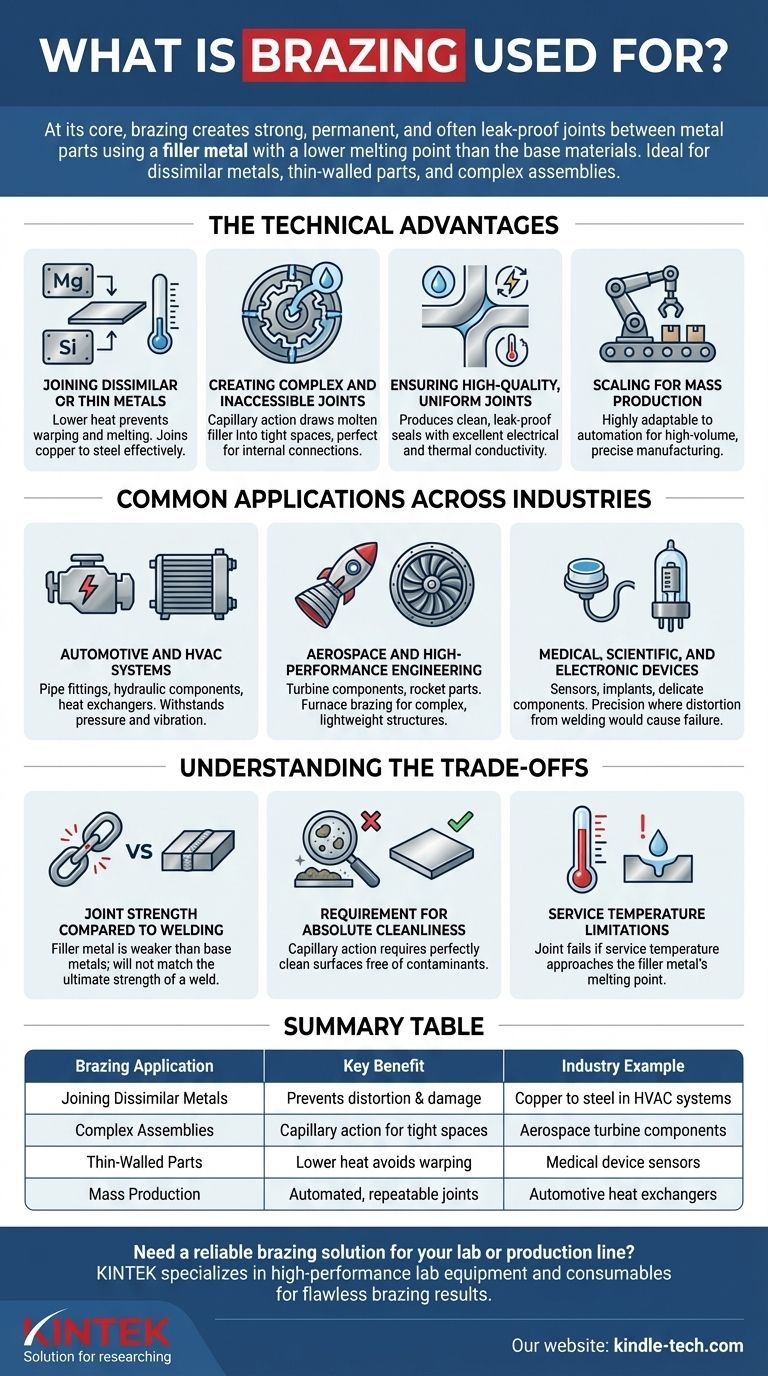
At its core, brazing is used to create strong, permanent, and often leak-proof joints between two or more metal parts. This highly versatile process is critical in manufacturing everything from complex aerospace components and automotive engines to common HVAC systems and delicate medical devices. Brazing uses a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base metals, allowing it to join parts without melting and distorting them.
The essential reason to choose brazing is for its ability to join dissimilar metals, thin-walled parts, and complex assemblies with clean, strong joints—scenarios where the intense, localized heat of welding would be damaging or impractical.

Why Choose Brazing? The Technical Advantages
Brazing is selected for specific engineering challenges where its unique characteristics offer a clear advantage over other joining methods like welding or soldering. Its value lies in the combination of strength, precision, and material versatility.
Joining Dissimilar or Thin Metals
Brazing operates at temperatures below the melting point of the base materials being joined.
This lower-heat process is critical for joining thin-walled tubes or sheets that would warp or melt under the high heat of welding. It is also one of the most effective methods for joining dissimilar metals, such as copper to steel, which can be very difficult to weld.
Creating Complex and Inaccessible Joints
Brazing relies on capillary action, where the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting gap between the base parts.
This phenomenon allows brazing to create complete, uniform joints in areas that are inaccessible to a welding torch, such as deep, internal connections. It is exceptionally well-suited for assemblies with a large number of joints, as they can all be made simultaneously in a furnace.
Ensuring High-Quality, Uniform Joints
The process naturally produces clean, smooth joints with minimal need for secondary finishing.
Because the filler metal flows across the entire joint surface, it creates a strong, leak-proof seal. Materials like copper-based brazing alloys also provide excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making the process ideal for electronic components and heat exchangers.
Scaling for Mass Production
Brazing is highly adaptable to automation for high-volume manufacturing.
Automatic brazing machines can be programmed to produce large quantities of components with precise tolerances and high repeatability, making it a cost-effective solution for industries like automotive and HVAC.
Common Applications Across Industries
The technical benefits of brazing make it a foundational process in numerous high-stakes and precision-oriented fields.
Automotive and HVAC Systems
These industries rely on brazing for components that must withstand pressure and vibration.
Common examples include pipe fittings, hydraulic components, heat exchangers, and other engine and cooling assembly parts. The leak-proof nature of a brazed joint is essential for these applications.
Aerospace and High-Performance Engineering
In aerospace, reliability is non-negotiable. Brazing is used for industrial gas turbine components, rocket engine parts, and other critical assemblies.
Furnace brazing, in particular, is used to join complex, lightweight structures that must perform under extreme temperatures and stresses.
Medical, Scientific, and Electronic Devices
Precision and material integrity are paramount in these fields.
Brazing is used to assemble delicate sensors, medical implants, vacuum tubes, and electromechanical components where distortion from welding would cause failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, brazing is not the solution for every metal-joining problem. Objectively understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Joint Strength Compared to Welding
A brazed joint's strength is determined by the filler metal, which is weaker than the base metals.
While a properly designed brazed joint is exceptionally strong and often exceeds the needs of the application, it will not match the ultimate strength of a properly executed welded joint, which can be as strong as the base metals themselves.
Requirement for Absolute Cleanliness
The success of brazing depends entirely on capillary action, which only works on perfectly clean surfaces.
Any oils, oxides, or contaminants on the base metals will prevent the filler metal from flowing and bonding, leading to a failed joint. This requires a thorough and often multi-step cleaning process before brazing.
Service Temperature Limitations
A brazed joint will lose its strength and fail if the component's service temperature gets too close to the filler metal's melting point.
This makes brazing unsuitable for applications that will operate in very high-temperature environments where a welded joint would be required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right joining process requires matching the method's strengths to your project's most critical outcome.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or thin sections: Brazing is often superior to welding because its lower temperatures prevent damage and distortion to the parent materials.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, multi-joint assemblies: Brazing's use of capillary action is ideal for creating uniform joints in tight spaces and across large areas simultaneously in a single furnace cycle.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength for a simple design: A properly executed weld may be a better choice, as its strength is limited only by the base metals, not a weaker filler.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select brazing not just as a joining method, but as a precise engineering solution.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Application | Key Benefit | Industry Example |
|---|---|---|
| Joining Dissimilar Metals | Prevents distortion & damage | Copper to steel in HVAC systems |
| Complex Assemblies | Capillary action for tight spaces | Aerospace turbine components |
| Thin-Walled Parts | Lower heat avoids warping | Medical device sensors |
| Mass Production | Automated, repeatable joints | Automotive heat exchangers |
Need a reliable brazing solution for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise tools and materials needed for flawless brazing results. Whether you're joining dissimilar metals in R&D or scaling up complex assemblies, our expertise ensures strong, leak-proof joints every time. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory and manufacturing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints



















