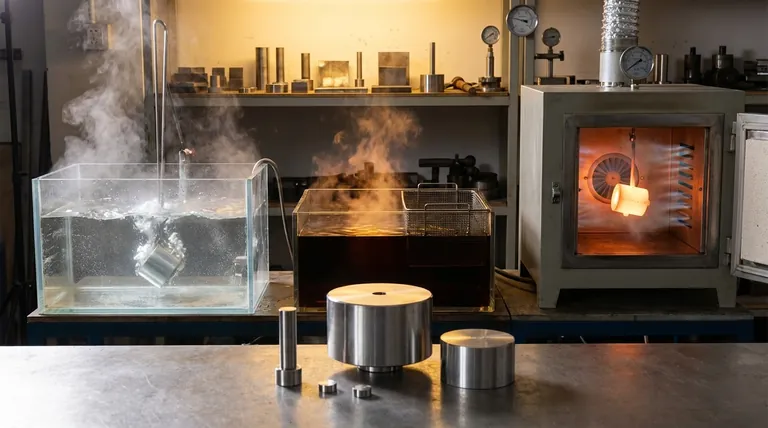
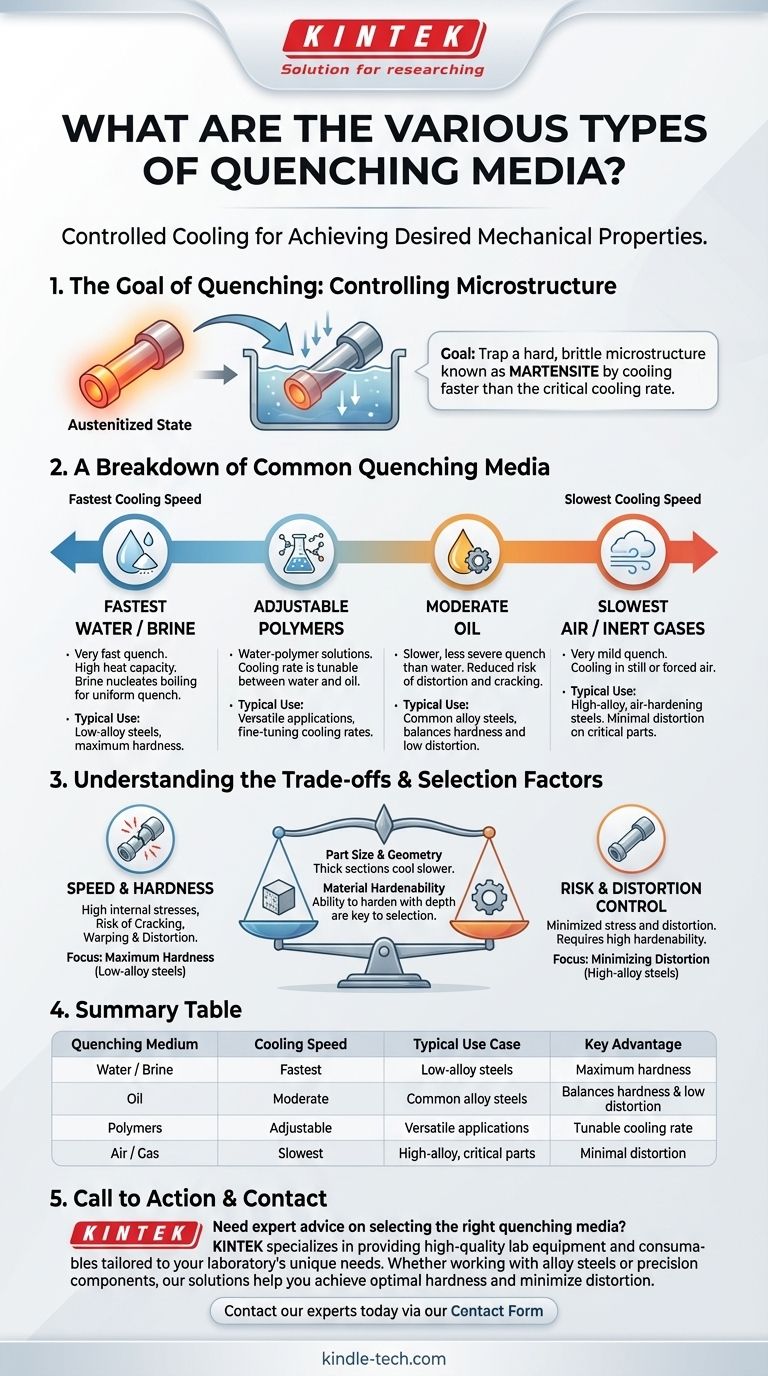
The most common quenching media are water, brine (salt water), oil, and air. The selection of a medium is not arbitrary; it is a critical decision in heat treatment that directly controls the rate of cooling, which in turn dictates the final mechanical properties, such as hardness and ductility, of the finished part.
The core principle of quenching is not just to cool a part rapidly, but to cool it at a specific, controlled rate. The choice of quenching medium—from fast-acting water to slow-acting air—is the primary tool for manipulating this rate to achieve a desired material structure while avoiding defects like cracking or warping.

The Goal of Quenching: Controlling Microstructure
Quenching is a foundational process in metallurgy, particularly for steels. The goal is to rapidly cool a component from its high-temperature austenitized state to "trap" a hard, brittle microstructure known as martensite.
The Cooling Rate is Everything
To form martensite, the material must be cooled faster than its critical cooling rate. If the cooling is too slow, softer, less desirable microstructures will form, and the part will not achieve its potential hardness.
The quenching medium's job is to extract heat fast enough to "win the race" against the formation of these softer structures.
A Breakdown of Common Quenching Media
Each medium offers a different cooling power, defined by its thermal conductivity and behavior as it boils on the part's surface. The cooling rates below are ordered from fastest to slowest.
Water and Brine
Water provides a very fast quench due to its high heat capacity. It is effective for materials with low hardenability (like plain carbon steels) that require an aggressive quench to harden properly.
Brine, a solution of salt in water, is even faster. The salt crystals nucleate boiling, which violently disrupts the insulating vapor jacket that can form around the part, ensuring a more uniform and rapid quench.
Oil
Oil is the workhorse of the heat-treating industry. It provides a slower, less severe quench than water, significantly reducing the risk of distortion and cracking, especially in parts with complex geometries.
Different oil formulations offer a range of cooling speeds, making them suitable for a wide variety of common alloy steels that have higher hardenability than plain carbon steels.
Polymers
Polymer quenchants are a modern, versatile alternative. These are solutions of polymer in water, and by adjusting the polymer concentration, their cooling rate can be fine-tuned to fall anywhere between that of water and oil.
This adjustability gives metallurgists precise control over the cooling process, allowing them to optimize properties while minimizing defects.
Air and Inert Gases
Air provides the slowest cooling rate and is considered a very mild quench. This method is reserved for air-hardening steels—highly alloyed materials with extremely high hardenability that will form martensite even when cooled slowly in still or forced air.
Gas quenching is primarily used to minimize distortion to an absolute minimum in dimensionally critical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a quenching medium is a balancing act between achieving the desired metallurgical properties and maintaining the physical integrity of the part.
The Speed-vs-Risk Spectrum
A faster quench (water) delivers maximum potential hardness but introduces high internal stresses. This raises the risk of catastrophic failure through cracking or unacceptable changes in shape through warping and distortion.
A slower quench (oil or air) is gentler on the part, minimizing stress and distortion. However, if used on a steel with insufficient hardenability, it will fail to produce the required hardness.
The Role of Part Size and Geometry
Thick sections of a part cool more slowly than thin sections. An aggressive quench can create a massive temperature difference between the surface and the core, or between thick and thin sections, generating stresses that cause distortion.
For this reason, parts with complex shapes or drastic changes in thickness often require a slower medium like oil to ensure a more uniform cooling process.
Material Hardenability is Key
Hardenability is a measure of a steel's ability to harden with depth. High-alloy steels have high hardenability and can be hardened with slower quenches (oil or air). Low-alloy and plain carbon steels have low hardenability and require a very fast quench (water or brine).
Practical and Cost Considerations
The decision is also driven by practical factors. Oil requires post-quench cleaning to remove residue. Brine is highly corrosive and demands robust equipment. Air and gas quenching often require specialized furnaces, which can increase costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection must align with the material being treated and your primary objective for the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness on low-alloy steels: Water or brine is the necessary choice, but you must account for a high risk of distortion.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness and distortion control in common alloy steels: Oil is the industry standard and offers the best all-around compromise.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion on high-alloy, critical-dimension parts: Air or gas quenching is the only method that provides sufficient control.
- If your primary focus is process optimization and fine-tuning cooling rates: Polymer quenchants offer an adjustable solution to bridge the gap between water and oil.
Ultimately, mastering quenching is about using the right medium as a precise tool to dictate the final character of your material.
Summary Table:
| Quenching Medium | Cooling Speed | Typical Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water / Brine | Fastest | Low-alloy steels | Maximum hardness |
| Oil | Moderate | Common alloy steels | Balances hardness & low distortion |
| Polymers | Adjustable | Versatile applications | Tunable cooling rate |
| Air / Gas | Slowest | High-alloy, critical parts | Minimal distortion |
Need expert advice on selecting the right quenching media for your lab's heat treatment processes? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're working with alloy steels or precision components, our solutions help you achieve optimal hardness and minimize distortion. Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can support your metallurgical success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What roles do graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing of Al-Sc alloys? Ensure Precision & Purity
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during hot pressing? Optimize Boron Carbide Sintering at 1850°C
- What are the specific functions of graphite molds in the vacuum hot-press sintering process? Expert Insights for Ceramics
















