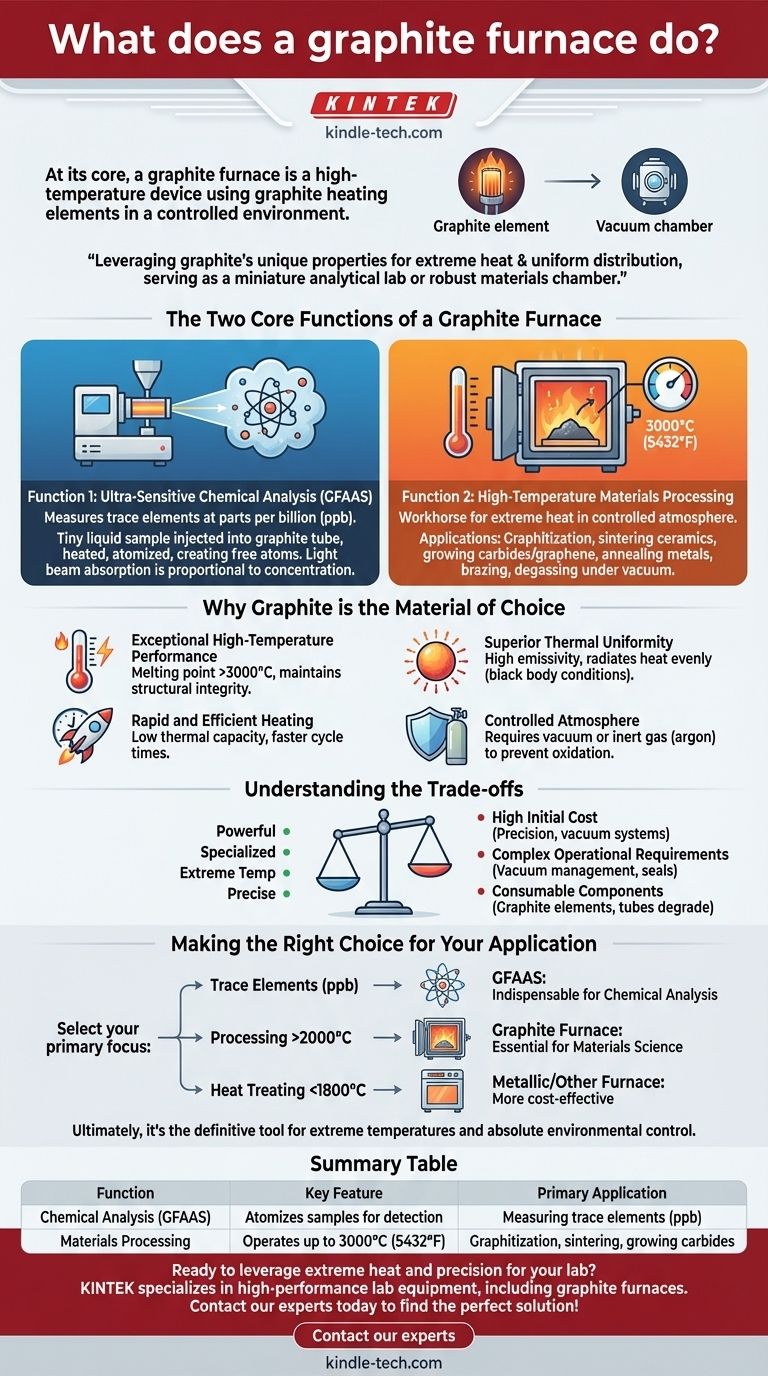
At its core, a graphite furnace is a high-temperature device that uses graphite as a heating element to create a precisely controlled environment. It serves two primary, distinct purposes: performing ultra-sensitive chemical analysis of elements and processing advanced materials at extreme temperatures that most other furnaces cannot achieve.
A graphite furnace is not a single-purpose tool. It leverages the unique physical properties of graphite—its ability to withstand extreme heat and distribute it uniformly—to serve as either a miniature, high-precision laboratory for chemical analysis or a robust production chamber for materials science.
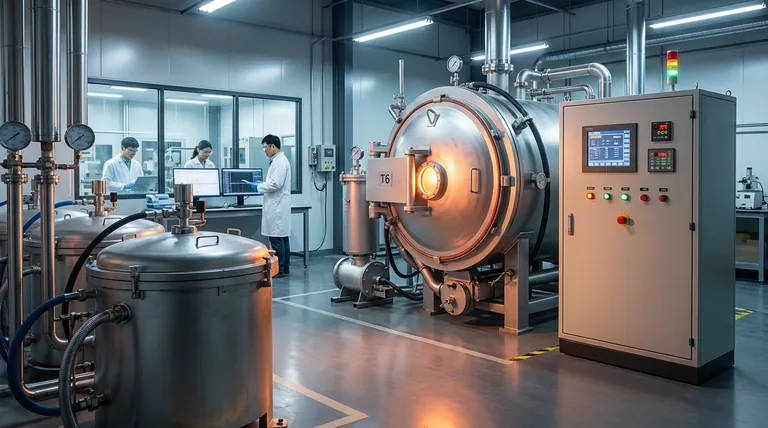

The Two Core Functions of a Graphite Furnace
While the term "graphite furnace" is singular, its application falls into two major categories that solve very different problems.
Function 1: Ultra-Sensitive Chemical Analysis
In analytical chemistry, the device is more accurately called a Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (GFAAS). Its function is to measure trace elements at incredibly low concentrations (parts per billion).
A tiny liquid sample is injected into a graphite tube. The tube is then rapidly heated in stages to dry, ash, and finally atomize the sample, creating a cloud of free atoms. A beam of light specific to the element being measured is passed through this atom cloud, and the amount of light absorbed is directly proportional to the element's concentration.
Function 2: High-Temperature Materials Processing
In materials science and industrial manufacturing, a graphite furnace is a workhorse for processes requiring extreme heat in a controlled atmosphere. These furnaces can routinely operate at temperatures up to 3000°C (5432°F).
Common applications include graphitization (converting carbon materials into crystalline graphite), sintering ceramics, growing carbides or graphene, annealing metals, brazing components, and degassing materials under vacuum.
Why Graphite is the Material of Choice
The selection of graphite is not arbitrary; its specific properties make these applications possible.
Exceptional High-Temperature Performance
Graphite has an extremely high melting point and maintains its structural integrity at temperatures far beyond the limits of metal heating elements. This is the primary reason it can be used for processes reaching 3000°C.
Superior Thermal Uniformity
Graphite naturally creates near-perfect black body conditions within the heating chamber. Its high emissivity (close to 1.0) means it radiates heat very efficiently and evenly, ensuring the entire workload receives a uniform temperature. This is critical for process consistency and quality.
Rapid and Efficient Heating
Due to graphite's relatively low density and modest thermal capacity, the furnace can heat up and cool down very quickly. This allows for faster cycle times compared to other high-temperature furnace types.
Controlled Atmosphere
Graphite will rapidly oxidize (burn) in the presence of air at high temperatures. Therefore, these furnaces are always designed with a vacuum-tight chamber. They operate either under a deep vacuum or are backfilled with an inert gas (like argon), preventing contamination and protecting the heating elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a graphite furnace is a specialized piece of equipment with specific operational considerations.
High Initial Cost
The precision engineering, vacuum systems, and high-purity graphite components make these furnaces significantly more expensive to purchase than standard atmosphere or metallic-element furnaces.
Complex Operational Requirements
Operating a graphite furnace requires managing a vacuum system, which involves pumping down the chamber before each run and handling large, vacuum-tight seals. This adds a layer of complexity and potential failure points compared to simpler furnace designs.
Consumable Components
The graphite heating elements, tubes, and insulation shields are consumable items. While they can be protected with sacrificial layers to extend their life, they will eventually degrade and require replacement, representing an ongoing operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your specific temperature and atmospheric requirements.
- If your primary focus is measuring trace elements at parts-per-billion levels: A Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (GFAAS) is an indispensable analytical tool.
- If your primary focus is processing materials above 2000°C: A graphite furnace is one of the only practical solutions for applications like graphitization, advanced ceramic sintering, or carbide growth.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating below 1800°C without strict atmospheric purity: A furnace with metallic heating elements or a different design may be a more cost-effective and simpler solution.
Ultimately, a graphite furnace is the definitive tool when your process demands extreme temperatures and absolute environmental control.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Feature | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Analysis (GFAAS) | Atomizes samples for detection | Measuring trace elements at parts-per-billion levels |
| Materials Processing | Operates up to 3000°C (5432°F) | Graphitization, sintering ceramics, growing carbides |
Ready to leverage extreme heat and precision for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including graphite furnaces, to meet your most demanding materials processing and analytical chemistry needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the disadvantage of graphite furnace? Managing Reactivity and Contamination Risks
- What gas is used in graphite furnace? Maximize Accuracy with the Right Inert Gas
- What is the melting point of graphite and why? Unlocking Extreme Heat Resistance
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What are the interferences of graphite furnace? Overcome Matrix & Spectral Issues for Accurate GFAAS
- What is the process of isostatic graphite? A Guide to High-Performance, Uniform Material Creation
- What is the principle of graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures with Direct Resistive Heating
- Does graphite conduct electricity when melted? Discover the Secrets of Liquid Carbon Conductivity



















