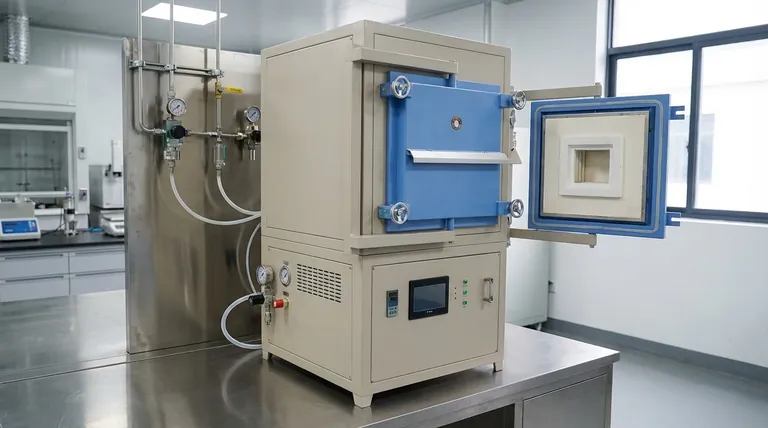
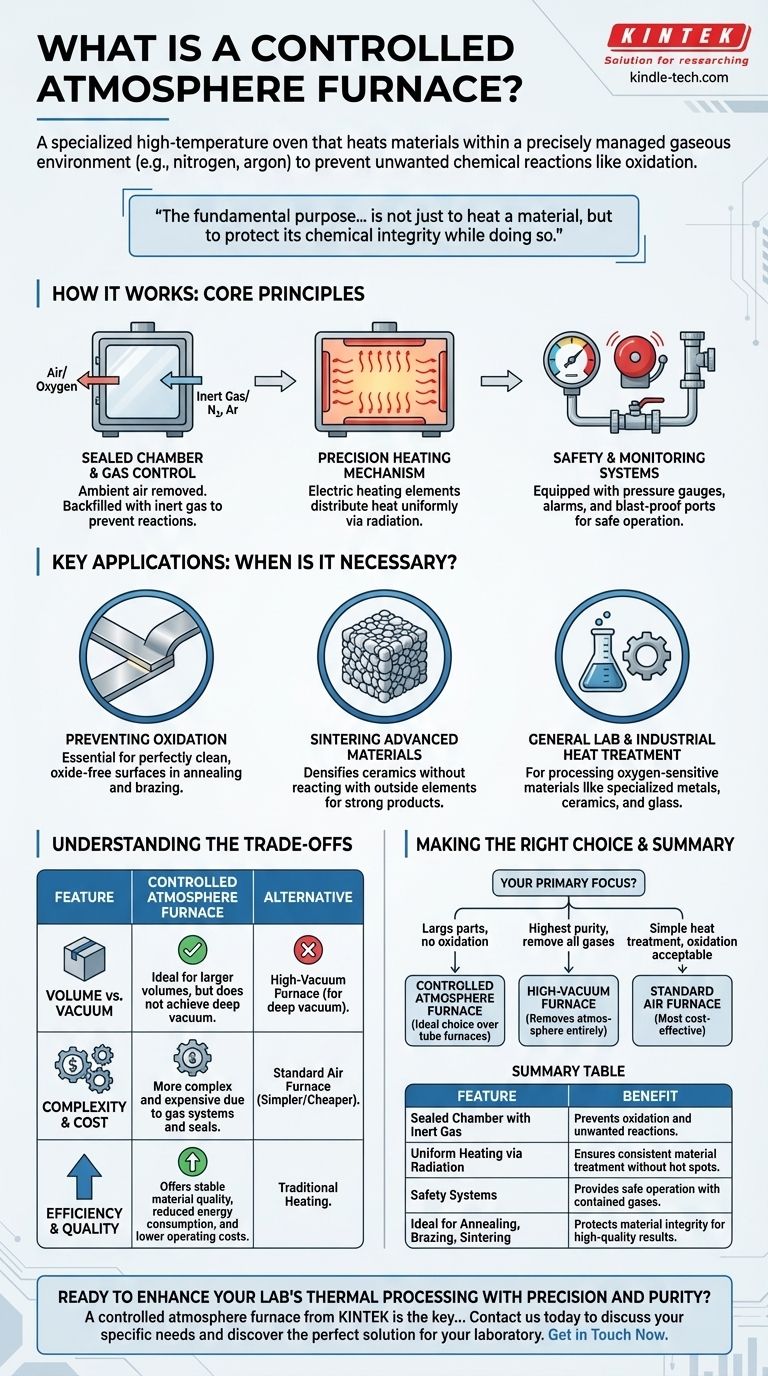
In short, a controlled atmosphere furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven that heats materials within a precisely managed gaseous environment. Instead of heating in normal air, it replaces the atmosphere with a specific gas—like nitrogen or argon—to prevent unwanted chemical reactions such as oxidation (rusting) during the process.
The fundamental purpose of a controlled atmosphere furnace is not just to heat a material, but to protect its chemical integrity while doing so. By eliminating reactive oxygen, it ensures that processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering result in a high-quality, pure, and uncontaminated final product.

How It Works: The Core Principles
A controlled atmosphere furnace operates on a few key principles that distinguish it from a standard oven. The goal is to create a stable, predictable environment at high temperatures.
The Sealed Chamber and Gas Control
The process begins with an airtight chamber. All ambient air, which is nearly 21% oxygen, is first removed from this chamber.
It is then backfilled with a specific gas. This is typically an inert gas like nitrogen or argon that will not react with the material being heated. This step is the defining feature of the furnace.
Precision Heating Mechanism
Once the desired atmosphere is established, electric heating elements, often resistance wires, generate heat. This heat is distributed evenly throughout the chamber, primarily through radiation.
The combination of a controlled gas environment and uniform heating ensures the material is treated consistently, without hot spots or undesirable chemical changes.
Safety and Monitoring Systems
Because these systems operate with contained gases under pressure and at high temperatures, safety is critical.
They are equipped with pressure gauges, safety alarms, and blast-proof relief ports to prevent over-pressurization and ensure safe operation.
Key Applications: When Is This Furnace Necessary?
Controlled atmosphere furnaces are indispensable in fields where material purity and surface quality are non-negotiable. They are used when heating in open air would damage or destroy the component.
Preventing Oxidation in Metals
Processes like annealing (softening metal) and brazing (joining metals) require perfectly clean, oxide-free surfaces. A controlled atmosphere prevents the formation of oxide layers that can compromise the material's strength and finish.
Sintering Advanced Materials
Sintering is a process that uses heat to densify and strengthen materials like ceramics. Under a controlled atmosphere, the ceramic particles bond together without reacting with outside elements, resulting in a dense, strong final product.
General Laboratory and Industrial Heat Treatment
These furnaces are ideal for any lab or industrial application involving materials that are sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures. This includes processing specialized metals, ceramics, and even some types of glass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a controlled atmosphere furnace is not the solution for every heating task. Understanding its specific place among other thermal processing equipment is key.
Volume vs. Vacuum Level
This furnace is the perfect alternative to a tube furnace when larger chamber volumes are needed. However, it does not achieve a deep vacuum.
If your process requires the removal of nearly all gas molecules, a dedicated high-vacuum furnace is necessary. A controlled atmosphere furnace simply displaces air with another gas.
Complexity and Cost
Managing gas systems, ensuring proper seals, and implementing safety protocols makes these furnaces more complex and expensive than a simple air furnace. The benefits of a pure environment must justify the added operational overhead.
Efficiency and Quality
Compared to traditional heating equipment, the sealed environment offers higher thermal efficiency and more uniform heating. This leads to stable material quality, reduced energy consumption, and lower operating costs over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on the chemical and physical requirements of your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is processing large parts without oxidation: A controlled atmosphere furnace is an ideal choice over smaller tube furnaces.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity by removing all gases: A high-vacuum furnace is the correct tool, as it removes the atmosphere rather than replacing it.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment where surface oxidation is acceptable or desired: A standard, less complex air furnace is the most cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the level of environmental control to the specific chemical needs of your material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sealed Chamber with Inert Gas | Prevents oxidation and unwanted chemical reactions |
| Uniform Heating via Radiation | Ensures consistent material treatment without hot spots |
| Safety Systems (Pressure Gauges, Relief Ports) | Provides safe operation with contained gases |
| Ideal for Annealing, Brazing, Sintering | Protects material integrity for high-quality results |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with precision and purity?
A controlled atmosphere furnace from KINTEK is the key to preventing oxidation and contamination during critical processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering. Our specialized lab equipment ensures your materials maintain their chemical integrity and achieve superior quality.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Get in Touch Now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the inert gases in a heat treatment furnace? Choose the Right Shield for Your Metal
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















