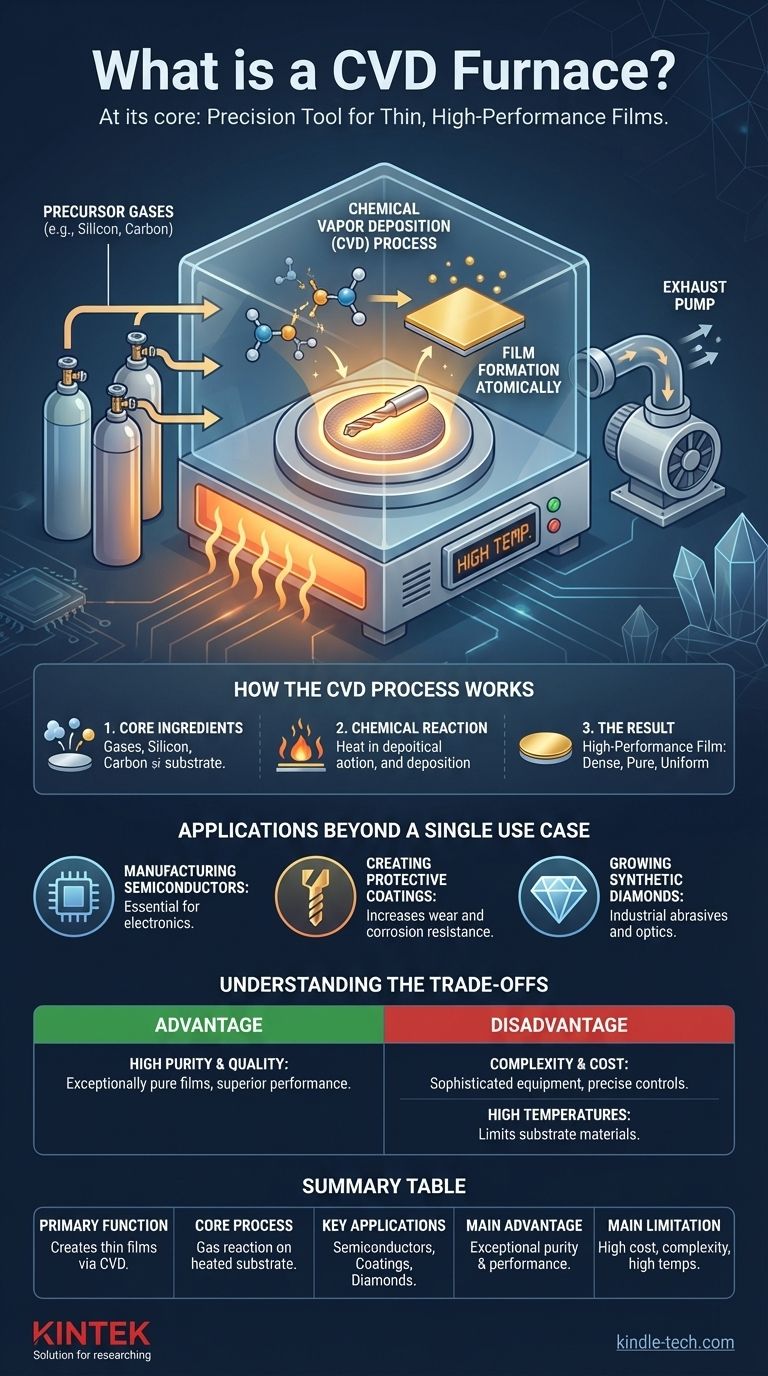
At its core, a CVD furnace is a highly controlled chamber designed to create exceptionally thin, high-performance films on the surface of an object. It accomplishes this through a process called Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where specific gases are introduced into the chamber, react, and deposit a solid material layer by layer onto a substrate. This method is fundamental to advanced manufacturing, from semiconductors to protective tool coatings.
The central concept to grasp is that a CVD furnace isn't defined by a single product, like diamonds, but by its versatile process. It is a precision tool that uses chemical reactions from gases to "grow" a solid coating with specific, engineered properties onto a target object.
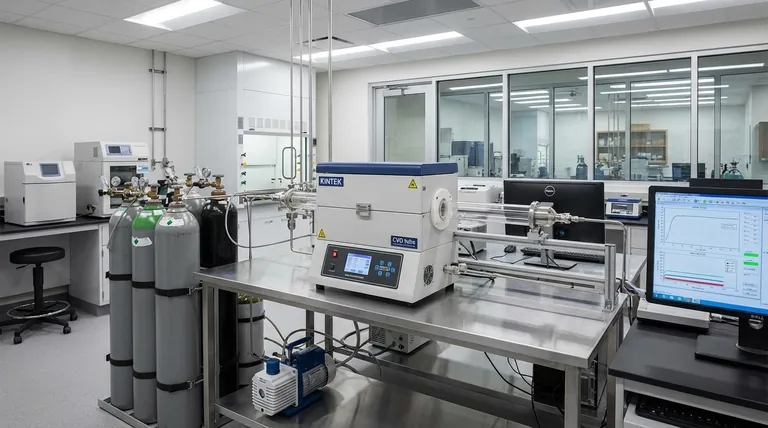

How the CVD Process Works
The function of a CVD furnace is best understood by breaking down its core process into its essential components and stages. It's a method of building materials from the atom up.
The Core Ingredients
Every CVD process requires a few key elements. The furnace itself is a vacuum chamber that provides a pristine, controllable environment, preventing contamination. Inside, you have the substrate—the object to be coated—and a carefully selected mixture of precursor gases, which contain the atoms needed for the final film.
The Chemical Reaction
Once the substrate is heated to a precise temperature, the precursor gases are introduced into the chamber. The energy from the heat causes these gases to react or decompose on the surface of the substrate. This chemical reaction results in the deposition of a solid, thin film, while any byproducts are removed by the vacuum system.
The Result: A High-Performance Film
The film that forms is not merely a layer of paint; it is a dense, pure, and highly uniform coating that is chemically bonded to the substrate. This process allows for incredible control over the film's thickness, purity, and material properties, making it essential for high-technology applications.
Applications Beyond a Single Use Case
While the creation of synthetic diamonds is a well-known application, it represents only a fraction of what CVD technology is used for. Its primary value lies in its versatility for creating performance-critical materials.
Manufacturing Semiconductors
CVD is indispensable in the electronics industry. It is used to deposit the various thin films of silicon, silicon dioxide, and other materials that form the intricate circuits on a microchip. The purity and uniformity provided by CVD are essential for modern computing.
Creating Protective Coatings
The original industrial use of CVD is still one of its most important. A thin layer of a material like titanium nitride can be deposited onto cutting tools, bearings, or engine parts. This coating dramatically increases resistance to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures, extending the life of the component.
Growing Synthetic Diamonds
The references correctly identify that CVD is a leading method for growing synthetic diamonds. By using a carbon-containing gas like methane, the process deposits carbon atoms onto a diamond "seed," crystallizing them into a high-purity diamond layer used for industrial abrasives, optics, and jewelry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any advanced manufacturing process, Chemical Vapor Deposition has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for specific goals.
Advantage: High Purity and Quality
Because the process occurs in a sealed, high-vacuum environment, the resulting films are exceptionally pure and free from defects. This allows for the creation of coatings with superior performance characteristics that are difficult to achieve with other methods.
Disadvantage: Complexity and Cost
CVD furnaces are sophisticated and expensive pieces of equipment. They require precise control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow. Furthermore, many of the precursor gases used can be toxic or hazardous, requiring significant safety infrastructure.
Disadvantage: High Temperatures
Traditional CVD processes often require very high temperatures to initiate the chemical reaction. This can limit the types of substrate materials that can be coated, as some may melt or deform under the required heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coating technology depends entirely on the required outcome. CVD excels where material performance and purity are the absolute priorities.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity for electronics: CVD is the industry standard for creating the foundational layers of semiconductors for a reason.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: CVD provides incredibly hard and resilient coatings for industrial tools and mechanical parts.
- If your primary focus is growing a specific crystalline material: CVD offers the atomic-level control needed to produce high-quality synthetic diamonds, graphene, and other advanced materials.
Ultimately, a CVD furnace is a foundational tool for engineering materials at the atomic scale, enabling the creation of components that are stronger, faster, and more resilient.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates thin, high-performance films via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). |
| Core Process | Precursor gases react on a heated substrate in a vacuum chamber, depositing a solid layer. |
| Key Applications | Semiconductor manufacturing, protective tool coatings, synthetic diamond growth. |
| Main Advantage | Exceptional film purity, uniformity, and material performance. |
| Main Limitation | High equipment cost, process complexity, and often high temperatures required. |
Ready to Engineer Superior Materials with Precision?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including CVD furnaces, to help you achieve the high-purity, high-performance coatings essential for semiconductors, protective layers, and advanced materials. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your specific application, from R&D to full-scale production.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our CVD technology can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is meant by chemical vapour deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Growth
- What is sputter damage? A Guide to Protecting Sensitive Materials During Thin-Film Deposition
- What is an advantage of sputtering over older vacuum deposition? Superior Control for Complex Material Films
- What are the main applications of thin films? Unlock Performance in Electronics, Optics & Protection
- How does chemical Vapour deposition work? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Growth
- What are the advantages of physical vapour deposition? Superior, Durable Coatings for Your Components
- How do substrate heating and temperature control devices influence coating quality? Enhance Film Adhesion and Structure
- How much does a chemical vapor deposition system cost? From $50k to $10M+



















