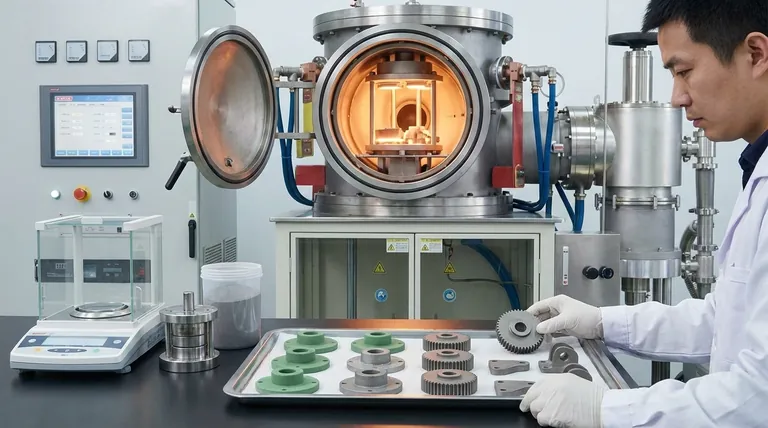
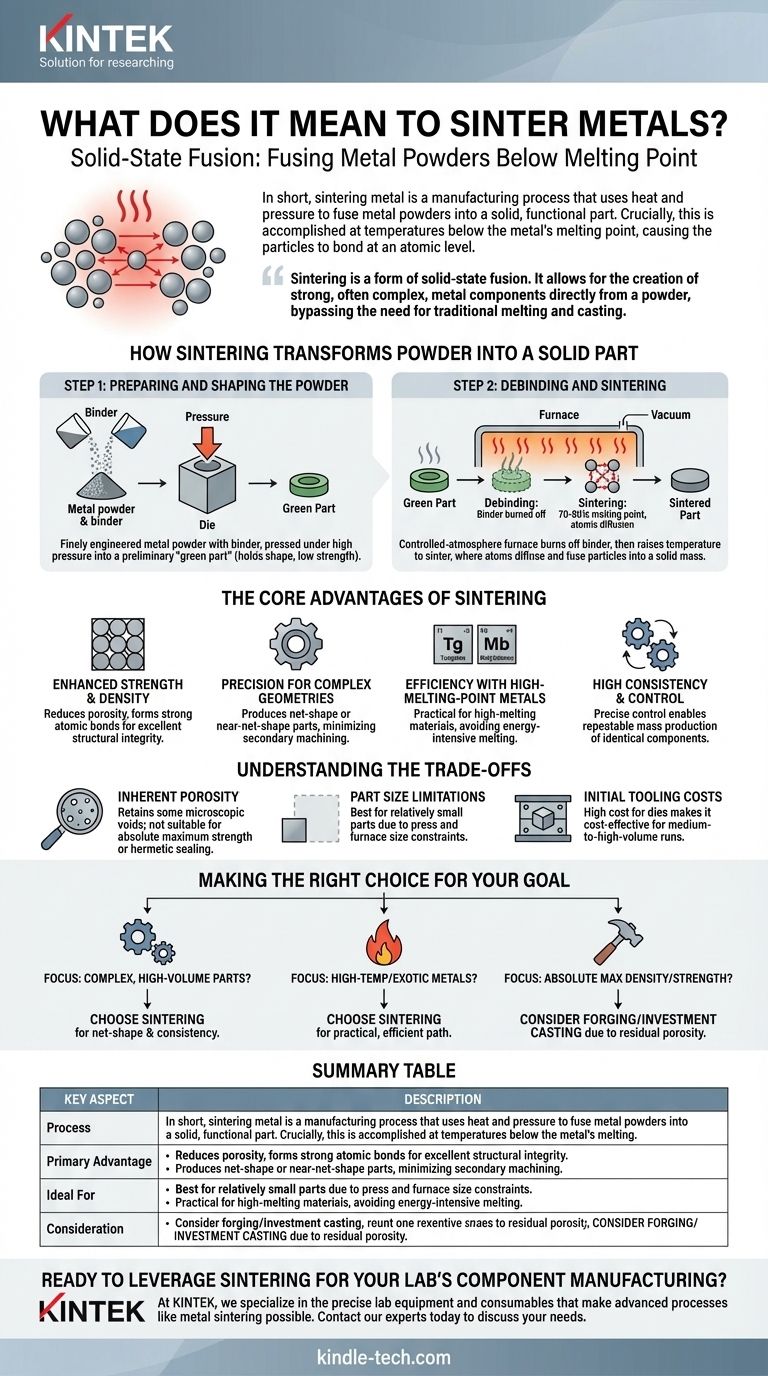
In short, sintering metal is a manufacturing process that uses heat and pressure to fuse metal powders into a solid, functional part. Crucially, this is accomplished at temperatures below the metal's melting point, causing the particles to bond at an atomic level without ever turning into a liquid.
The central concept to grasp is that sintering is a form of solid-state fusion. It allows for the creation of strong, often complex, metal components directly from a powder, bypassing the need for traditional melting and casting.

How Sintering Transforms Powder into a Solid Part
The process isn't just about applying heat; it's a precise, multi-step method designed to create parts with specific properties. It fundamentally relies on the principle of atomic diffusion—where atoms from individual powder granules migrate across boundaries to form strong metallic bonds with their neighbors.
Step 1: Preparing and Shaping the Powder
The journey begins with finely engineered metal powder. This powder is often mixed with a temporary polymeric binder to improve its molding characteristics.
This mixture is then poured into a die and compacted under high pressure to form a fragile, preliminary shape known as a "green part." This part holds its shape but has not yet developed its final strength.
Step 2: Debinding and Sintering
The green part is placed into a controlled-atmosphere furnace, often a vacuum furnace. The initial heating phase is called debinding, where the binder material is carefully burned off.
Next, the temperature is raised to the sintering point. At this high temperature—typically 70-90% of the metal's melting point—the atoms in the metal particles become highly agitated and begin to diffuse across the particle boundaries, fusing them together into a solid, coherent mass.
The Core Advantages of Sintering
Manufacturers choose sintering not just because it's interesting, but because it offers distinct advantages for creating certain types of components, from automotive gears to electrical contacts.
Enhanced Strength and Density
The process significantly reduces the empty space, or porosity, that existed between the loose powder granules. This densification, combined with the formation of strong atomic bonds, results in a part with excellent structural integrity and durability.
Precision for Complex Geometries
Sintering is exceptionally good at producing net-shape or near-net-shape parts. This means the component comes out of the furnace very close to its final dimensions, drastically reducing or even eliminating the need for expensive and time-consuming secondary machining.
Efficiency with High-Melting-Point Metals
For metals like tungsten or molybdenum, which have extremely high melting points, melting and casting is an energy-intensive and difficult process. Sintering provides a more practical and cost-effective method to form these materials into usable parts.
High Consistency and Control
Because the process is based on precise control over powder composition, pressure, temperature, and time, it is highly repeatable. This makes sintering an ideal choice for the mass production of consistent, identical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No manufacturing process is perfect for every application. To use sintering effectively, it's critical to understand its limitations.
Inherent Porosity
While sintering dramatically increases density, it rarely eliminates all porosity. Most sintered parts retain a small percentage of microscopic voids. For applications requiring absolute maximum strength or hermetic sealing, this residual porosity can be a disqualifying factor.
Part Size Limitations
The need for high-pressure compaction and large, specialized furnaces means that sintering is typically best suited for producing relatively small parts. Creating very large components via sintering is often impractical or economically unfeasible.
Initial Tooling Costs
The dies required to press the metal powders into their green shapes are made from hardened tool steel and can be expensive to produce. This initial investment means sintering is most cost-effective for medium-to-high-volume production runs that can amortize the cost of the tooling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on the specific requirements of your component and production scale.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, high-volume parts: Sintering is an excellent choice for its ability to create near-net-shape components with high consistency, minimizing machining costs.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature or exotic metals: Sintering offers a more practical and energy-efficient manufacturing path than attempting to melt and cast these materials.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute maximum density and fatigue strength: You may need to consider a process like forging or investment casting, as the residual porosity in sintered parts can be a limiting factor for extreme-performance applications.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage sintering as a powerful tool for efficient and precise metal component manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Fusing metal powders using heat and pressure below the melting point (solid-state diffusion). |
| Primary Advantage | Creates complex, net-shape parts with high consistency and minimal machining. |
| Ideal For | High-volume production and working with high-melting-point metals like tungsten. |
| Consideration | Parts have slight inherent porosity; initial tooling costs are high. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's component manufacturing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precise lab equipment and consumables that make advanced processes like metal sintering possible. Whether you're developing new materials or scaling up production, our expertise and high-quality solutions can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum annealing? Achieve Clean, Oxide-Free Metal Parts for Superior Performance
- What are the applications of induction hardening? Boost Component Durability for Automotive & Industrial Parts
- What metals Cannot be brazed? Understanding the Challenges of Low Melting Points and Reactive Oxides
- Can stainless steel be soldered or brazed? Master the Process for Strong, Durable Joints
- What role does a vacuum drying oven play in PEO-RPPO composite membrane fabrication? Optimize Solid Electrolyte Purity
- How is furnace temperature controlled? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing with PID Control
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Performance
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding



















