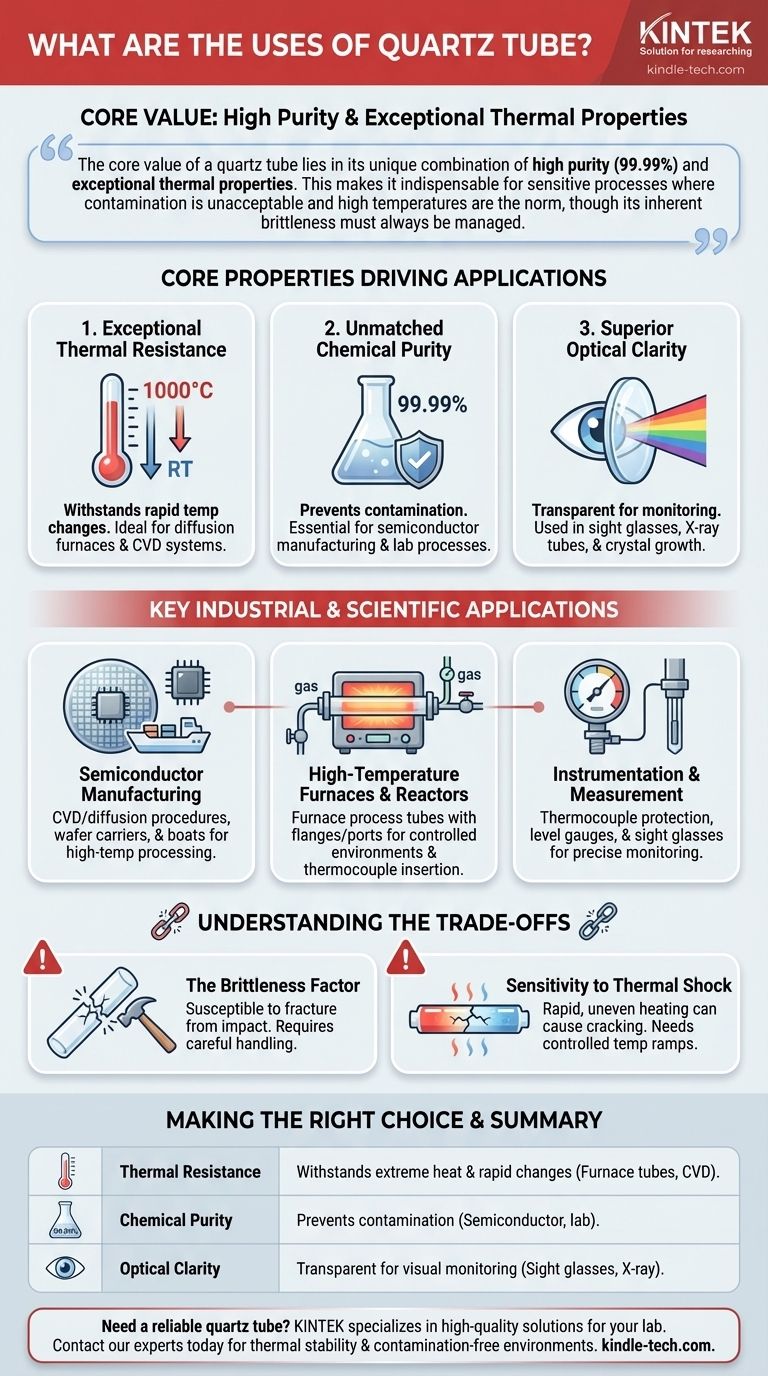
The primary uses of quartz tubes are centered on applications demanding extreme purity and the ability to withstand very high temperatures. You will find them used as furnace tubes in semiconductor manufacturing, as protective sheaths for thermocouples, and in scientific instruments like level gauges and sight glasses where both heat resistance and optical clarity are required.
The core value of a quartz tube lies in its unique combination of high purity (99.99%) and exceptional thermal properties. This makes it indispensable for sensitive processes where contamination is unacceptable and high temperatures are the norm, though its inherent brittleness must always be managed.
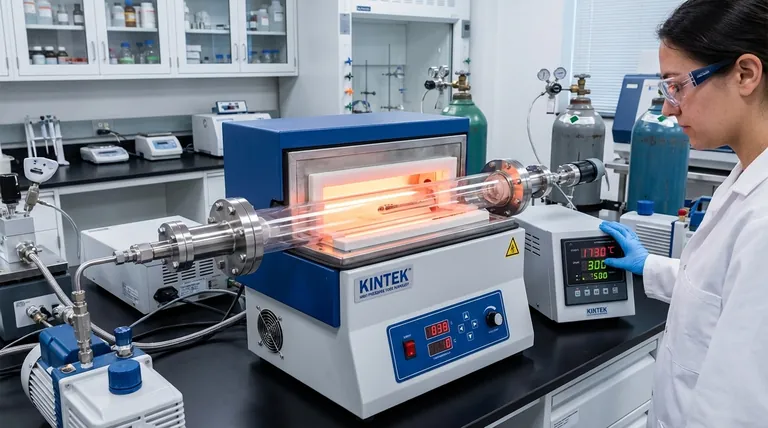

Core Properties Driving Quartz Tube Applications
To understand where quartz tubes are used, we must first understand the material itself. A few key characteristics make it the superior choice for specific technical challenges.
Exceptional Thermal Resistance
Quartz tubes offer excellent performance at high temperatures and can withstand significant thermal shock. They can often handle a rapid temperature change from 1000°C down to room temperature without failing.
This property is critical for processes involving rapid heating and cooling cycles, such as in diffusion furnaces or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems.
Unmatched Chemical Purity
The material used is typically 99.99% pure fused quartz. This extreme purity is prized in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, where even trace amounts of metallic contaminants can ruin a batch of microchips.
It is used for cleaning baths and heat treatment tubes specifically because it does not introduce harmful elements into the process.
Superior Optical Clarity
Quartz is transparent to a wide spectrum of light, making it ideal for applications that require visual monitoring or utilize specific light wavelengths.
This is why it's chosen for sight glasses on high-temperature reactors, X-ray tubes, and in processes like crystal growth where observing the material is part of the procedure.
Key Industrial and Scientific Applications
The properties of quartz translate directly into its use in several high-value industries.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
This is arguably the most critical application. The high-purity environment required for creating silicon wafers relies heavily on quartz components.
They are used for CVD and diffusion procedures, as transfer carriers for wafers, and as boats that hold wafers during high-temperature processing.
High-Temperature Furnaces and Reactors
Quartz is a standard material for furnace process tubes. Its ability to contain a controlled environment at extreme temperatures is essential.
These tubes are often fitted with stainless steel flanges, valves, and ports for thermocouple insertion, allowing them to be connected to vacuum pumps and gas systems for advanced material processing.
Instrumentation and Measurement
The stability and clarity of quartz make it valuable for precise instrumentation.
Applications include thermocouple protection tubes, which shield sensitive temperature sensors from corrosive environments, as well as high-pressure level gauges and sight glasses.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. To use quartz effectively, you must be aware of its limitations.
The Brittleness Factor
The primary drawback of quartz is its brittleness. While strong under compression and thermally resilient, it is a ceramic material that is susceptible to fracture from mechanical impact.
Careful handling is non-negotiable, as dropping or striking a quartz tube will almost certainly cause it to break.
Sensitivity to Thermal Shock
While its thermal shock resistance is excellent for a ceramic, it is not indestructible. Rapid, uneven heating or cooling can create internal stresses that lead to cracking.
Proper furnace design and controlled temperature ramps are crucial to ensure the longevity of quartz components in high-cycle applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination: Quartz is the ideal choice due to its extreme purity, making it essential for semiconductor and lab-grade processes.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing: Quartz is an excellent and common choice for furnace tubes, provided you implement controlled heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability and impact resistance: You should consider alternative materials like high-alumina ceramics or specific metal alloys, as quartz is too brittle for robust mechanical applications.
Understanding both the exceptional strengths and the practical limitations of quartz is the key to leveraging it successfully in your work.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Advantage | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands extreme heat & rapid temperature changes | High-temperature furnace tubes, CVD systems |
| Chemical Purity | 99.99% purity prevents contamination | Semiconductor wafer processing, lab-grade processes |
| Optical Clarity | Transparent for visual monitoring & light transmission | Sight glasses, X-ray tubes, crystal growth observation |
Need a reliable quartz tube for your high-purity or high-temperature process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including quartz tubes designed for superior performance in semiconductor manufacturing, research, and industrial applications. Our products ensure the thermal stability and contamination-free environment your work demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are the sample holders made of? Engineered with PTFE and PEEK for Purity
- How does a high-precision platinum-rhodium thermocouple contribute to calculating activation energy? | KINTEK
- What is the role of a heating magnetic stirrer in the precursor preparation of ZnS nanopowder? Achieve Phase Purity
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding
- Why is ultrasonic cleaning essential for FeCrAl coating tests? Ensure Precise High-Temperature Corrosion Data
- What is basic lining material? The Key to High-Temperature Chemical Compatibility
- What is the strength of a quartz tube? Withstand 1,000 PSI in High-Temp, High-Purity Applications
- Why is an alumina insulation disk required in a CCPD reactor? Enhance Coating Quality with Floating Potential



















