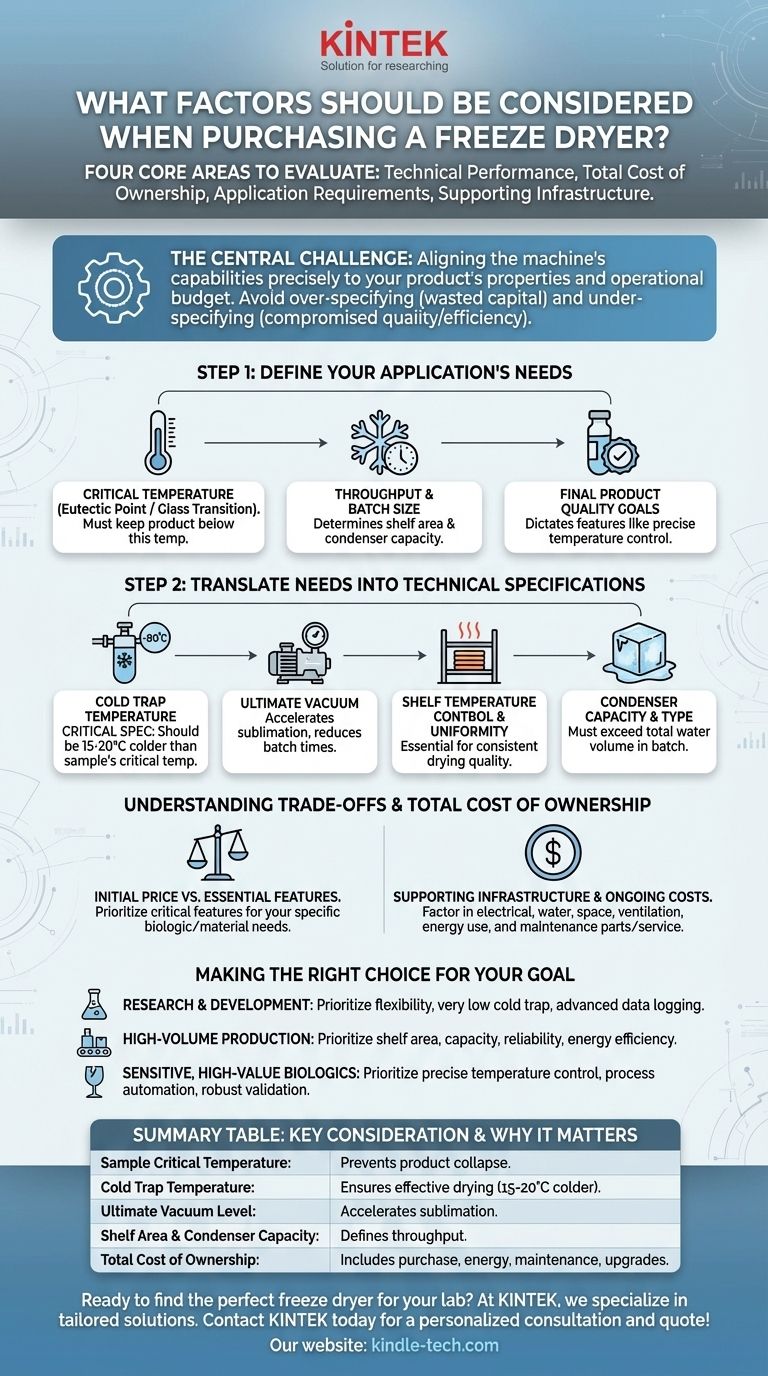
When purchasing a freeze dryer, you must evaluate four core areas: the machine's technical performance, its total cost of ownership, your specific application requirements, and the necessary supporting infrastructure. This involves analyzing key specifications like cold trap temperature and vacuum level, but also considering long-term operational costs like energy consumption, maintenance, and the facility upgrades required to support the unit. A successful purchase depends on aligning the machine's capabilities with your scientific or production goals.
The central challenge is not finding the most powerful freeze dryer, but the one that is precisely matched to your product's physical properties and your operational budget. Over-specifying features leads to wasted capital, while under-specifying compromises product quality and process efficiency.

Step 1: Define Your Application's Needs
Before looking at any machine, you must first deconstruct the requirements of the product you intend to dry. The machine's specifications are meaningless without this context.
Identify Your Sample's Critical Temperature
The most important property of your sample is its eutectic point (for crystalline structures) or glass transition temperature (for amorphous structures). This is the temperature at which the frozen product begins to soften or melt.
A freeze dryer's primary job is to keep the product below this critical temperature during the main drying phase to prevent collapse and ensure a high-quality result.
Determine Required Throughput and Batch Size
Consider the volume of sample you need to process and how quickly. This will determine the required shelf area and condenser capacity of the unit.
An academic lab processing small, varied samples has vastly different needs than a commercial facility running large, uniform batches.
Assess Final Product Quality Goals
Your desired outcome dictates the necessary features. If you need a uniform, elegant final product, specifications like shelf temperature uniformity and precise cooling rate control become non-negotiable.
For less sensitive materials, a simpler machine with basic controls may be perfectly adequate.
Step 2: Translate Needs into Technical Specifications
Once you understand your application, you can evaluate a machine's technical data sheet to see if it is a suitable match.
Cold Trap Temperature: The Most Critical Spec
The cold trap (or condenser) is what captures the water vapor sublimating from your product. Its surface must be significantly colder than your product's critical temperature.
A standard rule is that the cold trap should be 15-20°C colder than your sample's eutectic point or glass transition temperature. A machine with an insufficient cold trap temperature will fail to dry your product effectively.
Ultimate Vacuum: The Engine of Drying
Sublimation—the transition of ice directly to vapor—occurs efficiently only at very low pressures. The ultimate vacuum level indicates the lowest pressure the system can achieve.
A lower vacuum pressure increases the pressure difference between the product and the condenser, accelerating the drying process and reducing batch times.
Shelf Temperature Control and Uniformity
During the drying process, shelves provide controlled heat to the product to fuel sublimation. The system's ability to maintain a precise and uniform temperature across all shelves is critical.
Poor uniformity leads to inconsistent drying, with some vials drying faster than others. This can result in melted product in some areas and unnecessarily long run times.
Condenser Capacity and Type
Condenser capacity refers to the total amount of ice the cold trap can hold before it needs to be defrosted. This must be larger than the total amount of water in your product batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Total Cost
The sticker price is only one part of the investment. A comprehensive evaluation prevents costly surprises down the line.
The Initial Price vs. Essential Features
More advanced features like automatic drying cycles, pressure-ramping controls, and comprehensive data logging significantly increase the purchase price.
It is crucial to prioritize features that are essential for your specific application. If you work with sensitive biologics, precise temperature control is a necessity, not a frill. For simple materials, it may be an unnecessary expense.
Factoring in Supporting Infrastructure
A freeze dryer, particularly a large one, has significant utility demands. You must confirm you have the required electrical service (voltage and amperage), access to cooling water if needed, and adequate floor space and ventilation.
These facility requirements can represent a substantial hidden cost if they require upgrades.
Ongoing Operational and Maintenance Costs
Look beyond the purchase to the long-term expenses. Consider the machine's electricity and water consumption, which contribute to daily operating costs.
Furthermore, factor in the cost and availability of future maintenance, including parts like vacuum pumps, gaskets, and sensors. The manufacturer's reputation for support and service is a key consideration here.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is research and development with diverse samples: Prioritize a flexible machine with a very low cold trap temperature (-85°C or lower) and advanced data logging to handle a wide range of unknown materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Prioritize shelf area, condenser capacity, reliability, and energy efficiency to maximize throughput and minimize operational costs.
- If your primary focus is drying highly sensitive, high-value biologics: Prioritize precise shelf temperature control, sophisticated process automation, and robust validation documentation capabilities.
By methodically matching your application's requirements to the machine's specifications and your total budget, you ensure your investment will be both productive and profitable.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Sample Critical Temperature | Determines the required cold trap temperature to prevent product collapse. |
| Cold Trap Temperature | Must be 15-20°C colder than your sample's critical temperature for effective drying. |
| Ultimate Vacuum Level | Lower pressure accelerates sublimation, reducing batch times. |
| Shelf Area & Condenser Capacity | Defines throughput; must match your batch size and volume needs. |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Includes purchase price, energy use, maintenance, and potential facility upgrades. |
Ready to find the perfect freeze dryer for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your specific research or production goals. Whether you're in R&D, producing high-volume batches, or working with sensitive biologics, our experts will help you select a freeze dryer that delivers the precise performance you need without overspending.
We'll guide you through the technical specifications and total cost of ownership to ensure your investment is productive and profitable.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What problems should be avoided when using a lyophilizer? Prevent Product Collapse and Equipment Overload
- What are the three stages of freeze drying? A Guide to Lyophilization for Lab Professionals
- How does freeze drying preserve the nutritional value of food? A Low-Temperature Solution for Maximum Nutrient Retention
- Why does freeze drying extend the shelf life of products? Preserve Nutrition & Flavor for Years
- In what ways does freeze drying improve pharmaceutical product quality? Extend Shelf-Life and Preserve Drug Efficacy



















