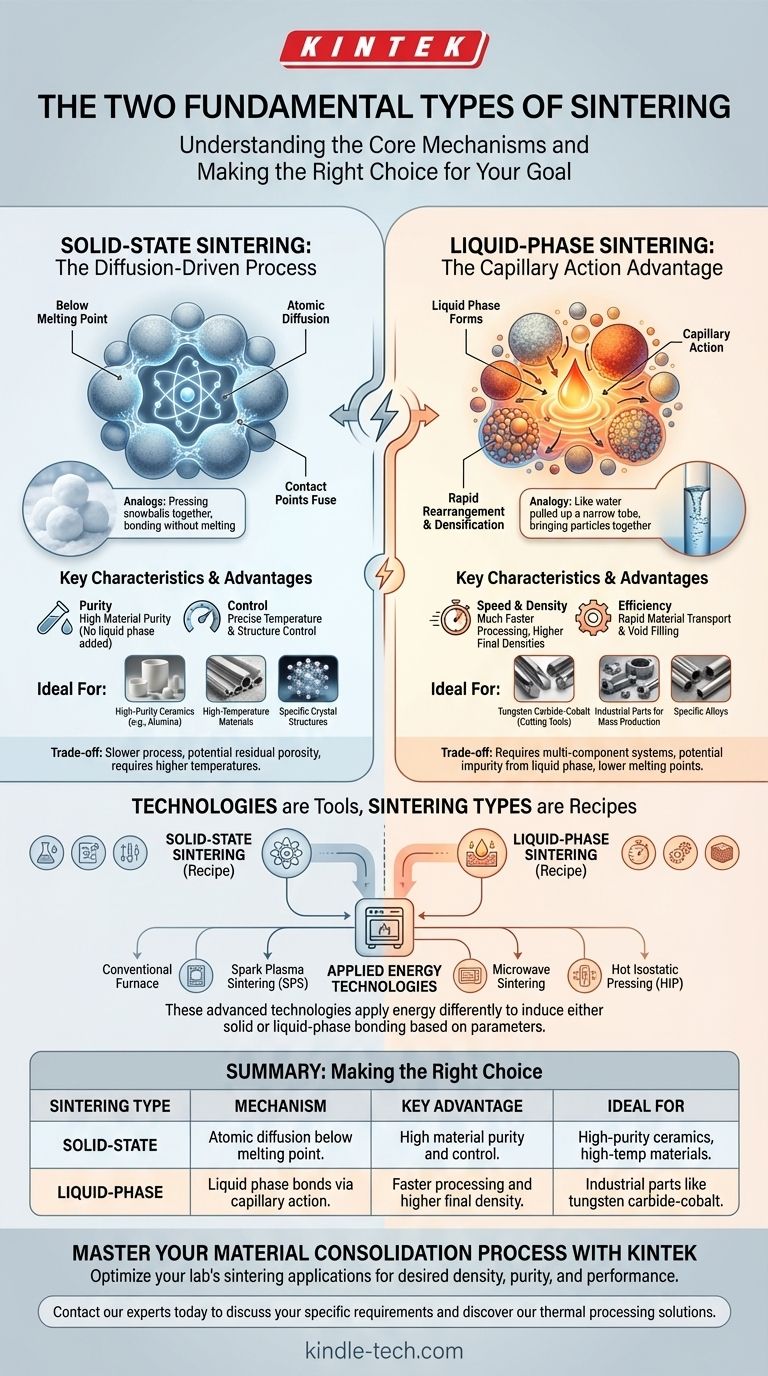
At its core, the two fundamental types of sintering are Solid-State Sintering and Liquid-Phase Sintering. The critical difference lies in whether the material consolidation happens entirely in the solid form through atomic diffusion or is accelerated by the presence of a liquid that acts as a bonding agent between solid particles.
The choice between Solid-State and Liquid-Phase Sintering is not merely a technical detail; it is a strategic decision that dictates the final density, purity, and processing speed of the manufactured component.

The Core Mechanisms: Solid vs. Liquid
To truly understand sintering, you must distinguish between the two primary physical mechanisms that bond powder particles into a solid mass.
Solid-State Sintering: The Diffusion-Driven Process
Solid-State Sintering (also called solid-phase sintering) involves heating compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point.
At this high temperature, atoms at the contact points of the particles become mobile. They migrate through a process called atomic diffusion, filling the gaps and forming "necks" that grow and fuse the particles together.
This process is analogous to pressing two snowballs together on a cold day; without any melting, the ice crystals slowly bond and fuse into a single, stronger mass.
Liquid-Phase Sintering: The Capillary Action Advantage
Liquid-Phase Sintering involves heating a powder mixture that contains at least two different materials, or a single material that will be partially melted. The temperature is raised high enough to melt one of the components, creating a liquid phase within the solid powder structure.
This liquid wets the solid particles and pulls them together through capillary action, the same force that pulls water up a narrow tube. This rearrangement leads to rapid densification.
As the material cools, the liquid solidifies, creating a strong, dense matrix that bonds the remaining solid particles.
Sintering Technologies vs. Fundamental Types
A common point of confusion arises from the various technologies used to perform sintering. Terms like "Spark Plasma Sintering" or "Microwave Sintering" describe the method of applying energy, not the fundamental type of sintering occurring.
The Technology is the "How," Not the "What"
Think of Solid-State and Liquid-Phase as the two basic recipes. The various technologies are like different types of ovens you can use to cook that recipe.
Any of these advanced technologies can be used to induce either Solid-State or Liquid-Phase sintering, depending on the temperature profile and materials used.
Key Sintering Technologies
- Conventional Sintering: Heating the material in a high-temperature furnace (resistance or induction).
- Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): Uses a pulsed DC current and pressure to heat the material extremely quickly.
- Microwave Sintering: Uses microwave energy for rapid and more uniform internal heating.
- Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Applies both high temperature and high-pressure inert gas to densify parts and eliminate almost all porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between Solid-State and Liquid-Phase Sintering involves balancing key performance and processing goals.
Speed and Density
Liquid-Phase Sintering is generally much faster and achieves higher final densities. The liquid provides a rapid pathway for material transport, quickly filling voids and pulling particles together.
Solid-State Sintering is a slower, diffusion-controlled process that often leaves behind some residual porosity.
Purity and Temperature Control
Solid-State Sintering is the method of choice for high-purity applications. Since no secondary material is added to create a liquid, the chemistry of the original material is preserved.
This method is also essential for materials with extremely high melting points, where creating a controlled liquid phase is impractical or impossible.
Material Compatibility
Some material systems are specifically designed for Liquid-Phase Sintering. A classic example is tungsten carbide-cobalt (used in cutting tools), where the cobalt melts and acts as a "glue" for the hard tungsten carbide grains.
Other materials, such as certain advanced ceramics, must be processed via Solid-State Sintering to maintain their specific crystal structure and performance properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements will determine which fundamental sintering type is appropriate.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and fast processing for industrial production: Liquid-Phase Sintering is typically the more effective path.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute material purity or working with very high-temperature materials: Solid-State Sintering is the necessary approach.
- If you need to select a manufacturing technology: Evaluate methods like SPS or HIP based on your budget and part specifications, recognizing they are tools to achieve either solid or liquid-phase bonding.
Understanding this core distinction is the first step toward mastering material consolidation and design.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Type | Mechanism | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Atomic diffusion bonds particles below melting point. | High material purity and control. | High-purity ceramics, high-temperature materials. |
| Liquid-Phase Sintering | A liquid phase wets and bonds particles via capillary action. | Faster processing and higher final density. | Industrial parts like tungsten carbide-cobalt tools. |
Master Your Material Consolidation Process
Choosing the right sintering process is critical for achieving the desired density, purity, and performance in your lab's materials. Whether your project requires the high purity of Solid-State Sintering or the rapid densification of Liquid-Phase Sintering, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can provide the precise thermal processing solutions you need.
Let us help you optimize your sintering applications. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our reliable furnaces and technical support can enhance your research and development outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering time? A Critical Process Variable for Material Density and Strength
- What are the defects in sintered parts? Avoid Warping, Cracking, and Porosity Issues
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- What is the sintering process of powder metallurgy? Transform Powder into Durable Metal Parts
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?



















