To ensure measurement integrity, you must primarily control for mechanical vibrations, magnetic fields, and ambient temperature. These external factors can introduce noise and instability into your electrochemical system, compromising the quality of your data. A stable physical and thermal environment is the foundation for reliable results when using a platinum electrode.
The core challenge is not merely avoiding external disturbances, but protecting the pristine, catalytically active state of the platinum surface itself. Every environmental factor, from physical shock to chemical contamination, directly impacts the electrode-electrolyte interface where all critical reactions occur, making surface integrity the true determinant of measurement accuracy.

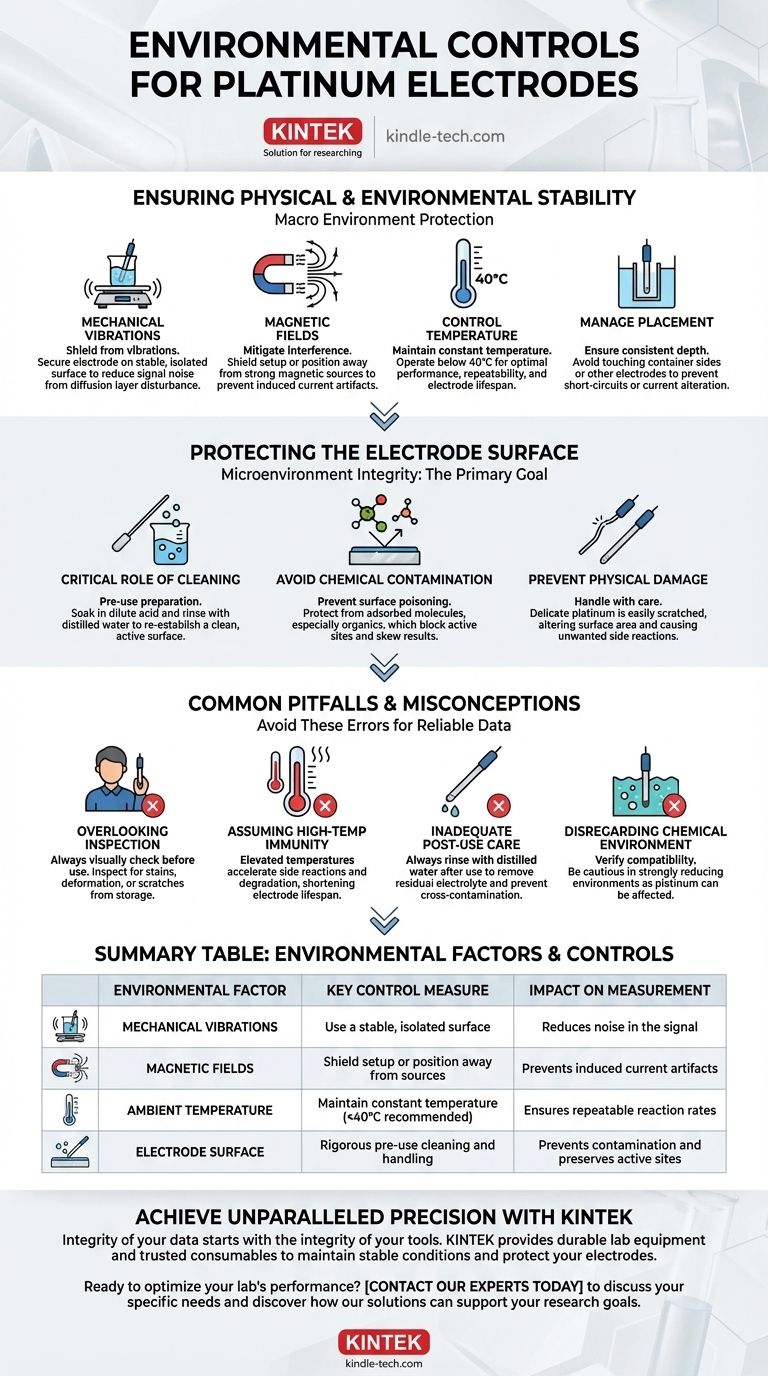
Ensuring Physical and Environmental Stability
The macro environment surrounding your experiment is the first line of defense against inaccurate data. Any instability here will be directly reflected in your measurements as noise or drift.
Shielding from Mechanical Vibrations
Even subtle vibrations from lab equipment or foot traffic can disturb the diffusion layer of ions at the electrode surface. This constant agitation introduces noise into your signal, making precise measurements difficult. Securing the electrode and cell on a stable, isolated surface is critical.
Mitigating Magnetic Fields
Strong magnetic fields, often generated by nearby equipment, can interfere with electrochemical measurements. These fields can induce small currents or affect ion transport, creating artifacts in your data. It is best practice to shield the setup or position it away from known magnetic sources.
Controlling Temperature
Electrochemical reaction rates and solution conductivity are highly dependent on temperature. The references recommend operating below 40°C for optimal performance and lifespan. Maintaining a constant, known temperature is essential for achieving repeatable and comparable results.
Managing Electrode Placement
The physical position of the electrode within the electrochemical cell is a crucial environmental parameter. Ensure the platinum wire is inserted to a consistent depth and does not touch the sides of the container or other electrodes, which could cause short-circuiting or alter the expected current distribution.
Protecting the Electrode Surface: The Primary Goal
While the external environment is important, the microenvironment at the electrode surface is where accuracy is won or lost. Protecting this surface from contamination and damage is paramount.
The Critical Role of Cleaning
Before any use, the electrode surface must be free of impurities and oxides. A standard procedure involves soaking the platinum in a dilute acid solution, followed by a thorough rinse with distilled water. This re-establishes a clean, active surface ready for the experiment.
Avoiding Chemical Contamination
The platinum surface can be easily "poisoned" by adsorbed molecules, especially organic substances. These contaminants block active sites where the electrochemical transfer is meant to occur, leading to skewed or completely inaccurate results. Handle the electrode with care and prevent contact with anything other than your target solution.
Preventing Physical Damage
Platinum wire is soft, delicate, and easily scratched or deformed. Physical damage alters the electrode's effective surface area, which is a key variable in many electrochemical calculations. A scratch can also create sites for unwanted side reactions, further compromising data integrity.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Understanding what can go wrong is as important as knowing the correct procedures. Awareness of these common errors can save significant time and prevent flawed data collection.
Overlooking Pre-Use Inspection
Always visually inspect the electrode before use. Look for stains, deformation, or scratches that may have occurred during storage. Assuming the electrode is in perfect condition without a quick check is a frequent and avoidable mistake.
Assuming High-Temperature Immunity
While platinum as a metal has excellent high-temperature resistance, its performance as an electrode in a solution is different. Elevated temperatures accelerate side reactions, cause solution degradation, and can shorten the electrode's lifespan, even if the metal itself is unharmed.
Inadequate Post-Use Care
Proper care does not end when the measurement is complete. Rinsing the electrode with distilled water after use removes residual electrolyte and impurities. This simple step prevents cross-contamination in future experiments and preserves the electrode's condition.
Disregarding the Chemical Environment
Platinum is not inert in all conditions. Be particularly cautious in strongly reducing environments, as the platinum itself can be affected. Always verify that your experimental medium is compatible with the electrode material.
Key Controls for Your Experimental Goal
The level of control you need to exert depends on the objective of your measurement. Tailor your approach based on your specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-precision quantitative analysis: Prioritize absolute stability by controlling temperature precisely and shielding the setup from all vibrations and electronic noise.
- If your primary focus is routine qualitative checks: Concentrate on rigorous cleaning protocols and avoiding cross-contamination between samples to ensure reliable, comparative results.
- If your primary focus is long-term or automated experiments: Emphasize proper electrode placement, secure connections, and choosing a chemical environment that ensures the electrode's long-term stability.
Ultimately, meticulous control over your electrode's environment is direct control over the quality and reliability of your data.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Factor | Key Control Measure | Impact on Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Vibrations | Use a stable, isolated surface | Reduces noise in the signal |
| Magnetic Fields | Shield setup or position away from sources | Prevents induced current artifacts |
| Ambient Temperature | Maintain constant temperature (<40°C recommended) | Ensures repeatable reaction rates |
| Electrode Surface | Rigorous pre-use cleaning and handling | Prevents contamination and preserves active sites |
Achieve unparalleled precision in your electrochemical experiments with KINTEK.
As specialists in laboratory equipment and consumables, we understand that the integrity of your data starts with the integrity of your tools. Properly controlling your electrode's environment is critical, but it's only one part of the equation. Using reliable, high-quality equipment forms the foundation of reproducible science.
KINTEK provides the durable lab equipment and trusted consumables you need to maintain stable experimental conditions and protect your valuable electrodes from contamination and damage. Let us help you enhance the reliability of your results.
Ready to optimize your lab's performance? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can support your research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What is the expected lifespan of a platinum sheet electrode? Maximize Your Electrode's Service Life
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be pretreated before use? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be operated during an experiment? Ensure Accurate and Reproducible Results



















