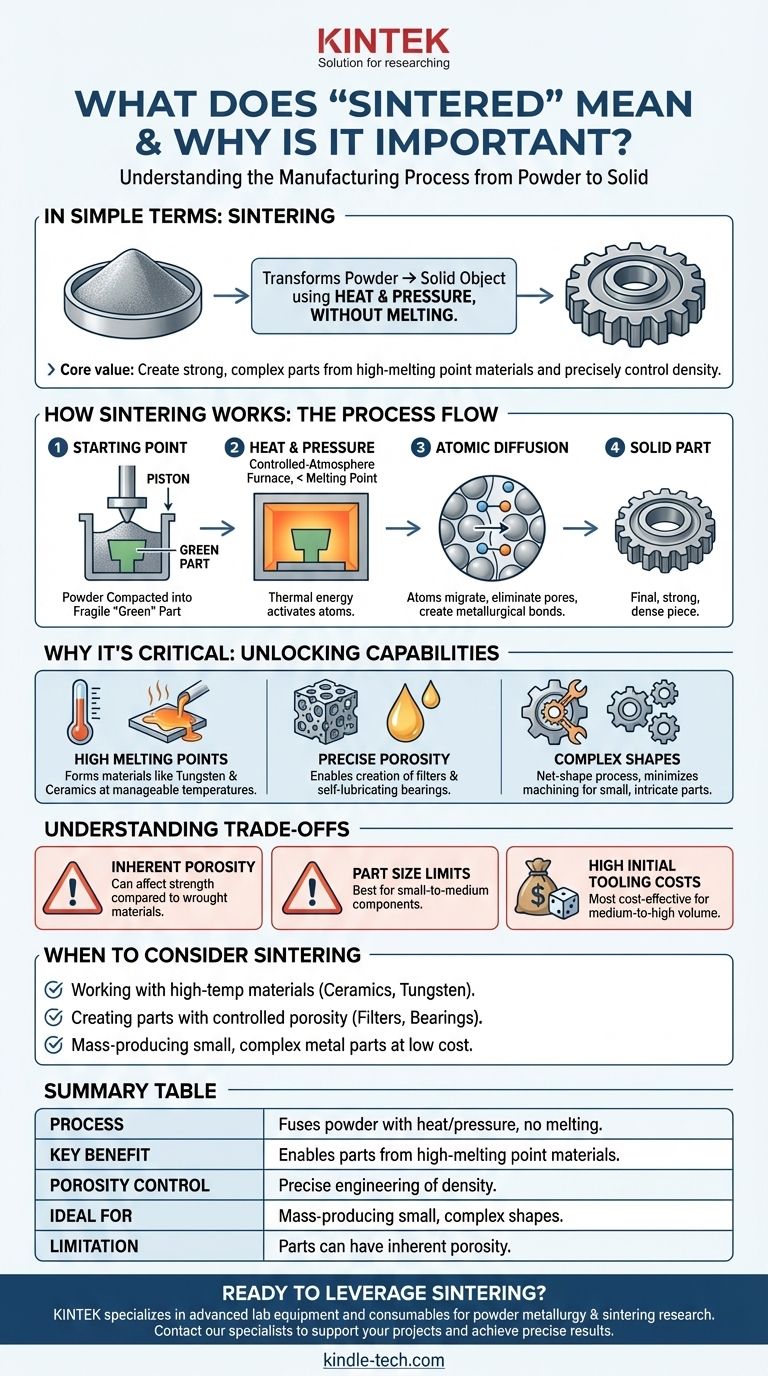
In simple terms, "sintering" is a manufacturing process that transforms a powder into a solid object using heat and pressure. Crucially, this happens without melting the material, allowing for the creation of components from metals and ceramics that are otherwise difficult to form.
Sintering's core value lies in its ability to create strong, complex parts from materials with extremely high melting points or to precisely control a part's final density and porosity, which is impossible with traditional melting and casting methods.

How Sintering Works: From Powder to Solid Part
Sintering is not melting. It is a unique solid-state process where individual particles fuse together, fundamentally changing the material's structure.
The Starting Point: A Bed of Powder
The process begins with a fine powder of a specific material, such as a metal alloy, ceramic, or a composite blend. This powder is often placed into a die or mold and compacted under pressure to form a "green" part, which is fragile but holds its shape.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
The green part is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below its melting point. This thermal energy causes the atoms within the powder particles to become highly active.
Atomic Diffusion: The Science at the Core
At these elevated temperatures, atoms begin to migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This process, known as atomic diffusion, eliminates the pores between the particles and creates strong metallurgical bonds, effectively welding the powder into a single, dense piece.
Why Sintering is a Critical Manufacturing Process
Understanding sintering is key to understanding how many modern, high-performance components are made. The process unlocks capabilities that other methods cannot match.
Creating Parts with High Melting Points
For materials like tungsten (melts at 3,422°C) or advanced ceramics, melting and casting them is often impractical or impossible. Sintering provides a way to form these materials into usable, solid components at lower, more manageable temperatures.
Achieving Precise Porosity and Density
Because the process starts with powder, manufacturers can precisely control the final density of the part. This allows for the creation of intentionally porous components, such as filters or self-lubricating bearings that are designed to hold oil.
Manufacturing Complex Shapes
Sintering is a net-shape (or near-net-shape) process. This means parts come out of the furnace very close to their final dimensions, minimizing the need for expensive and wasteful secondary machining. This is ideal for producing large quantities of small, intricate parts like gears and connectors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any manufacturing technique, sintering has specific limitations that are critical to consider during the design and material selection phase.
Inherent Porosity and Mechanical Properties
Unless secondary steps are taken, sintered parts almost always retain some level of microscopic porosity. This can make them less strong or more brittle than components forged or machined from a solid, fully dense block of the same material.
Limitations on Part Size
The need for uniform pressure during compaction and uniform heat during sintering places practical limits on the size of components that can be produced. The process is best suited for small-to-medium-sized parts.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The hardened steel dies used to press the powder into its green state can be expensive to create. This initial investment means sintering is most cost-effective for medium-to-high volume production runs where the tool cost can be amortized over many parts.
When to Consider Sintering for Your Project
Choosing a manufacturing process depends entirely on your material, geometry, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature materials like ceramics or tungsten: Sintering is not just an option; it is often the most viable or only practical manufacturing method.
- If your primary focus is creating parts with controlled porosity for applications like filters or bearings: Sintering offers a unique level of control over density that is unmatched by casting or machining.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing small, complex metal parts at a low per-unit cost: Sintering can be significantly more economical than CNC machining once the initial tooling costs are covered.
Understanding sintering empowers you to select the right process for creating components with unique and highly engineered properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Fuses powder into a solid using heat and pressure, without melting the material. |
| Key Benefit | Enables the creation of parts from materials with extremely high melting points. |
| Porosity Control | Allows for precise engineering of density, from fully dense to intentionally porous parts. |
| Ideal For | Mass-producing small, complex shapes (gears, filters) with minimal material waste. |
| Limitation | Parts can have inherent porosity, potentially affecting strength compared to wrought materials. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your high-performance components?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for research and development in powder metallurgy and sintering processes. Whether you are experimenting with new materials or scaling up production, our expertise can help you achieve precise results.
Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering projects and help you create stronger, more complex parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More



















