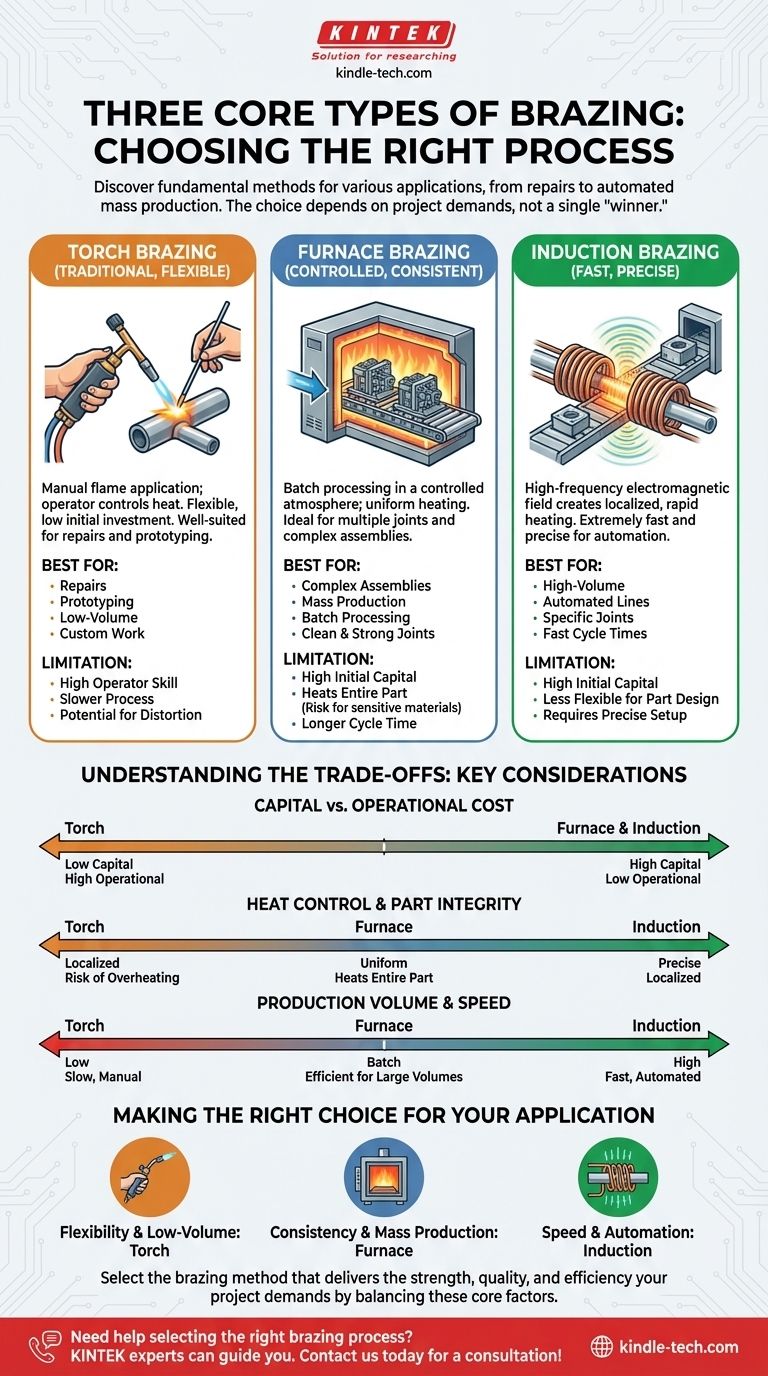
While many specialized methods exist, three of the most fundamental and widely used types of brazing are Torch Brazing, Furnace Brazing, and Induction Brazing. Each method uses a different technique to apply heat, making them suitable for distinct applications, from one-off repairs to high-volume automated production.
The best brazing method is not a single "winner," but a choice dictated by your project's specific demands. Your decision should balance factors like production volume, part complexity, joint quality requirements, and upfront equipment cost.

A Closer Look at the Core Brazing Processes
Brazing relies on heating a filler metal above its melting point (but below the melting point of the base metals) and drawing it into a joint via capillary action. The primary difference between brazing types is the method used to deliver that heat.
Torch Brazing
Torch brazing is the most traditional method, involving a gas-fueled flame directed at the joint by an operator. A separate brazing rod or wire is typically fed into the heated joint.
This process is highly flexible and requires minimal initial investment in equipment. It is exceptionally well-suited for repairs, prototyping, and low-volume production runs where automation is not practical.
The quality of a torch-brazed joint is highly dependent on the skill of the operator, who must control the heat application to avoid overheating or distorting the part.
Furnace Brazing
In furnace brazing, the filler metal is pre-placed onto the parts, and the entire assembly is heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace. This allows for multiple joints, and even multiple parts, to be brazed simultaneously.
This method is ideal for mass-produced parts and complex assemblies with multiple joints. The controlled atmosphere (often a vacuum or inert gas) prevents oxidation, resulting in clean, strong, and highly consistent joints without the need for post-braze cleaning.
Because the entire part is heated and cooled uniformly, furnace brazing minimizes thermal distortion, which is critical for large or oddly-shaped components.
Induction Brazing
Induction brazing uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates an electromagnetic field that precisely and rapidly heats the conductive metal parts placed within it.
This process offers extremely fast heating cycles, making it perfect for high-volume, automated production lines, such as those found in the automotive industry. The heat is localized specifically to the joint area, increasing energy efficiency and protecting the rest of the component from thermal effects.
Induction brazing provides exceptional repeatability and process control, producing highly consistent joints with minimal operator intervention once the system is configured.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a brazing process involves weighing the benefits of one method against the limitations of another. Your application's requirements will determine which trade-offs are acceptable.
Capital Cost vs. Operational Cost
Torch brazing has the lowest upfront equipment cost but often has the highest per-part labor cost and can be less consistent.
Furnace and induction brazing require a significant initial capital investment. However, for mass production, they dramatically reduce the per-part cost through automation and high throughput.
Heat Control and Part Integrity
The direct flame in torch brazing can cause localized overheating or distortion if not managed carefully by a skilled operator.
Furnace brazing heats the entire assembly. While this reduces stress and distortion, it is unsuitable for components that contain heat-sensitive materials (like electronics or plastics) away from the joint.
Induction brazing offers the best of both worlds: precise, localized heating that protects the overall component while being highly controllable and repeatable.
Production Volume and Speed
Torch brazing is inherently a manual, one-at-a-time process, making it slow and unsuitable for high volumes.
Furnace brazing is ideal for batch processing. Its cycle time can be long, but its ability to handle hundreds of parts at once makes it efficient for large production runs of complex or small parts.
Induction brazing is the champion of speed for specific, repeatable joints, often completing a single braze in a matter of seconds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct process, analyze your primary manufacturing goal.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and low-volume production: Torch brazing offers the lowest barrier to entry and is perfect for repairs, prototypes, and custom work.
- If your primary focus is high-quality joints on complex or mass-produced parts: Furnace brazing provides unmatched consistency and cleanliness for batch production.
- If your primary focus is speed and automated mass production of specific joints: Induction brazing delivers the fastest, most repeatable results for high-volume manufacturing lines.
By understanding these core processes and their inherent trade-offs, you can select the brazing method that delivers the strength, quality, and efficiency your project demands.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Main Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Repairs, prototyping, low-volume work | Low equipment cost, high flexibility | Dependent on operator skill, slower |
| Furnace Brazing | Complex assemblies, mass production | Consistent quality, batch processing | High initial cost, heats entire part |
| Induction Brazing | High-volume, automated production | Fast, precise, localized heating | High initial cost, less flexible for part design |
Need help selecting the right brazing process for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose the optimal brazing solution to ensure strength, quality, and efficiency for your specific application. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service



















